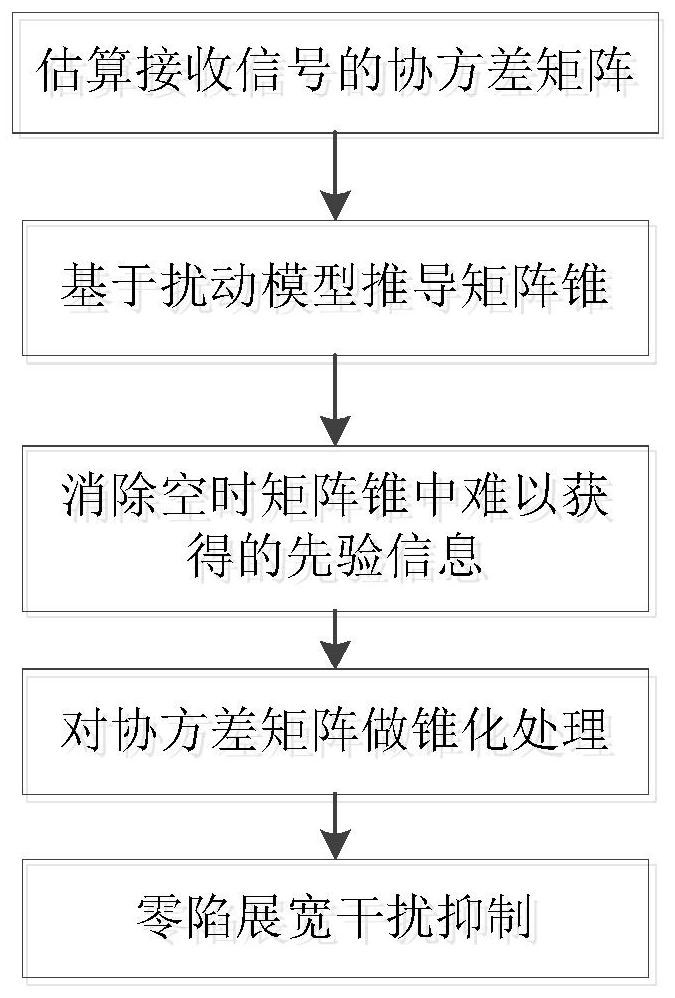
A highly dynamic GNSS null-broadening interference suppression method based on space-time processing
A technology of zero trap widening and interference suppression, which is applied in the direction of instruments, measuring devices, satellite radio beacon positioning systems, etc., can solve problems such as the complexity of the covariance matrix structure, increase the degree of freedom of anti-interference, increase computational complexity, suppress interference effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
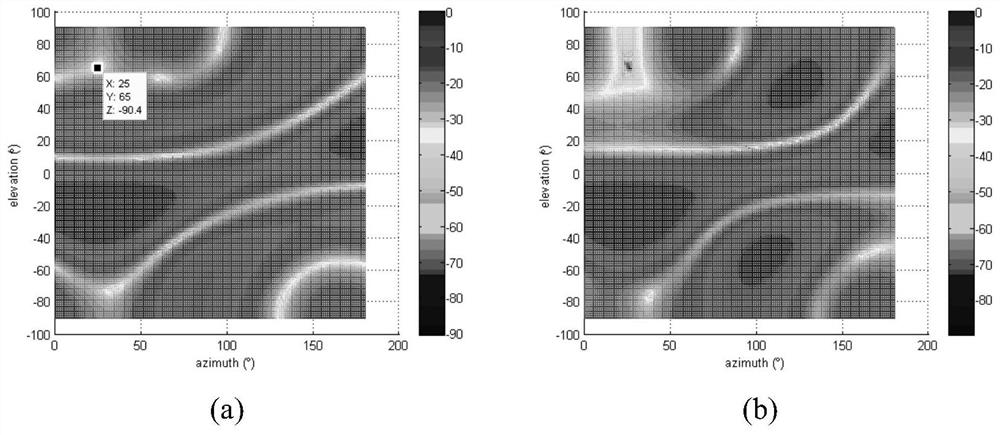
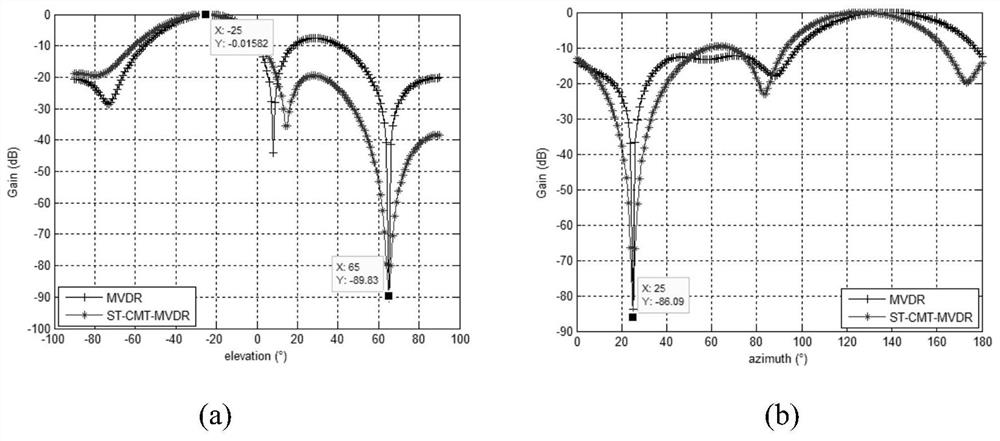
[0070] Embodiment 1: Consider that the pitch angle and azimuth angle of the GNSS signal arriving at the array element reference point are (-25°, 25°); the interference is a 3MHz linear frequency modulation (Linear Frequency Modulation, LFM) signal, and the direction is (65° ,25°), the center frequency is 14.98MHz, and the interference-to-noise ratio INR=60dB; the standard deviation parameter σ in the tapering matrix; the fixed frequency is the center frequency, and the following is obtained: figure 2 The beamforming diagram is shown, and the profile is shown in image 3 shown;
[0071] The simulation found that the ST-CMT invented in this paper can be combined with the MVDR beamforming technology, which can point the main beam to the direction of the desired signal, and form a wider null in the pitch angle and azimuth angle of the interference, so as to suppress the interference in high dynamics Purpose.
Embodiment 2
[0072] Embodiment 2: the elevation angle and the azimuth angle of the desired signal are (-15°, 25°); the interference signal is far-field LFM, its center frequency is 14.98MHz, the bandwidth is 2MHz, and the interference signal direction is (55°, 105°) , the interference-to-noise ratio INR=60dB, 20 Monte Carlo experiments; when there is a mismatch in the pitch angle, the simulation results under different taper matrix parameters σ are as follows Figure 4 Shown in (a); similarly, we obtain the change situation of the ST-CMT-MVDR anti-jamming performance when there is a mismatch in the azimuth angle; σ=0° corresponds to the traditional MVDR algorithm without zero trap broadening;
[0073] like Figure 4 As shown, in a highly dynamic environment, that is, when there is a mismatch in the interference null direction, the anti-jamming performance of the traditional space-time minimum variance distortion-free response algorithm ST-MVDR deteriorates rapidly with the increase of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3: the elevation angle and azimuth angle of desired signal are (-25 °, 25 °); Interference signal is far-field LFM, and its center frequency is 14.98MHz, bandwidth 2MHz, and interference comes from (60 °, 100 °), The interference-to-noise ratio is 60dB; the number of Monte Carlo tests is 3000; on the one hand, the parameter σ of ST-CMT-MVDR is set to 0.2° and 1.2° respectively, and it is applied to a Gaussian mismatch high dynamic environment with different standard deviations , to observe the variation of its anti-jamming performance with the standard deviation of the mismatch magnitude; on the other hand, we explored how the anti-jamming performance varies with the mismatch degree when the parameter σ of ST-CMT-MVDR just matches the standard deviation of the disturbance magnitude. Changes.
[0075] like Figure 5 As shown, setting the parameters of ST-CMT-MVDR properly can effectively ensure the robustness of the anti-jamming algorithm. In addition, it ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com