How to make a photodetector
A technology of photodetectors and manufacturing methods, applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as cost increase, low device yield, and complicated device manufacturing process, and achieve the effect of low loss and low optical transmission loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
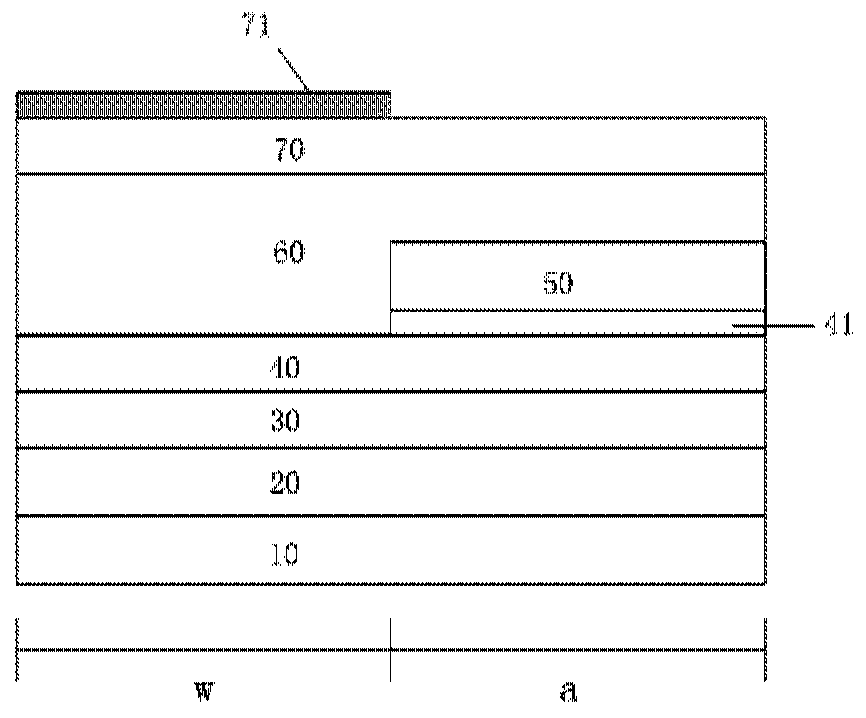
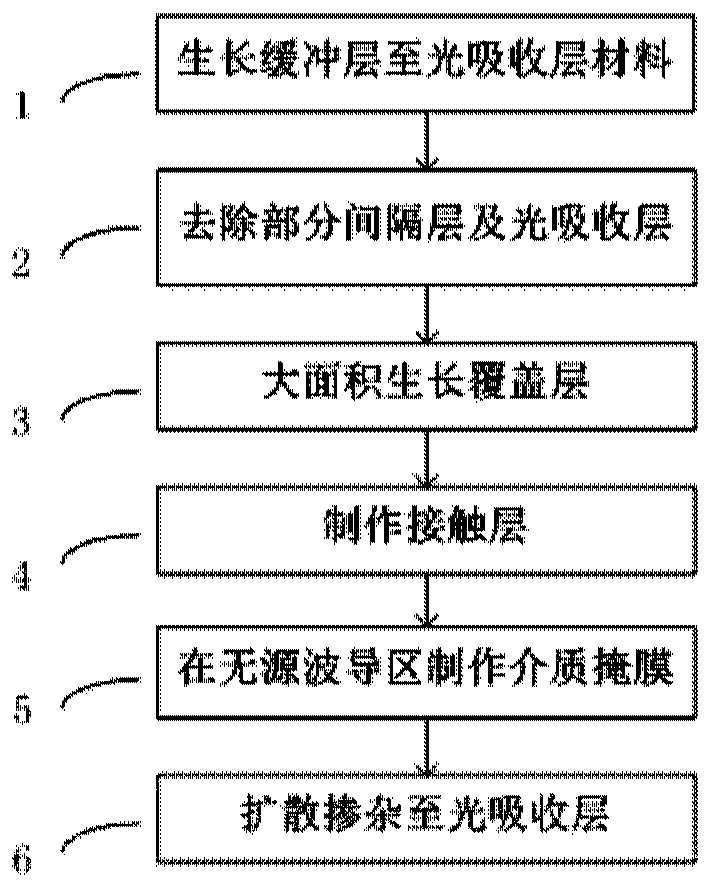
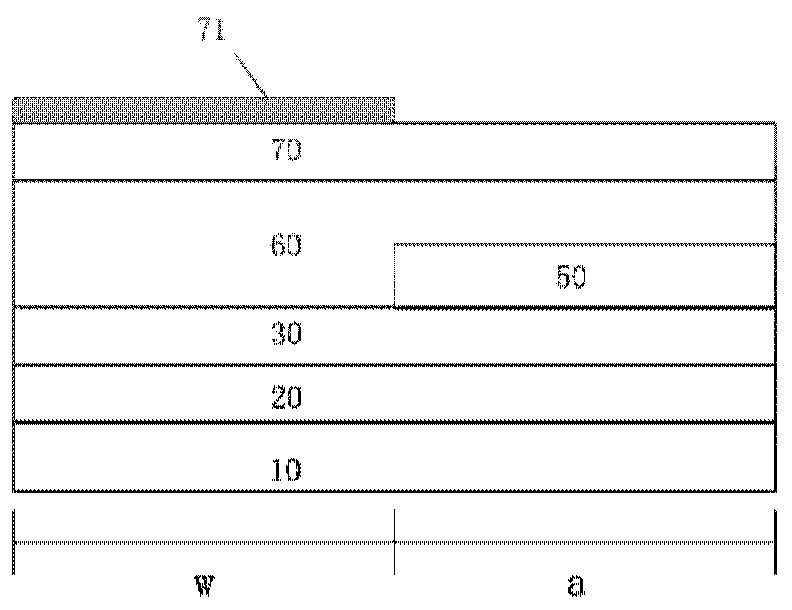
[0026] Please refer to the first example of figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, taking the InP-based material system as an example, the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a photodetector, which includes the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: growing an InP buffer layer 20 , an InGaAsP waveguide layer 30 , an InP light collecting layer 40 , an InGaAsP spacer layer 41 , and an InGaAs light absorbing layer material 50 sequentially on the InP substrate 10 . Wherein the InGaAsP waveguide layer 30 is doped with Si as the n-type contact material of the detector, the InP light collection layer 40 is not doped or low-concentration doped, and the InGaAs light absorption layer material 50 is not doped. The InGaAsP spacer material 41 can reduce the influence of the conduction bandgap difference between the InP light collecting layer 40 and the InGaAs light absorbing layer 50, and is composed of one layer of InGaAsP with a single wavelength or two layers of InGaAsP with two...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com