Low-melting-point metal wire for 3D printing
A technology of low melting point metal and metal wire, applied in metal processing equipment, 3D object support structure, additive processing, etc., can solve the problem that metals cannot be printed together at the same time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
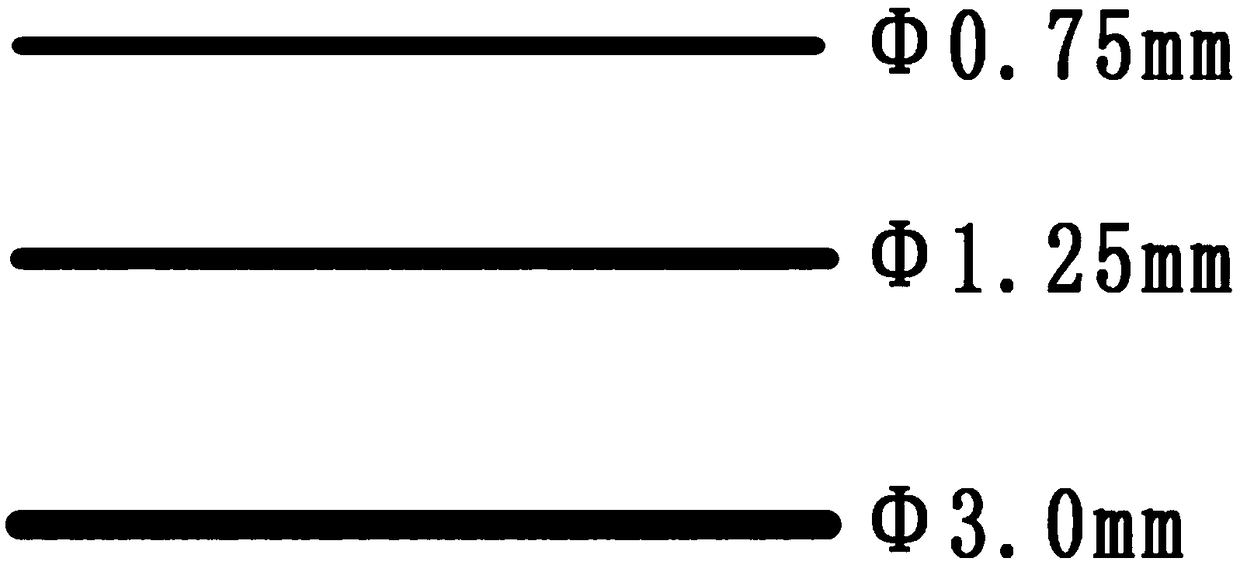
[0041] This embodiment relates to a low-melting-point metal wire for 3D printing, which is prepared from the following raw materials in terms of mass percentage: 40% Bi, 35% Sn, and the rest is In.
[0042] This embodiment also relates to the preparation method of this metal wire, comprising the following steps:
[0043] 1) Add 40kg of pure Bi, 35kg of pure Sn, and 25kg of pure In raw materials weighed into a 200kg melting furnace, totaling 100kg, add 100g of ZnCl2 melting covering agent, heat to 350°C, and keep warm for 30min.
[0044] 2) Stir the obtained melt for 30 minutes, remove the surface covering agent, and pour it into a mold to make a low-temperature metal ingot.
[0045] 3) extruding the ingot obtained in step (2) into strips and filaments on an extruder.
[0046] The metal wire prepared in this embodiment can ensure that the mechanical properties such as strength and toughness of the wire are relatively good, which is beneficial to the printing operation of the wir...
Embodiment 2
[0048] This embodiment relates to a low-melting-point metal wire for 3D printing, prepared from the following raw materials in terms of mass percentage: Bi 40%, Sn 35%, Zn 0.2%, Al 0.15%, Cu 0.1%, P 0.15%, The rest are In.
[0049] This embodiment also relates to the preparation method of this metal wire, comprising the following steps:
[0050] 1) Add 40kg of pure Bi, 35kg of pure Sn, 200g of pure Zn, 150g of pure Al, 100g of pure Cu, 150g of pure P, and 24.4kg of pure In into a 200kg smelting furnace, totaling 100kg, and add 100g of ZnCl2 for melting and covering agent, heated to 650°C, and kept warm for 30min.
[0051] 2) Stir the obtained melt for 30 minutes, remove the surface covering agent, and pour it into a mold to make a low-temperature metal ingot.
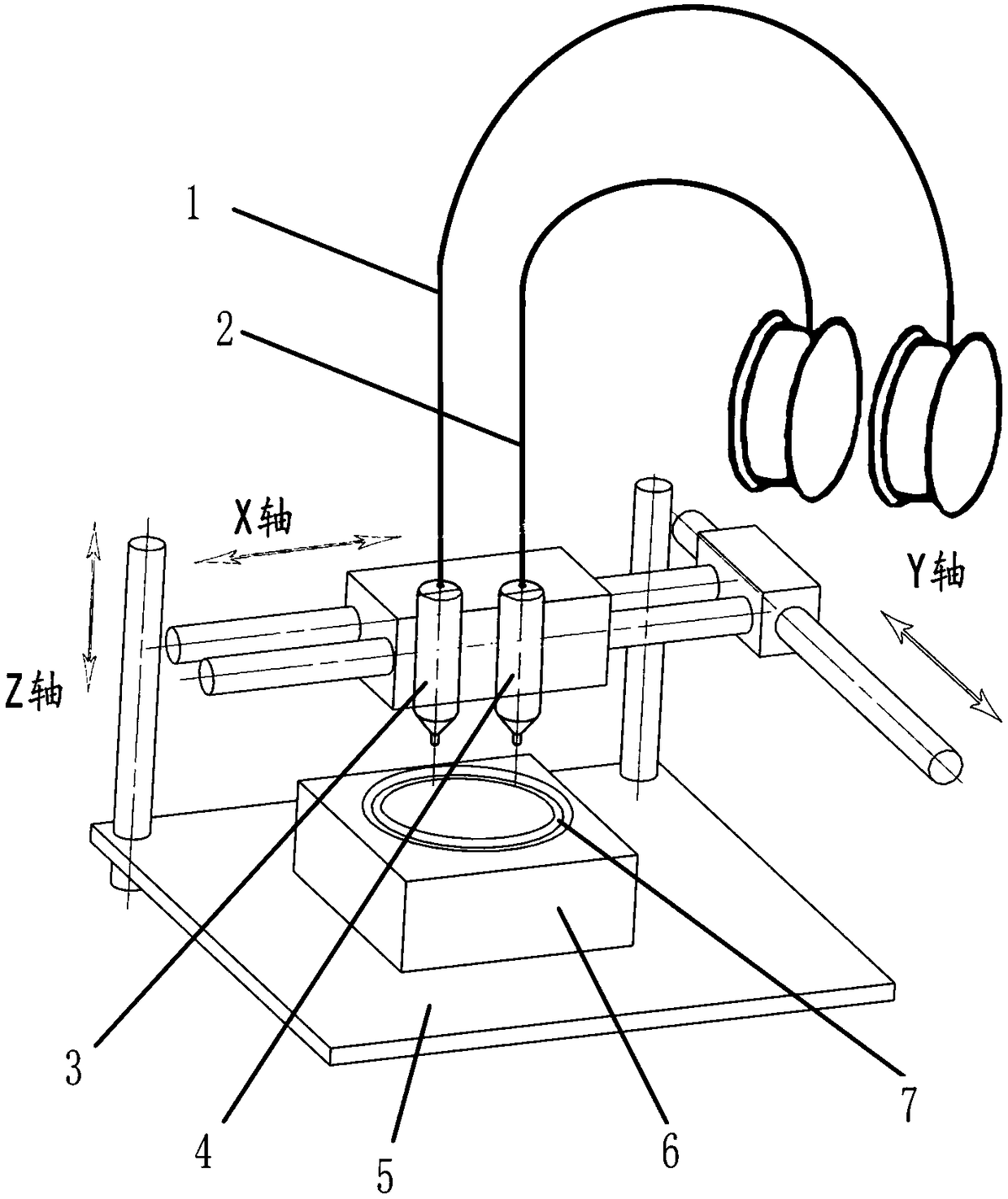
[0052] 3) Extrude the ingot obtained in step (2) into strips and filaments on the extruder, and its structure is shown in figure 1 .
[0053] The metal wire prepared in this embodiment can ensure that the mechanical...
Embodiment 3
[0055] This embodiment relates to a low-melting-point metal wire for 3D printing, which is prepared from the following raw materials in terms of mass percentage: Bi 40%, Sn 34%, Ag 0.1%, Zn 0.5%, Al 0.1%, Cu 0.1%, The rest are In.
[0056] This embodiment also relates to the preparation method of this metal wire, comprising the following steps:
[0057] 1) Add 40kg of pure Bi, 34kg of pure Sn, 100g of pure Ag, 500g of pure Zn, 100g of pure Al, 100g of pure copper, and 25.2kg of pure In into a 200kg smelting furnace, totaling 100kg, and add 100g of ZnCl2 for melting and covering agent, heated to 650°C, and kept warm for 30min.
[0058] 2) Stir the obtained melt for 30 minutes, remove the surface covering agent, and pour it into a mold to make a low-temperature metal ingot.
[0059] 3) extruding the ingot obtained in step (2) into strips and filaments on an extruder.
[0060] The metal wire prepared in this embodiment can ensure that the mechanical properties such as strength...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com