Enzyme-free glucose electrochemical sensor and detection method thereof
A glucose and electrochemical technology, applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, scientific instruments, instruments, etc., can solve tedious, time-consuming, limited, and limited problems, and achieve good electrode stability, broad application prospects, and good repeatability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
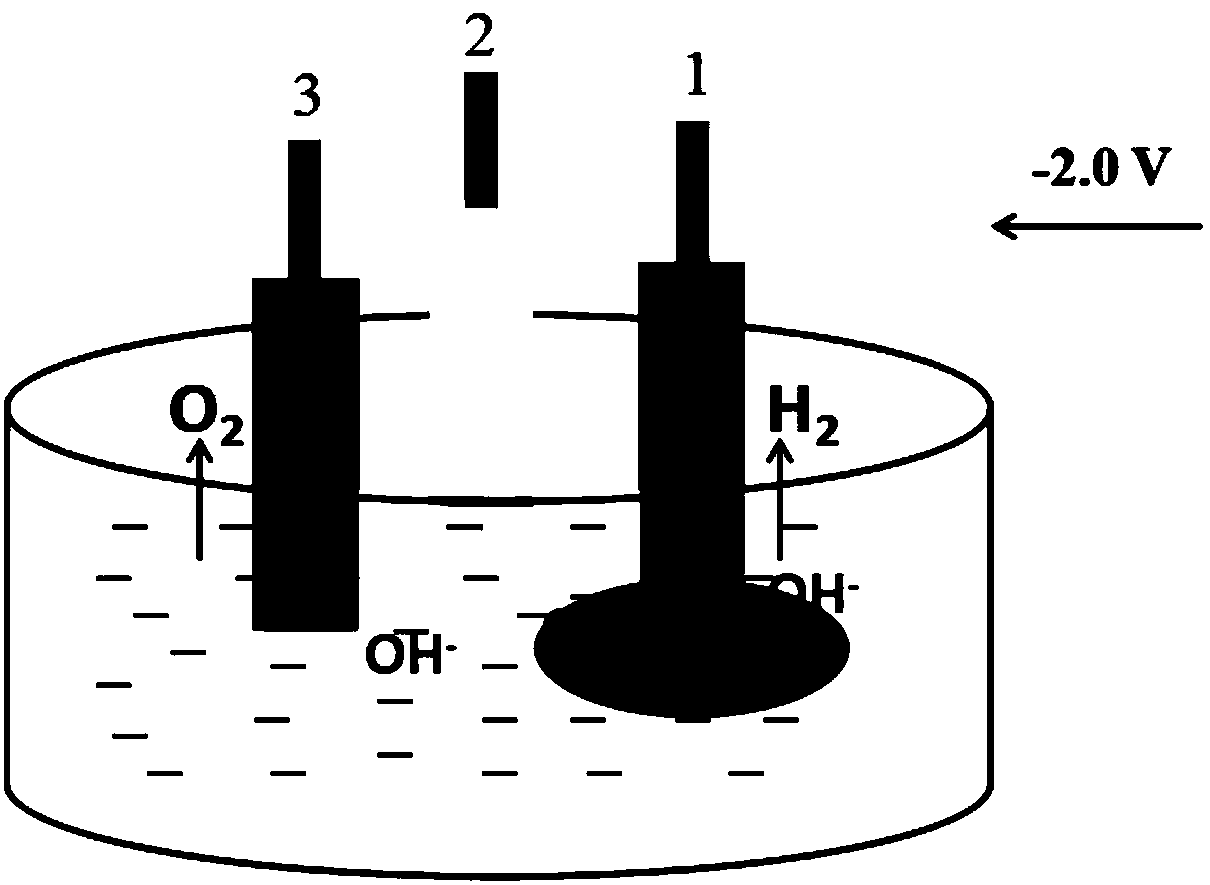
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, a gold electrode (2mm cross-sectional diameter) is used as the working electrode 1, silver-silver chloride is used as the reference electrode 2, and platinum wire is used as the counter electrode 3 to form a three-electrode system. In 0.1M pH 5.0 phosphate buffer, the glucose in the buffer was detected using an electrochemical workstation. Select multi-potential detection in the technology menu bar in the settings, and set the potentials that need to be applied in sequence in the parameter settings. In this test, the three potential settings are: apply -2.0V potential for 24s, +0.2V potential for 5s, and +1.0V potential for 2s. The detection is a cyclic process. During the detection process, the glucose concentration is changed to obtain the relationship between the glucose oxidation current and the concentration. , the detection current has a linear relationship with the glucose concentration in the range of 10 μM to 1025 μM.
Embodiment 2
[0033] A platinum electrode (2mm cross-sectional diameter) was used as the working electrode, silver-silver chloride was used as the reference electrode, and platinum wire was used as the counter electrode to form a three-electrode system. Glucose in the test. Use a pipette to draw 2.5 μL of 0.5% perfluorosulfonic acid solution and drop it on the surface of the platinum electrode, and let it dry naturally. The detection operation process is similar to Example 1. In this detection, the three potential settings are: -1.8V, 20s; +0.1V, 5s; +1.0V, 5s. The detection current has a linear relationship with the glucose concentration in the range of 30 μM to 750 μM.
Embodiment 3
[0035] A copper-nickel alloy (copper: nickel = 1:5) electrode (2mm diameter) is used as the working electrode, a saturated calomel electrode is used as the reference electrode, and a platinum wire is used as the counter electrode to form a three-electrode system. In 0.1M pH 7.0 phosphate buffer In , the glucose in the buffer was detected using an electrochemical workstation. Select the current-time curve in the technical menu bar of the setting, set the starting point as the detection potential +0.6V in the parameter setting, and set the time as 5s. Select pretreatment in the control menu bar, and set two pretreatment potentials in it, the potential 1 is +0.8V, and the time is 5s, which is used to remove the oxidation product adsorbed in the previous detection, and the potential 2 is set to -1.8V , the time is 20s. Each time the glucose concentration is changed, the detection is repeated, and finally the relationship between the detection current and the glucose concentration...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com