Method for predicting grain size of micro-alloy steel welding coarse grained region
A technology of grain size and micro-alloyed steel, which is applied in the direction of chemical property prediction, etc., can solve the problems of different reliability of calculation results and the inability to accurately describe the thermal stability of second-phase particles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
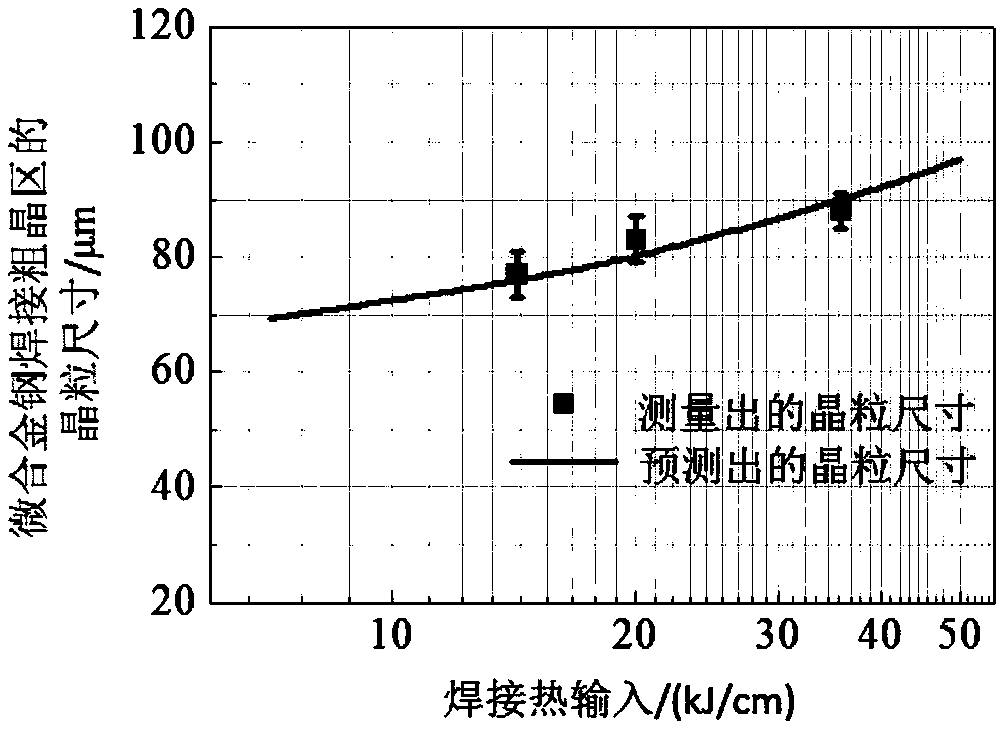
[0014] Thermal simulation of the thermal cycle of a microalloyed steel in the welding coarse grain zone, the heating rate is 200K / s, the peak temperature is 1643K, the peak temperature residence time is 1s, and the cooling process adopts Rykalin 3D thermal model λ=0.38J / (cm·s·K), T P=1643K, E is the welding heat input, T' is the temperature coordinate, τ is the time coordinate), the welding heat input parameters in the thermal model are 14, 20 and 36kJ / cm respectively. Through metallographic grinding, the average grain size of the welded coarse-grained region under three heat inputs is about 77±4, 83±4 and 88±3 μm, respectively, obtained by the intercept method. Grain Growth Formula Will M 0 and P Z It is an unknown constant, and the numerical scores of other parameters are taken as n=2, R=8.3J / (mol·K), Q a =400kJ / mol, γ=0.5J / m 2 . The time t of the integral interval is the duration from when the temperature exceeds 1100K in the heating process to when the temperatur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com