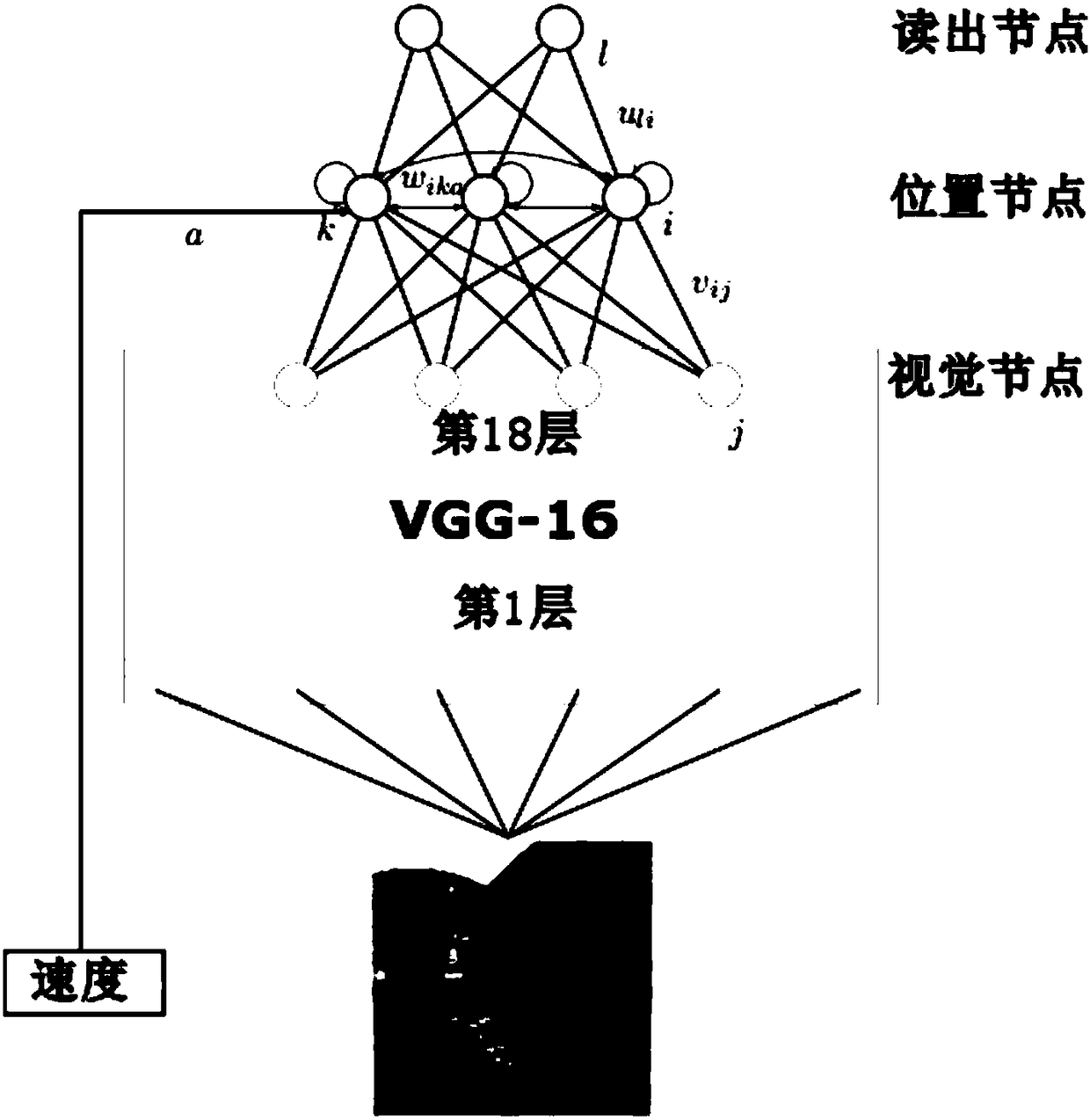
Robot navigation method based on visual perception and spatial cognitive neural mechanism
A technology of spatial cognition and visual perception, applied in the field of brain-like navigation, can solve the problems of high difficulty in brain science exploration and few breakthroughs, and achieve the effect of improving bionics, strong autonomy, and reducing computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Example 1 Robot Navigation under Illumination
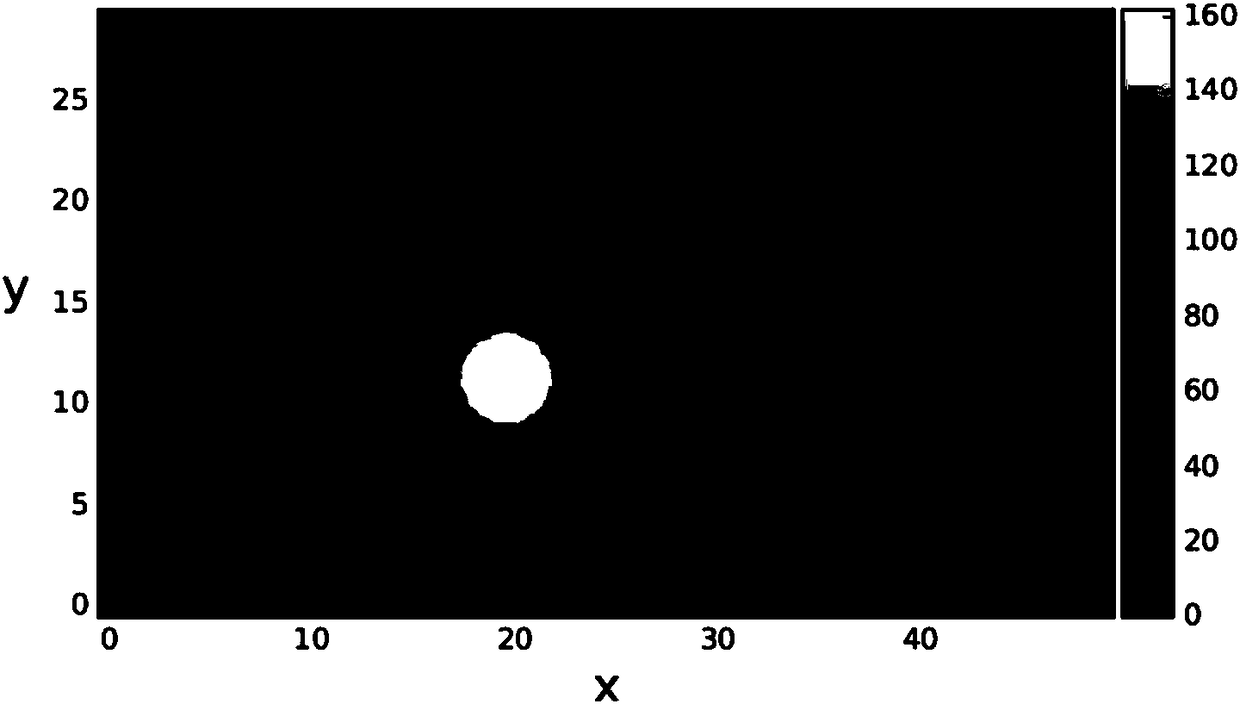
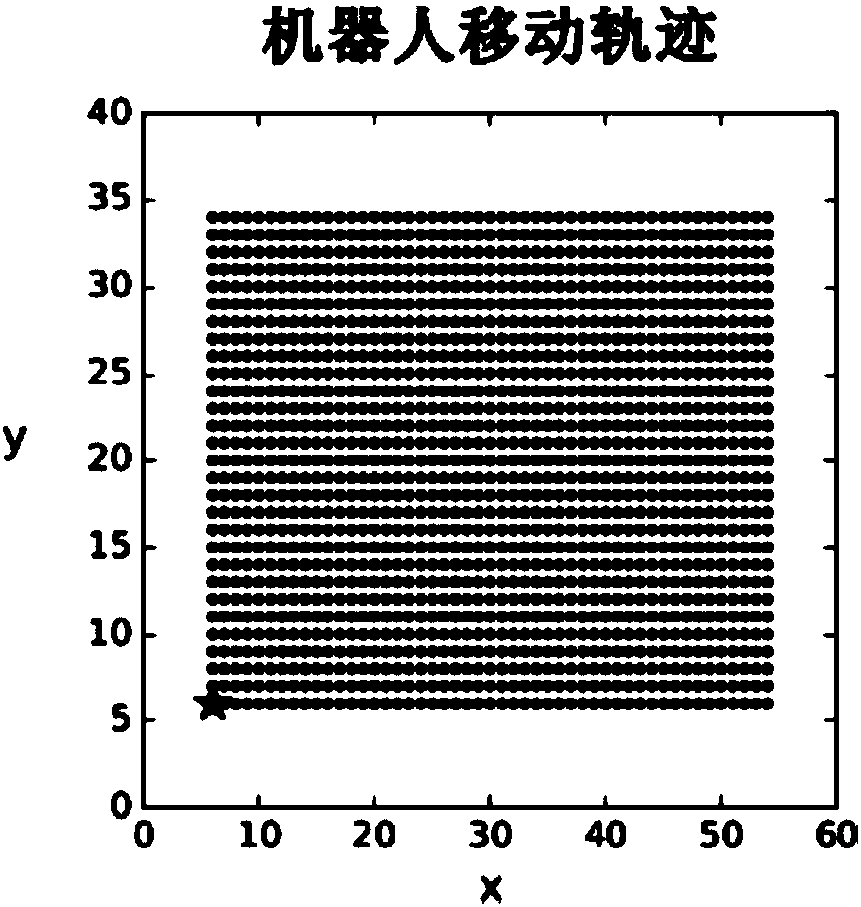
[0082] When illuminated, the system is stimulated by multiple sources of visual images and robot motion. Numerous location nodes at time t form such as figure 2 The discharge bump is shown. like Figures 3a to 3d As shown, x and y represent positions in the x and y directions, respectively. The motion of the bump on the spatial cortex is proportional to the motion of the robot in the simulated environment, and the normalized difference is close to zero. Therefore, the system designed by the present invention is dynamic, realizes the transformation between the robot motion plane and the spatial cortex, and helps the robot to learn a two-dimensional spatial cognitive map for the environment in which it is located. refer to Figure 4 , when the robot is in different head orientations, the spatial responses of the position nodes are consistent, forming a discharge pattern similar to the "position field" of the position c...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2 Robot Navigation in Darkness
[0084] In the dark, the stimulation of the visual image to the system disappears, but the bump formed by the position node in the spatial cortex at time t still exists, and as shown in Fig. Figures 6a-6b The shown has similar dynamics as in Example 1, ie the movement of the bump in the spatial cortex is proportional to the speed of the robot.
Embodiment 3
[0085] Example 3 Robot navigation in the presence of motion noise
[0086] When there is random noise in the speed information of the robot, the system is still anti-interference, such as Figure 7a As shown in ~7d, the normalized error between the motion of the bump and the actual robot motion fluctuates in a small range around 0.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com