Genetic biomarkers for predicting or assisting in predicting risk of radiation pneumonitis after pulmonary radiation and application of genetic biomarkers
A biomarker, radiation pneumonitis technology, applied in the determination/examination of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] The collection of embodiment 1 clinical sample
[0074] The clinical blood samples were obtained from a hospital in Beijing. The above samples were all obtained with the informed consent of the individual. The 72 samples obtained were all from lung cancer patients before radiotherapy. Blood collection was performed in accordance with clinical routines. 1ml of venous blood was collected and stored in conventional EDTA anticoagulant tubes for no more than one week.
Embodiment 2
[0075] The identification of embodiment 2 sample genotype
[0076] Genomic DNA was extracted from the collected blood samples using a DNA extraction kit.
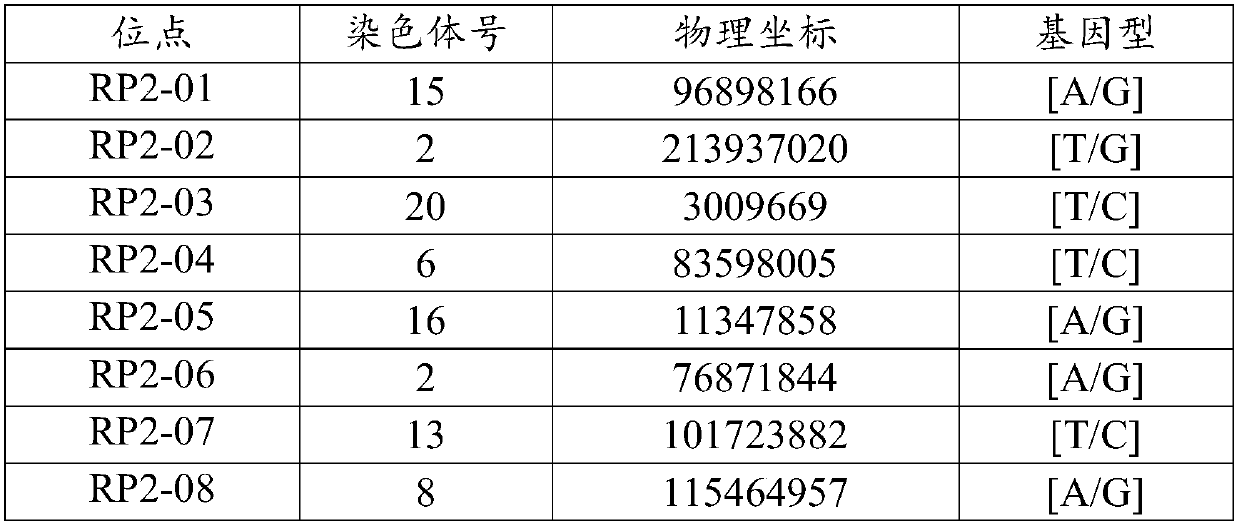
[0077] The 72 genomic DNAs extracted from the 72 samples in Example 1 were sequenced by the gene sequencing method, and the genotypes of the 31 single nucleotide polymorphism sites provided by the present invention were obtained.
Embodiment 3
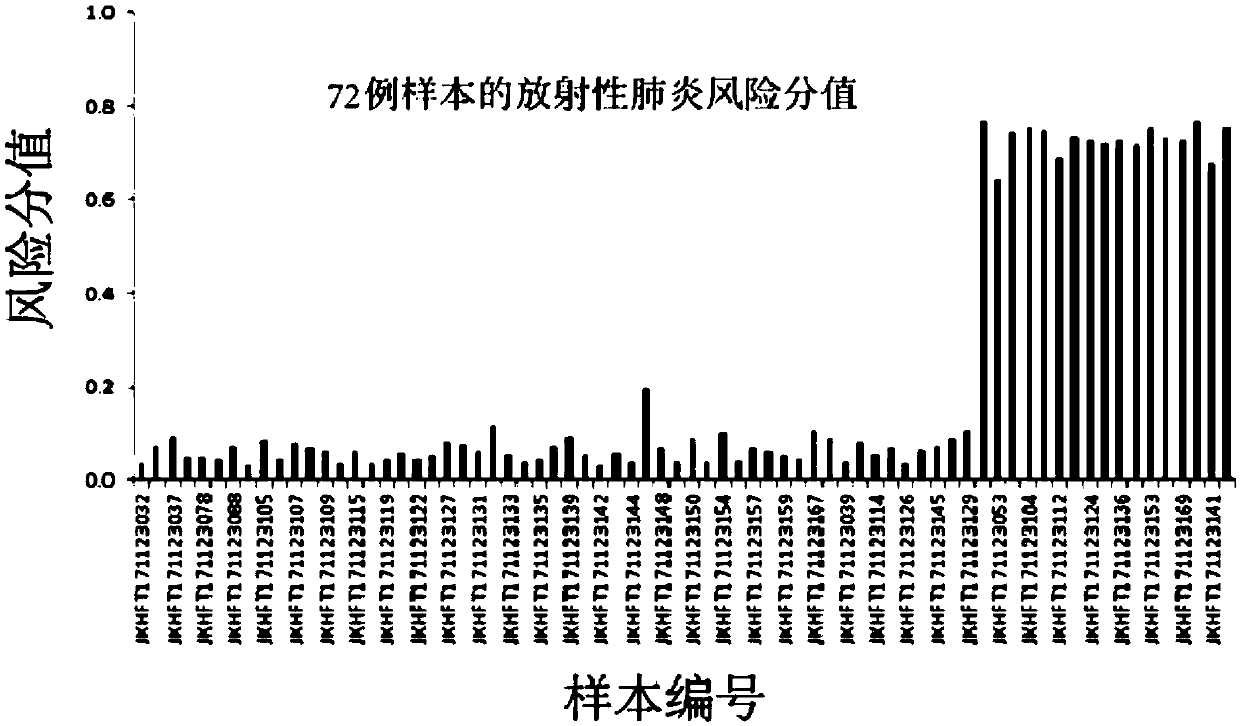
[0078] Example 3 Calculation of Risk Score
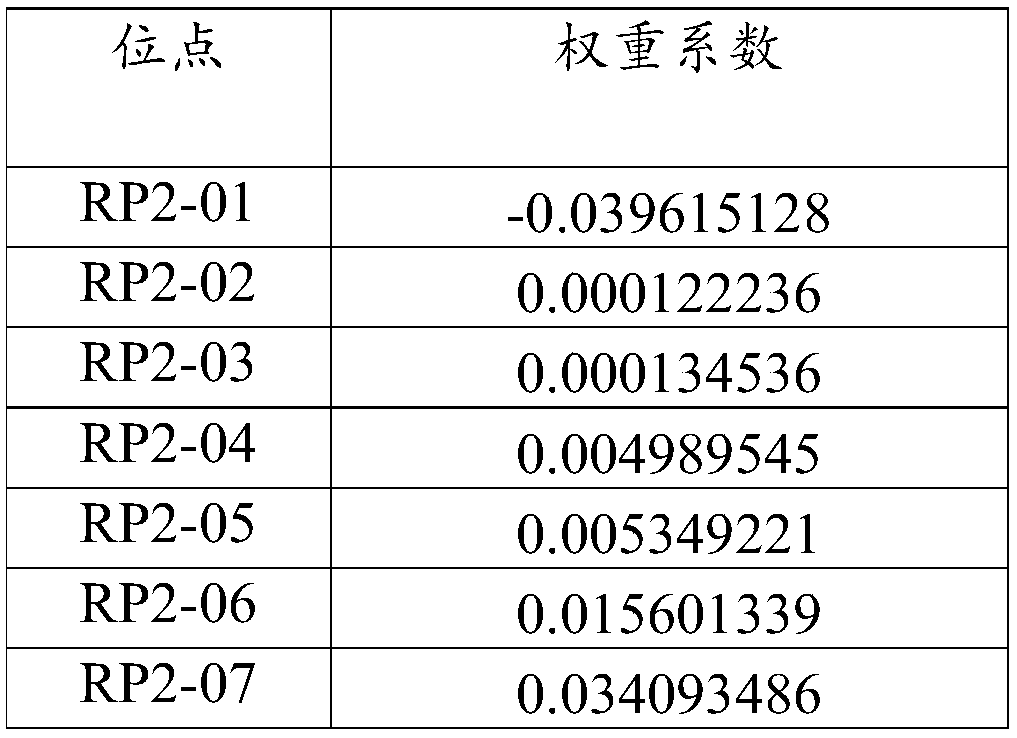
[0079] The genotypes of the 31 sites detected in the sample in Example 2 were compared with the human reference genome version 37 (GRCh37). The original assignment of this site is 0; when the result of the alignment of this site is that one copy is consistent, the original assignment of this site is 1; when the result of the comparison of this site is that both copies are variant, the The original assignment is 2. Then the original assignment of each site is multiplied by the weight coefficient of the site (see the table below), and the resulting value is the calculated score of the site. The calculated scores of 31 sites of a sample are added, and the sum obtained is the risk value corresponding to the sample. When the sum value is greater than 0.5, it is judged that the patient will develop radiation pneumonitis of grade 2 or above. Multiplying the risk value by 100% is the risk probability of the patient suffering from grade 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com