Free-stock scion grafting seedling raising method for cyclocarya paliurus
A technology of grafting and lichen, which is applied to the field of root-branch grafting and raising seedlings of fenugreek, can solve the problems of incompatibility, low quality of seedlings, difficult survival of grafted fenugreek, and achieves strong affinity and high afforestation survival rate. , adaptive and resistant effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
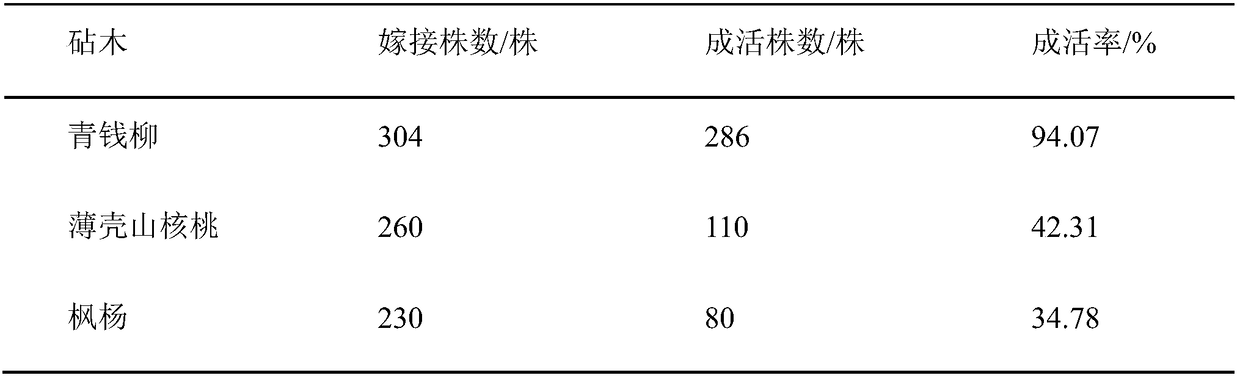
[0032] Embodiment 1: Grafting survival rate comparison of different stock and fringe combinations
[0033] Table 1 Comparison of graft survival rate of different rootstock and ear combinations
[0034]
[0035] As shown in Table 1, after 90 days of grafting, the graft survival rates of different rootstock and ear combinations were significantly different, and the graft survival rate of Cyclocarya paliurus as rootstock was the highest at 94.07%. The rates were 42.31% and 34.78%, respectively. The preservation rates in the second year of grafting were 92.10%, 26.92% and 18.26%, respectively, and the grafted seedlings with pecan and maple poplar as rootstocks grew poorly, and the preservation rate of grafted seedlings with Cyclocarya carya as rootstocks in the third year It was 92.10%, and the grafted seedlings of the remaining two rootstock and ear combinations all died.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Spring cut
[0037] 1) In early spring, transplant the sprouts in a cylindrical non-woven bag with a diameter of 12 cm and a height of 16 cm after filling the soil. The substrate is yellow core soil: perlite: chicken manure: peat = 2:2:3:3, growing season Strengthen fertilizer and water management to promote rootstock diameter growth.
[0038] 2) In the spring of the following year, select strong container seedlings with a ground diameter > 1 cm as rootstocks, and make scions with fully lignified 1-year-old branches of Cyclocarya paliurus. beyond the heart. Gently peel off the skin on the side of the bud, and cut forward with a flat knife, so as to just peel off the skin layer, without cutting the xylem or a little bit of the xylem. Cut off the rootstock at a distance of 10 to 15 cm from the ground, flatten the section, and then longitudinally cut down between the xylem and phloem. It is better not to damage the xylem just after reaching the cambium, and th...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: spring skin tongue joint
[0042] 1) In early spring, transplant the sprouts in a cylindrical non-woven bag with a diameter of 12 cm and a height of 16 cm after filling the soil. The substrate is yellow core soil: perlite: chicken manure: peat = 2:2:3:3, growing season Strengthen fertilizer and water management to promote rootstock diameter growth.
[0043] 2) In the spring of the following year, select strong container seedlings with a ground diameter > 1cm as rootstock, and make scions with fully lignified 1-year-old branches of Cyclocarya paliurus, cut flatly at 1 cm above the scion buds, and cut the lower end of the scion into 4-5cm long Horse-ear-shaped inclined surface, one side cuts off the xylem, the cutting edge should be cut downwards at the beginning, beyond the pith, and then turned over to cut a knife, the thickness should be inserted tightly between the cortex and xylem of the rootstock without cracking the skin. Cut a knife on both sides of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com