Processing method for nucleic acid third generation sequencing raw data and application thereof
A processing method and raw data technology, applied in special data processing applications, electrical digital data processing, sequence analysis, etc., can solve the problems of short sequencing read length, high single-base error rate, large interference of assembly software, etc., to improve accuracy good complementation and correction, and the effect of reducing the single-base error rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
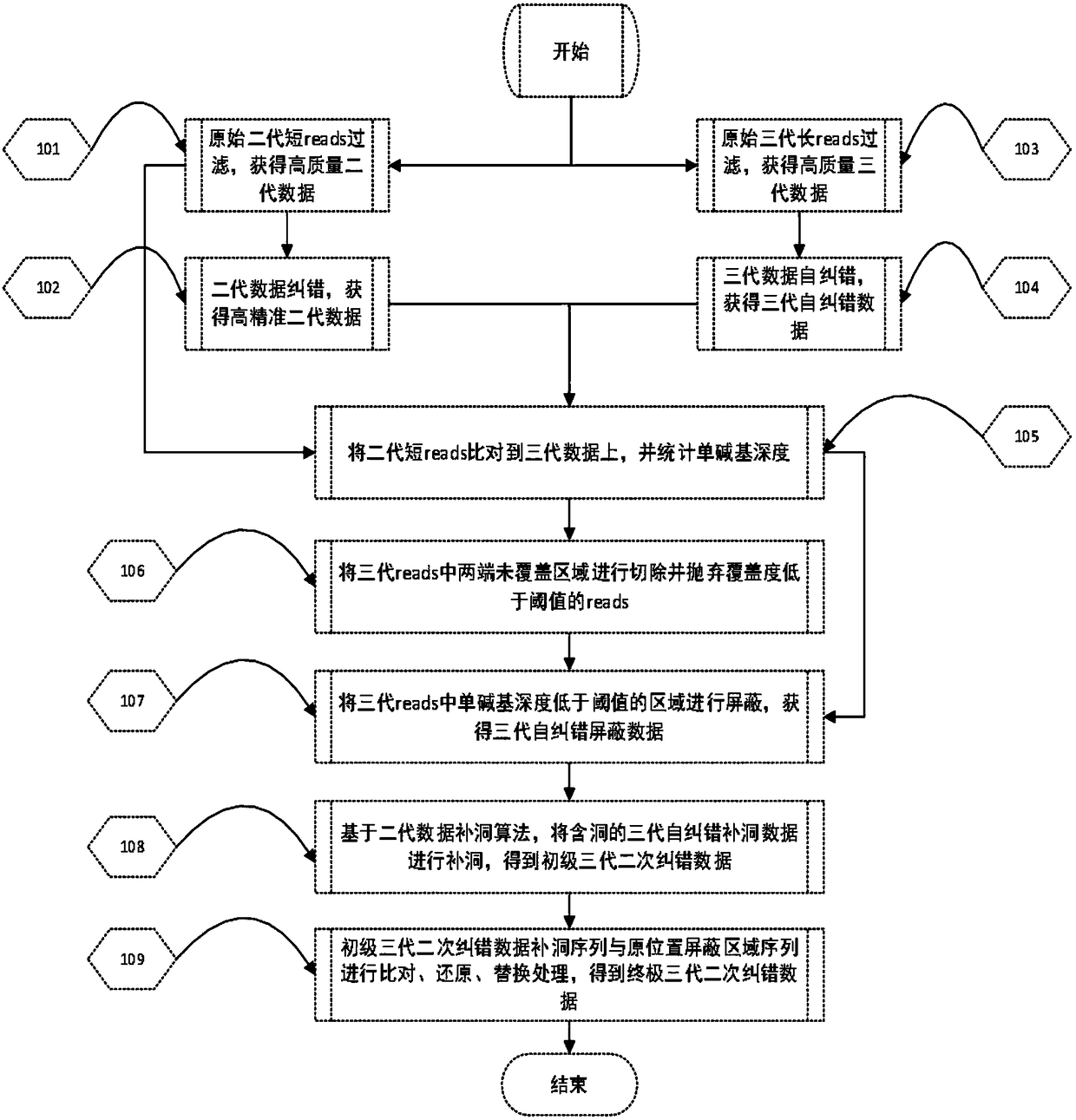
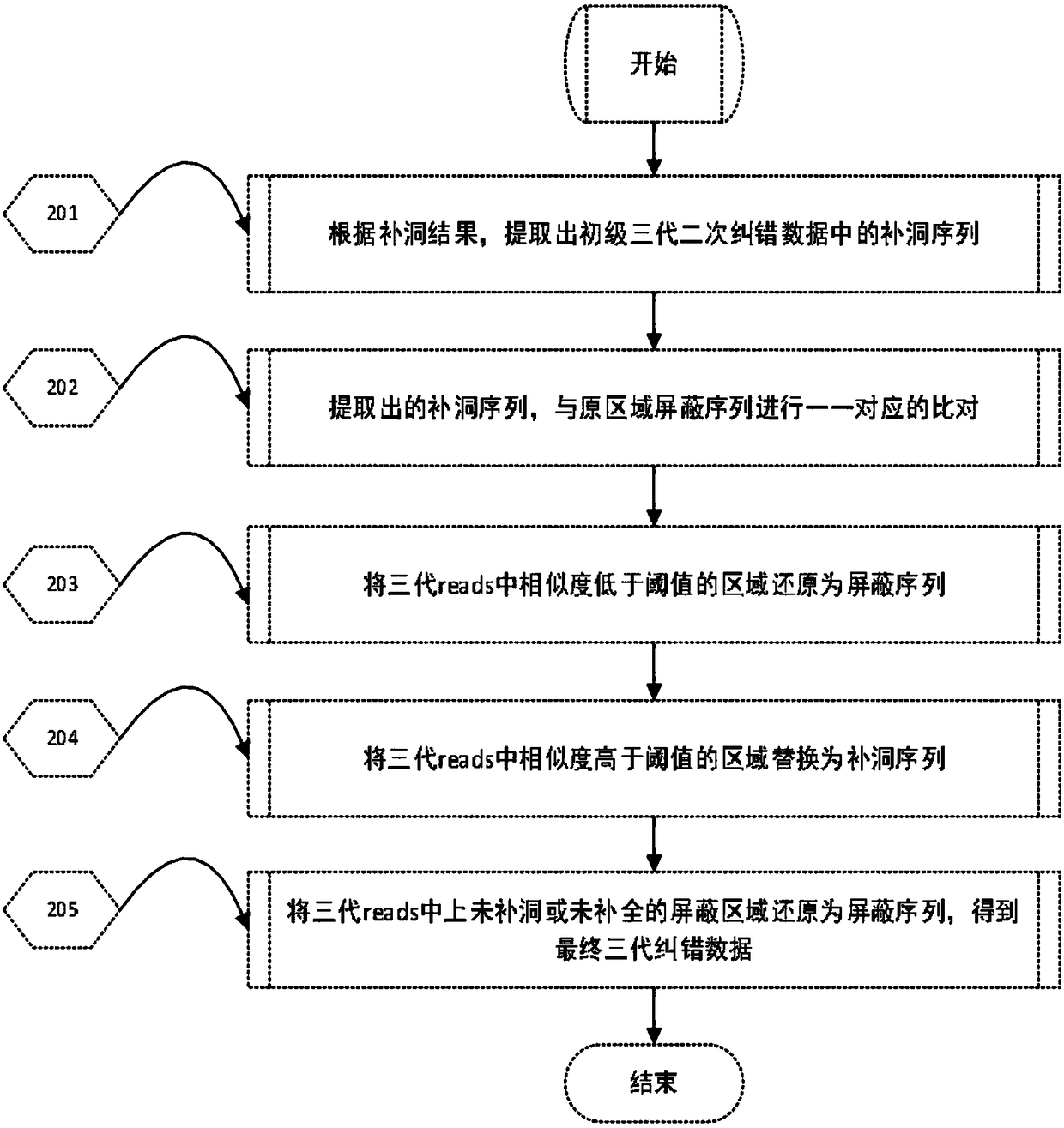
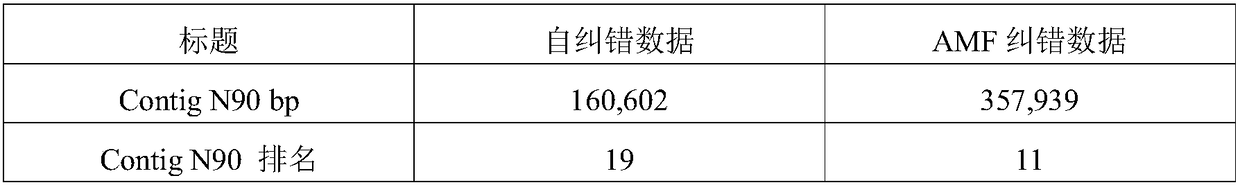
[0068] In this example, human chromosome 22 with an effective reference sequence size of 35Mb and an actual size of 51Mb is used as the analysis object, and the original data processing method of the third-generation nucleic acid sequencing of the application is used for error correction. details as follows:
[0069] 1 Data processing
[0070] 1) The second-generation data and the third-generation data of human samples were respectively obtained through NCBI for testing.
[0071] 2) Using blasr, a global comparison software for single-molecule real-time sequencing long sequences, compared the third-generation data to the human genome hg19, extracted the third-generation sequencing long sequences on chromosome 22, and obtained a data volume of 3.14Gb, N50 It is 11.46Kb. That is, the third-generation long sequence data of step (b) in the processing method of the present application.
[0072] It should be noted that the third-generation data in this example are directly compar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com