Application of important gene GmSWEET6 of soybean sucrose transporter
A sucrose transporter, soybean technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering and biology, can solve the problem of no SWEET transporter research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
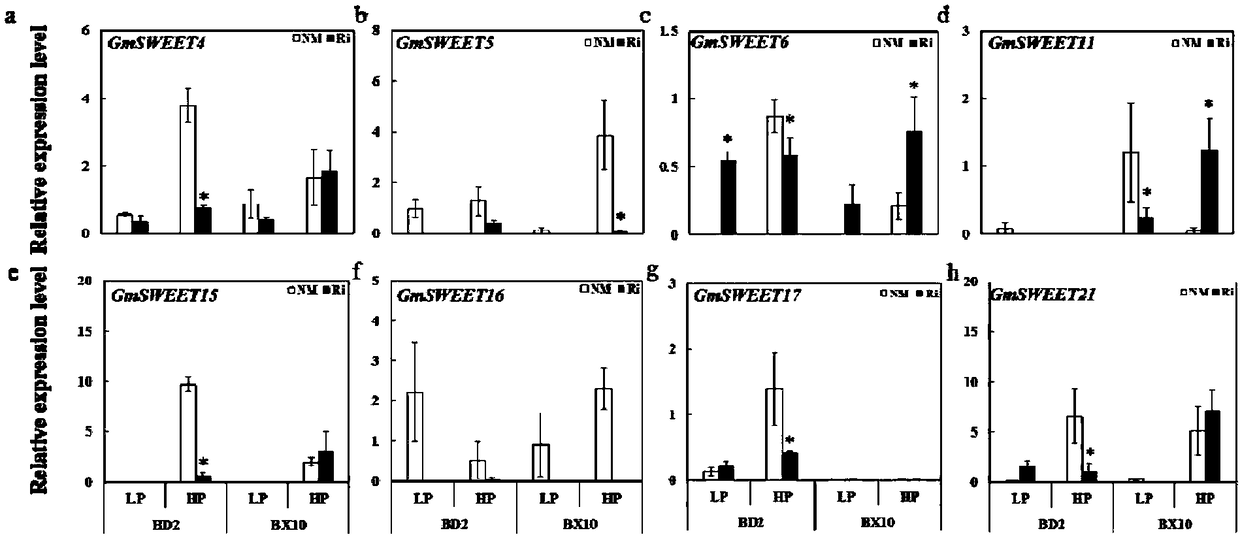
[0039] Analysis of the expression pattern of the GmSWEETs gene family in soybean roots: The soybean SWEET gene family has a total of 53 members (Patil et al., 2015). According to the evolutionary homologous relationship, the third branch related to sucrose transport and microbial symbiosis was screened28 Then, quantitative PCR technique was used to determine the expression of GmSWEETs family member genes under different soybean varieties, different inoculation treatments and different phosphorus levels.
[0040] Using two soybean varieties, phosphorus-efficient Brazilian 10 (BX10) and phosphorus-inefficient Native 2 (BD2), two AMF inoculation treatments were set up: no inoculation (NM) and inoculation with AM fungus Rhizophagus irregularis (Ri). Set up two phosphorus treatments, 50 μM KH 2 PO 4 As low phosphorus (LP) and 500 μM KH 2 PO 4 K as High Phosphorus (HP), Low Phosphorus Treatment + with K 2 SO 4 make up. Use 1 / 2 Hoagland nutrient solution for sand cultivation. ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] 1. Cloning of GmSWEET6 gene: using the soybean YC03-3 leaf cDNA as a template, using the upstream specific primer 5′-ATCG CCCGGG ATGTCGTCCCACAGTCATTCTAA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 5) and downstream specific primer 5'-ATCG CCCCGGG TCAAACTTCGCAACTGATCACCC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 6) amplified the full-length ORF sequence of 864bp of the GmSWEET6 gene, and sequenced and compared the obtained GmSWEET6 coding sequence, see Glyma.04G198600, and the corresponding protein sequence, see Glyma.04G198600.
[0056] 2. GmSWEET6 gene promoter cloning, vector construction and tissue expression localization analysis: Promoter analysis and expression vector construction: according to conventional methods, extract genomic DNA from leaves of soybean YC03-3 genotype, use soybean leaf genomic DNA as a template, and use Upstream specific primer 5′-CTATGACATGATTAC GAATTC CCACCTTGTTATACCTCATT-3' (SEQ IDNO: 7) and downstream specific primer 5'-GACTGACCTACCCGG GGATCC GGAATTTCTCTCTCTCCTCT-3′(SEQ IDNO:8) amplifie...
Embodiment 3
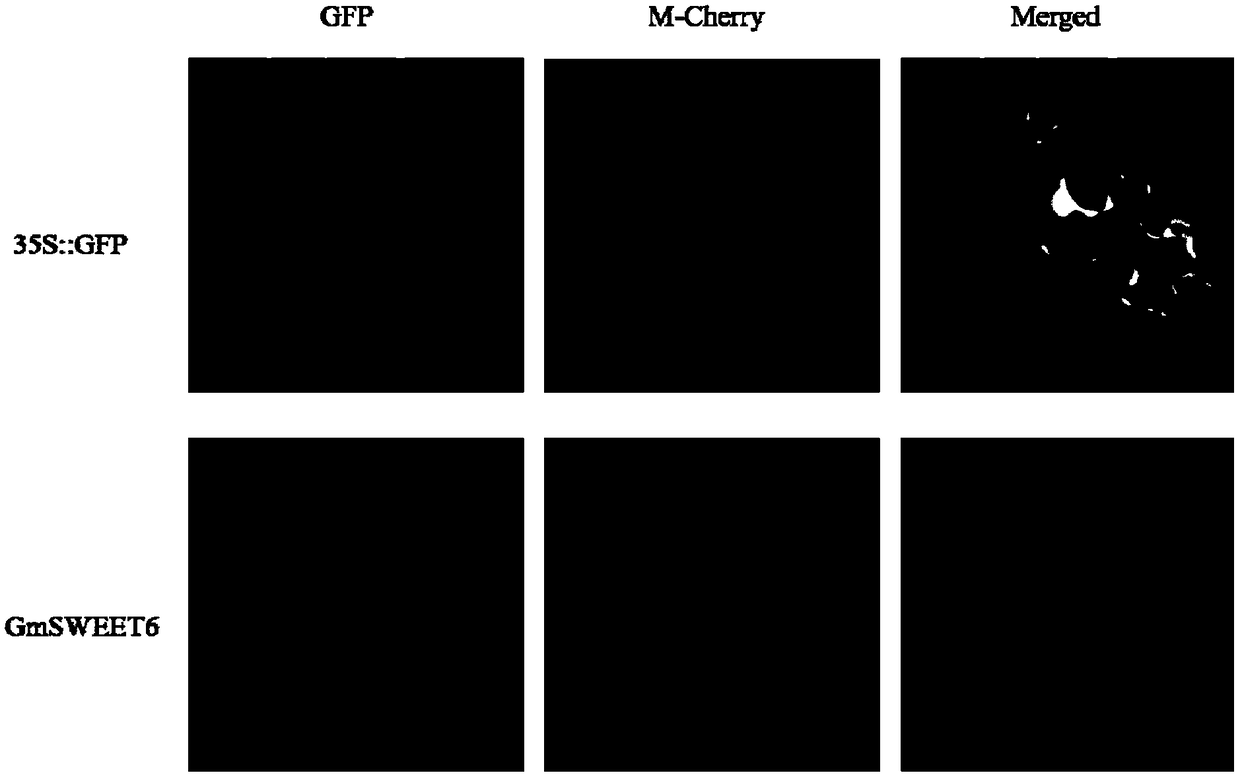
[0059] Construction of subcellular localization experiment vector: using soybean YC03-3 leaf cDNA as template, using upstream specific primer 5'-GGGGacaagtttgtacaaaaaagcaggcttcATGTCGTCCCACAGTCATTCTAA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 9) and downstream specific primer 5'-GGGGaccactttgtacaagaaagctgggtcTCAAACTTCGCAACTGATCACCC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 10) Amplify the full-length ORF sequence of 864bp of the GmSWEET6 gene, recover the fragment by PCR, and connect the GmSWEET6 gene to the destination vector pMDC43 by Gatway technology. Escherichia coli DH10B was transformed, and Agrobacterium GV3101 was transformed after the sequence was correct for subcellular localization experiments.
[0060] For the subcellular localization analysis of GmSWEET6, the method of transient transformation of tobacco epidermal cells was used. Shake the GV3101 bacterial liquid fused with the GmSWEET6 gene and the GV3101 bacterial liquid transformed into the membrane Marker plasmid 1008 overnight, then centrifuge, and use 2 And th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com