Method for clarifying macromolecular active aloe juice
A technology for macromolecules and aloe vera juice, which is applied in the field of clarification of macromolecular active aloe vera juice, can solve the problems of loss of functional components, complicated operation and high cost, and achieves the effects of satisfying appearance, simple process and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] A clarification method for macromolecular active aloe juice, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0021] (1) Preparation of components A and B of ZTC 1 + 1 clarifier:
[0022] Component A is prepared as 0.1% viscose solution with RO water: Accurately weigh 0.1g of component A, first use a small amount of RO water to make a paste, then add RO water to 100 mL, swell for 24 hours, and stir evenly to obtain 0.1 % viscose liquid.
[0023] Component B is prepared as 0.1% viscose solution with 1% citric acid aqueous solution or RO water: Accurately weigh 0.1g of component B, first make a paste with a small amount of 1% citric acid aqueous solution or RO water, then add 1% citric acid Aqueous solution or RO water to 100 mL, swell for 24 hours, stir evenly to obtain 0.1% viscose solution.
[0024] (2) According to the preparation method provided by the Chinese invention patent with application number 201510103907.5, macromolecular active aloe juice is prepared, and a...
Embodiment 2
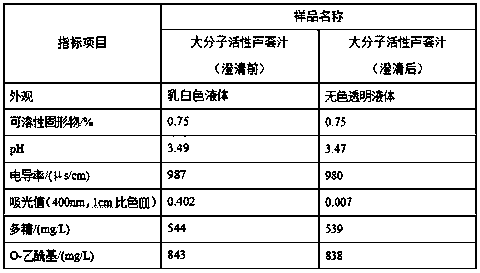
[0027] The comparison of each index before and after clarification made according to embodiment 1 is as follows:
[0028] Table 1 Comparison of physicochemical properties of macromolecular active aloe juice before and after clarification
[0029]
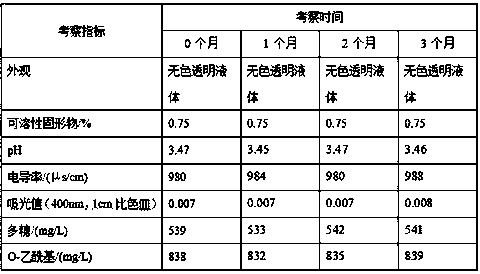
[0030] From the index comparison results, it can be seen that the physical and chemical indexes (soluble solids, pH value, electrical conductivity) and active ingredients (polysaccharides, O-acetyl) of the macromolecular active aloe juice before and after clarification are basically unchanged, and the light absorption value is significantly reduced. raised.
Embodiment 3
[0032] The relative molecular mass of the aloe polysaccharide before and after the clarification of the macromolecular active aloe juice made according to embodiment 1 is determined, and the specific GPC test conditions are as follows:
[0033] Chromatographic column: PL aquagel-OH 60 (8 μm, 300×7.5mm) and PL aquagel-OH 40 (8 μm, 300×7.5mm) are used in series
[0034] Mobile phase: pure water
[0035] Column temperature: 30°C
[0036] RID detector temperature: 40°C
[0037] Flow rate: 0.6 mL / min, injection volume is 50 μl
[0038] Sample processing method: alcohol precipitation dialysis treatment
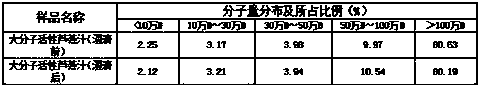
[0039] The relative molecular mass test results of aloe polysaccharides are as follows:
[0040] Table 2 Molecular weight distribution ratio of macromolecular active aloe vera juice before and after clarification
[0041]
[0042] From the molecular weight test results, it can be seen that the molecular weight distribution of aloe polysaccharides has basically no change befo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com