Method for in-situ blocking and remediating heavy metal contaminated bottom mud
A technology of polluted bottom sludge and remediation method, applied in the direction of sludge detoxification, water pollutants, sludge treatment, etc., can solve the problems of release and secondary pollution, and achieve the effect of preventing release and eliminating environmental risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0017] The in-situ barrier repair method of heavy metal polluted bottom mud of the present invention, its preferred embodiment is:
[0018] Include steps:
[0019] A. Division of treatment units and setting of temporary storage pools: According to the sediment thickness and heavy metal content of the target restoration area of the watershed to be restored, and the geographical distribution of the restoration area, the area to be repaired is divided into several unit areas. Set up temporary storage tanks for sediment disposal according to the amount of sludge to be treated in the divided unit area;
[0020] B. Transfer and stabilization of bottom sludge: transfer the bottom sludge in the unit area to the temporary storage tank, and add stabilizing agents to the sludge in the tank to achieve passivation of heavy metals in the sludge;
[0021] C. Laying of the bottom isolation mold bag: Lay the isolation layer to the bottom of the unit area after cleaning the bottom mud;
[0...
specific Embodiment
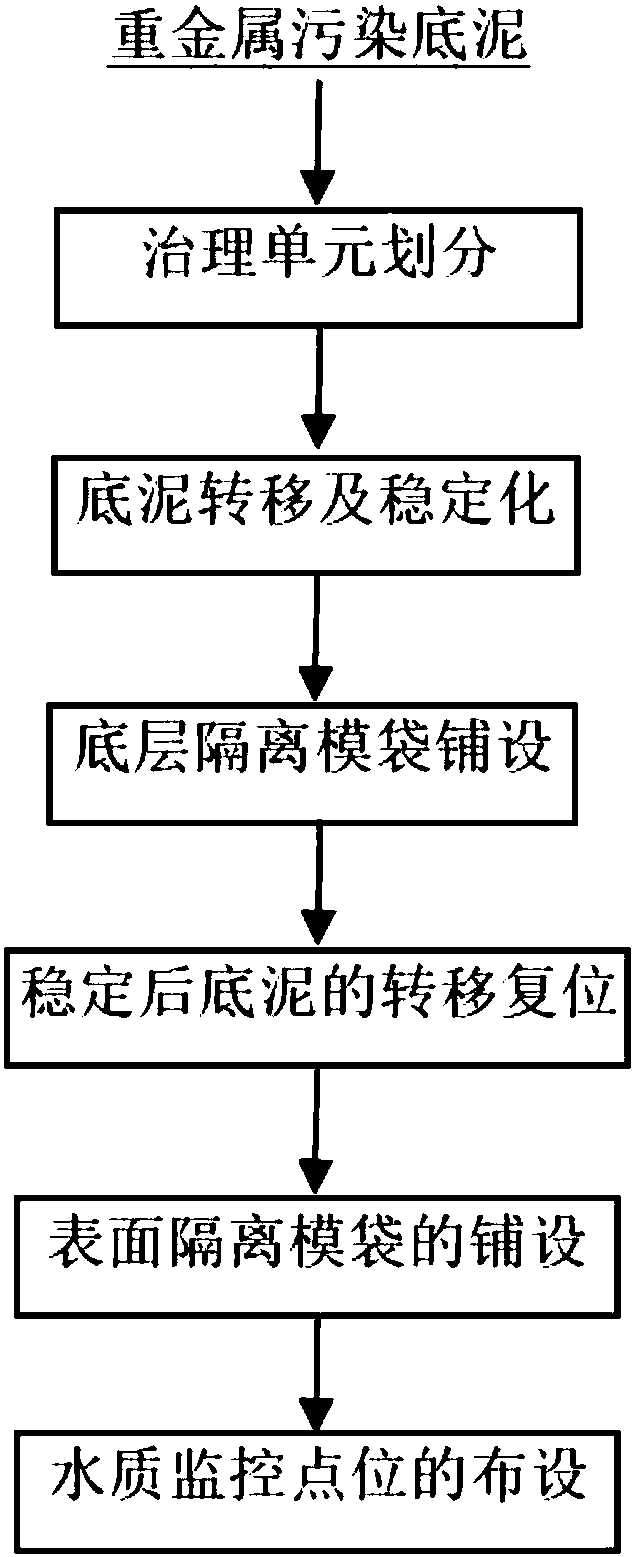
[0034] Such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0035] (1) Governance unit division and temporary storage pool settings:
[0036] According to the terrain characteristics of the area to be treated, the grid layout method is used to divide the area to be treated into governance units. The distance between two adjacent layout points is generally 30m-50m. The bottom mud excavation depth of the treatment unit is determined according to the heavy metal content in the bottom mud, generally 2m-3m. The temporary storage tank is a temporary structure built, and its volume is about 1.2-1.3 times the amount of sediment to be excavated in the treatment unit. The temporary storage tank is lined with HDPE anti-seepage membrane, and the thickness of the anti-seepage membrane is not less than 2mm.
[0037] (2) Sediment transfer and stabilization
[0038] Gradually excavate the sediment in the treatment unit by machinery, transfer it to a mechanical agitator after excavation...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com