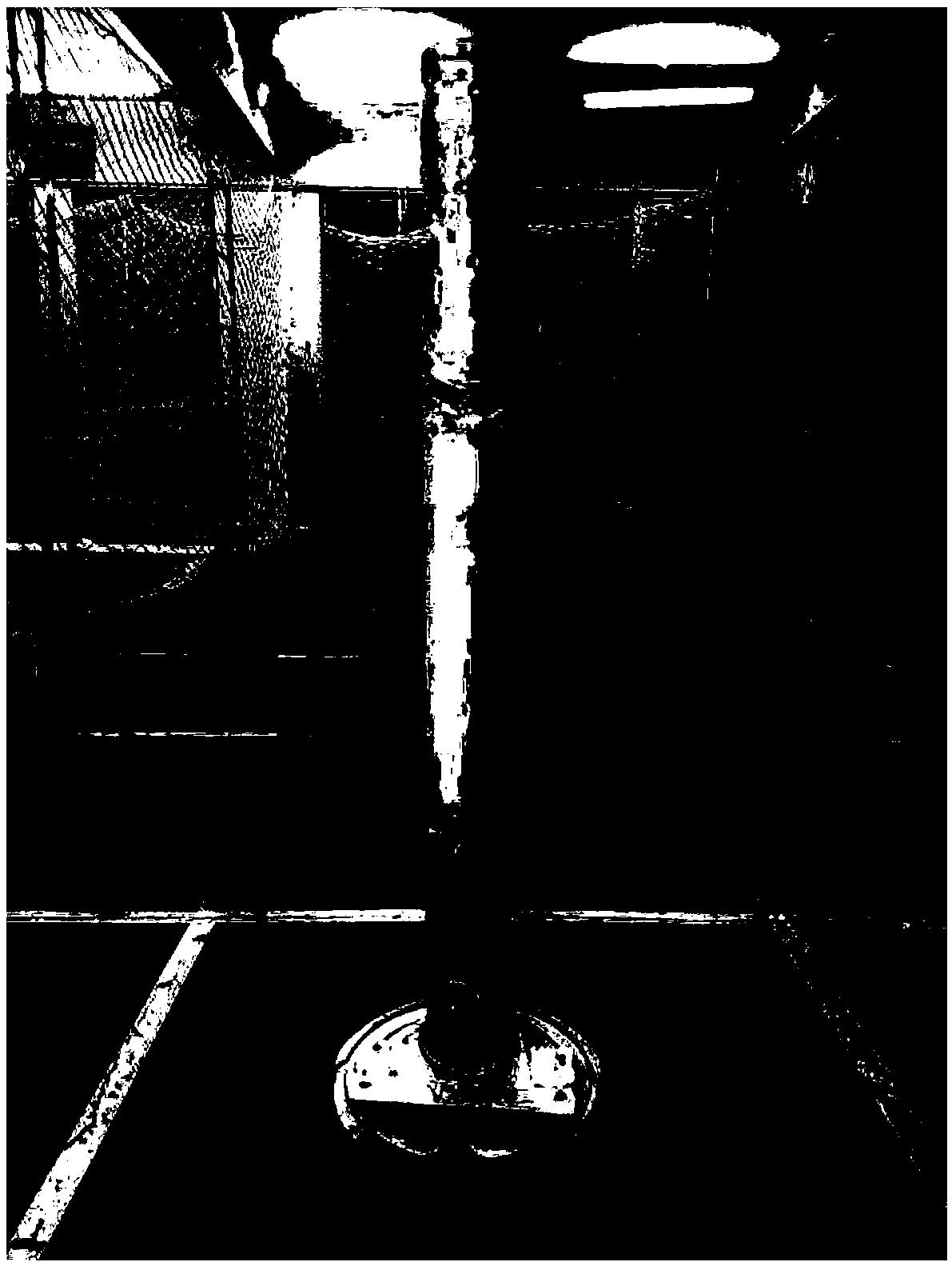Motion obstacle detection and positioning method based on depth images
A technology of obstacle detection and positioning method, which is applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing, etc., and can solve problems such as difficult to operate quickly and efficiently, difficult to identify obstacles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
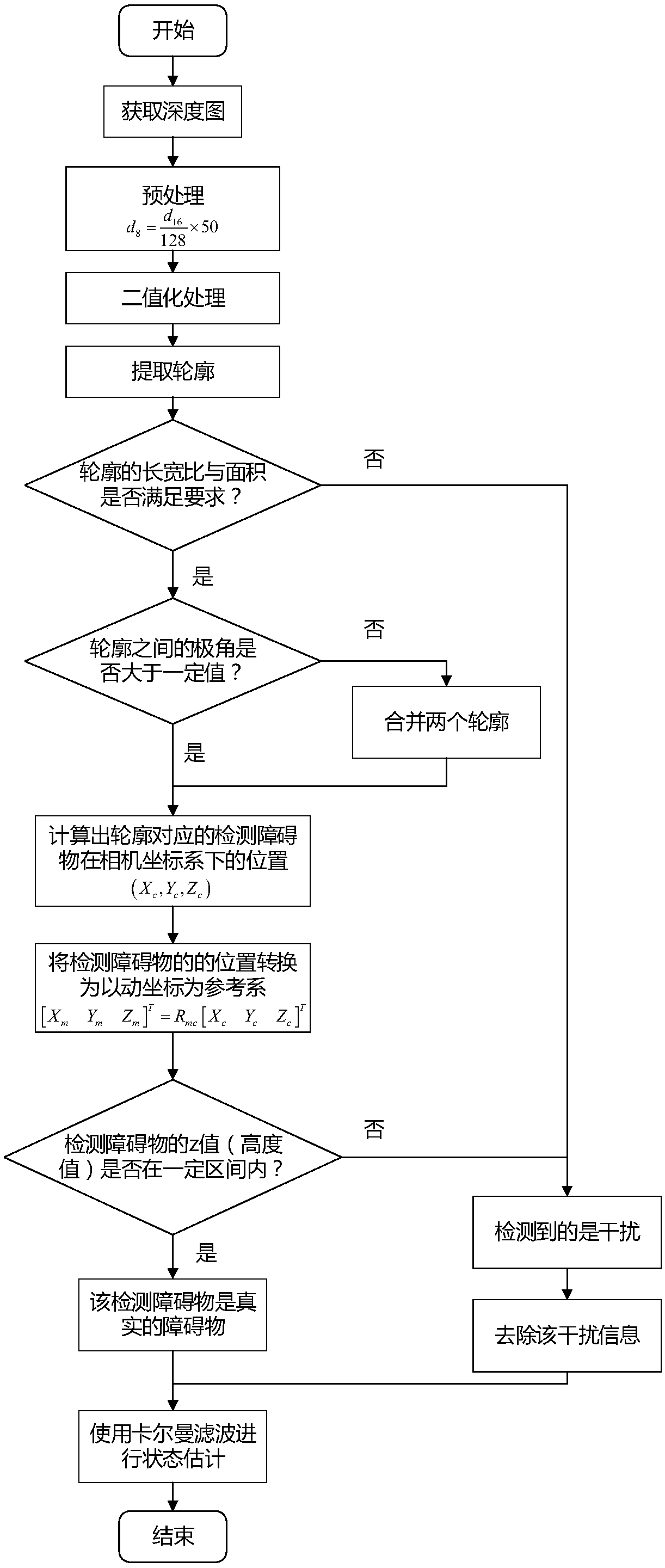
[0096] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, a method for detecting and locating a moving obstacle based on a depth map described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
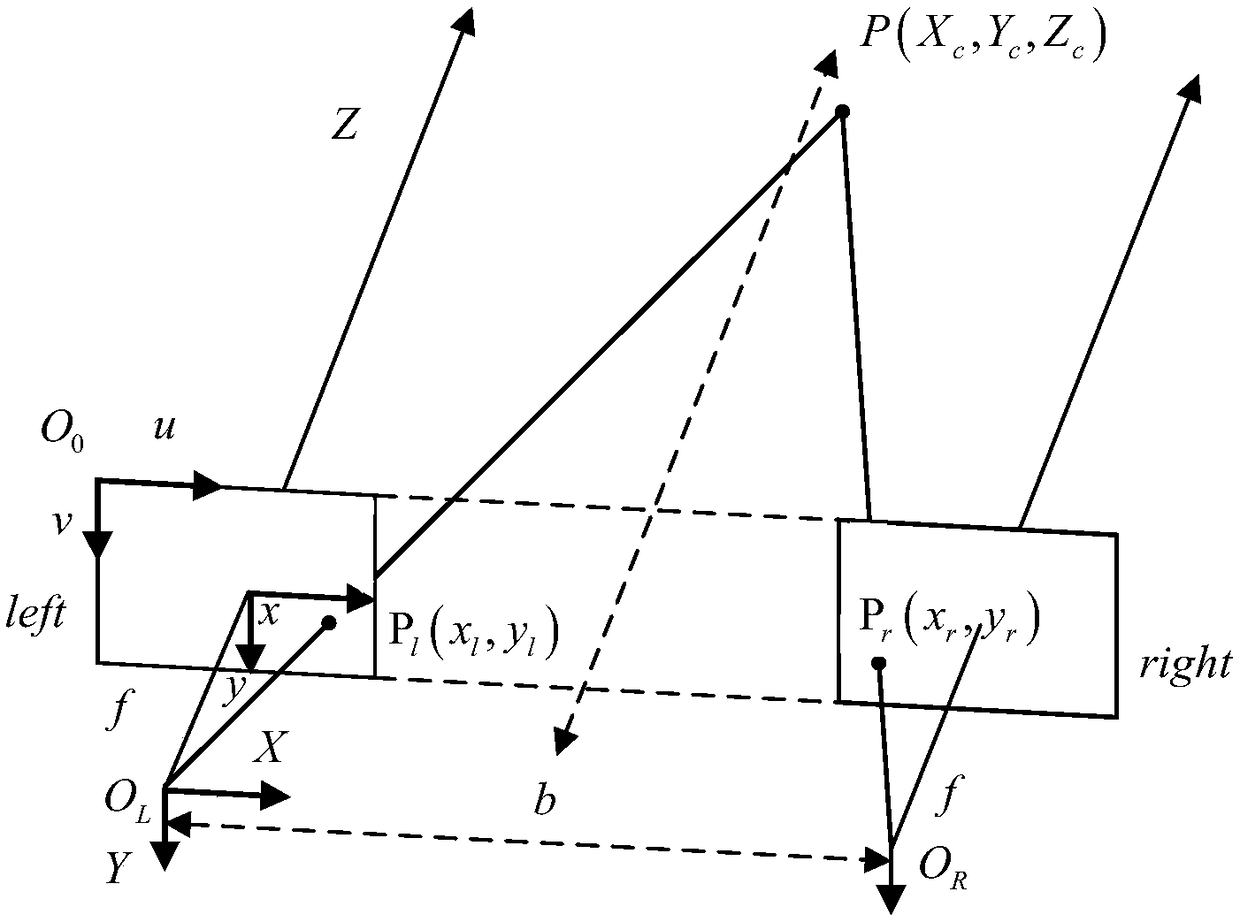
[0097] Step 1. Divide the eight cameras with the same focal length and the same internal parameters into four groups, two in each group, that is, four groups of binocular cameras are formed. Install four groups of binocular cameras on the front, rear, left and right directions of the quadrotor aircraft respectively. Configure each group of binocular cameras according to the parallel configuration method, and establish the imaging model of the flat configuration binocular cameras; figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of parallel configuration of binocular cameras.
[0098] Step 2: The cameras collect video images at the same time, and obtain the depth map formed by each group of binocular cameras. And displayed in the form of grayscale image;
[0099] Step 3....
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0105] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 2 To describe this embodiment,
[0106] The process of configuring each group of binocular cameras according to the parallel configuration described in step 1 of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0107] Two cameras C1 and C2 with the same focal length and the same internal parameters are fixed in such a way that the optical axes are parallel to each other. Since the optical axis is perpendicular to the image plane, the y axes of the image coordinate systems of the two cameras are parallel to each other, and the x axes coincide with each other. It can be considered that a camera is completely coincident with another camera after being translated for a certain distance along its x-axis.
[0108] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0109] The process of establishing the imaging model of parallel configuration binocular cameras described in step 1 of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0110] Firstly, determine the translation distance b that the two coordinate systems of the binocular cameras C1 and C2 configured in parallel differ only on the x-axis, which is the baseline length. Next assume that the coordinate system of C1 is O l x l Y l Z l , the coordinate system of C2 is O r x r Y r Z r , under the above camera configuration, the spatial point P(X c ,Y c ,Z c ) in the C1 coordinate system is (X l ,Y l ,Z l ), in the C2 coordinate system is (X l -b,Y r ,Z r ). Simultaneously assume that the image pixel coordinates of point P on the left camera image plane and the right camera image plane are (u 1 ,v 1 ), (u 2 ,v 2 ). According to the characteristics of the parallel configuration method, v 1 =v 2 , let the parallax d=u 1 -u 2 . According to the geometric relations...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com