Balancing control circuit of new energy electric vehicle
A technology for balanced control and electric vehicles, applied in electric vehicles, battery/fuel cell control devices, vehicle energy storage, etc., can solve problems such as large number of batteries, reduced service life of battery packs, and decreased mileage of electric vehicles. The effect of reducing the cost of use and prolonging the service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
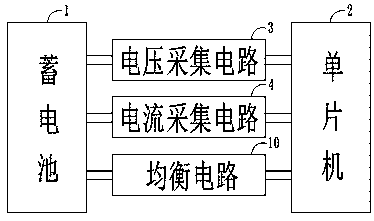
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, the new energy electric vehicle equalization control circuit includes: a battery 1, a single-chip microcomputer 2, a voltage acquisition circuit 3, a current acquisition circuit 4, and a temperature acquisition circuit 5. The output terminals of the battery 1 respectively pass through the input terminals of the voltage acquisition circuit 3. The input terminal of the current acquisition circuit 4 and the input terminal of the temperature acquisition circuit 5 are electrically connected to the single-chip microcomputer 2, and the model of the single-chip 2 is 89C51 series.
[0027] Such as figure 2 As shown, the voltage acquisition circuit 3 includes: diode D1, diode D2, voltage regulator W1, resistor R1, resistor R2, resistor R3, resistor R4, resistor R5, resistor R6, resistor R7, capacitor C1, capacitor C2, capacitor C3 and optocoupler Q1; one end of the resistor R7 is connected to the positive terminal and ground terminal of the voltage stabili...
Embodiment 2
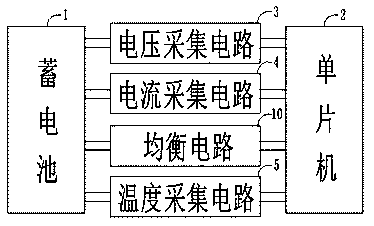
[0034] Such as image 3 As shown, the new energy electric vehicle equalization control circuit further includes a temperature collection circuit 5, and the output terminal of the battery 1 is electrically connected to the single-chip microcomputer 2 through the input terminal of the temperature collection circuit 5.
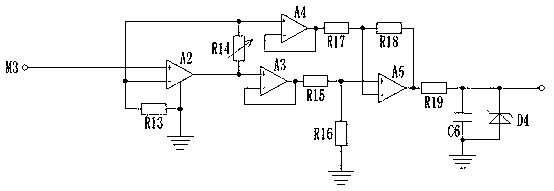
[0035] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the temperature acquisition circuit 5 includes: resistor R13, variable resistor R14, resistor R15, resistor R16, resistor R17, resistor R18, resistor R19, amplifier A2, amplifier A3, amplifier A4, amplifier A5, capacitor C6 and Zener diode D4; the models of the amplifier A2, amplifier A3, amplifier A4, and amplifier A5 are all LM358; the non-inverting input end of the amplifier A2 is connected to the terminal M3, and the inverting input end of the amplifier A2 is respectively connected to the variable resistor One end of the amplifier R14 is connected to the non-inverting input end of the amplifier A4, and the resistor R13 is connec...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Such as Figure 5 , Image 6 As shown, it also includes a wake-up circuit 6. The output terminal of the battery 1 is electrically connected to the single-chip microcomputer 2 through the input terminal of the wake-up circuit 6; the wake-up circuit 6 includes a clock chip U1 and a transistor Q2. The model of the clock chip U1 is SD2405, the wake-up circuit 6 includes the INT end of the clock chip U1 connected in series with the resistor R25 and then connected to the base of the transistor Q2. The connection between the resistor R25 and the base of the transistor Q2 is connected in series with the resistor R24 and then respectively connected with the emitter of the transistor Q2 , 5V power terminal connected, the collector of the transistor Q2 is connected to the resistor R27 in series and then connected to the terminal M4, the terminal M4 is electrically connected to the output terminal of the battery 1, and the connection between the collector of the transistor Q2 and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com