Artificial dermis
A dermal and artificial technology, applied in coatings, medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of no antibacterial and antibacterial effects, achieve low cost of use, facilitate clinical application, and reduce infection rates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Disinfectant Screening
[0043] 1. Experimental materials
[0044] (1) Alternative antibacterial ingredients
[0045] Including povidone iodine, chlorhexidine, bromogeramine, PHMB, compound lysozyme, and nitrofurazone. The main components, initial concentrations (that is, the concentrations routinely used in wound disinfection) and suppliers of each disinfectant are shown in Table 1.
[0046] Table 1 Information table of alternative antibacterial ingredients
[0047]
[0048] (2) Source of bacteria
[0049] The bacterial strains used in the experiment include sau, aba, and kpn. The standard strains were sau ATCC19606, abaATCC6538, and kpn CMCC(B)46117, all of which were purchased from China Common Microorganism Culture Collection Center. The clinical strains were all from Shanghai Changhai Hospital, all the strains were collected during 2015.01-2017.06, and repeated samples from the same patient at different times were removed. All strains were ident...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Embodiment 2: artificial dermis preparation
[0075] 1. Selection of artificial leather form
[0076] (1) Experimental materials
[0077] artificial leather, optional The double-layer artificial dermis repair material was provided by Shenzhen Tsinghua University Research Institute. It has a double-layer structure, a collagen layer and a silica gel layer. The collagen layer is made of bovine tendon collagen (mainly type I collagen) and has a pore size of 50-200 μm. A silicone layer and a collagen layer without adhesion were provided, respectively.
[0078] Bacteria are the aforementioned standard bacterial strains, which are made into a bacterial suspension with a concentration of 106cfu / mL, and the preparation method is the same as before.
[0079] Cell source, normal human dermal fibroblasts, supplied by PromoCell. Human vascular endothelial cells were supplied by Shanghai Bogu Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0080] 2. Preparation of PHMB slow-release hydrogel and gel...
Embodiment 3
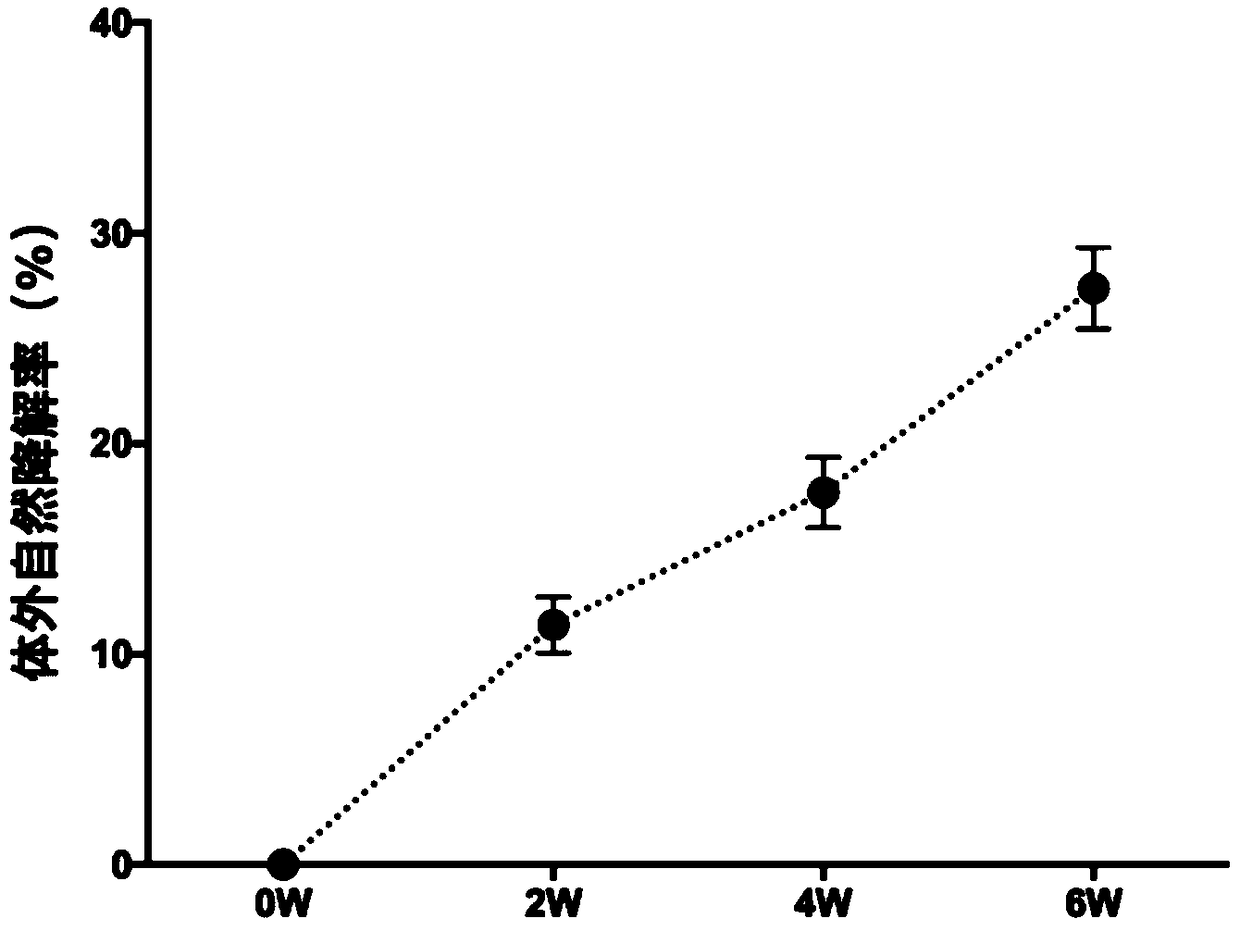
[0109] Embodiment 3: Cytotoxicity and degradation experiment of artificial dermis
[0110] 1. Cytotoxicity experiment
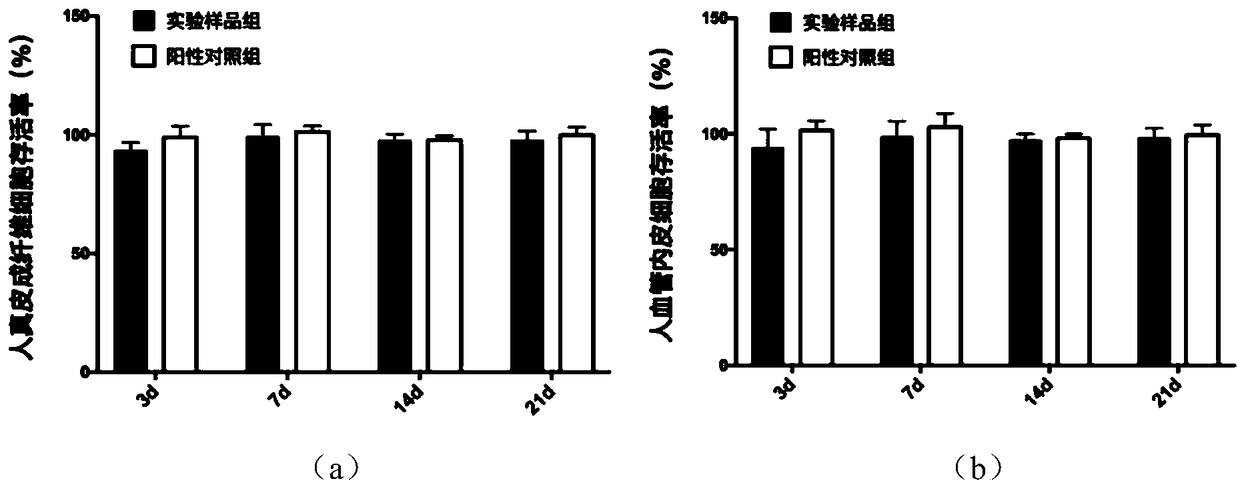
[0111] Fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells are one of the most important cells in the process of wound healing, so this study measured the in vitro cytotoxicity of experimental samples and artificial dermis without antibacterial ability to human dermal fibroblasts and human vascular endothelial cells. The target cells were subcultured in cell culture medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. The experimental samples and the artificial dermis without antibacterial ability were made into circles with a diameter of 16 mm, and placed in 24-well plates respectively. The artificial dermis without antibacterial ability was added as a positive control group, and a blank control group was set up in addition. For other treatments, add 500 μL containing 1×10 6 cell / L cell culture medium. 35°C, 5% CO 2 After incubation for 3, 7, 14, and 21 days, the num...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com