Food-borne fluorescent nanoparticles as well as preparation method and application thereof
A fluorescent nano, food-based technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanomedicine, etc., can solve the problems of hidden dangers in the biological safety of fluorescent nanoparticles, and achieve strong carrying capacity, high biological safety, and good cell compatibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0045] The present invention provides a method for preparing food-derived fluorescent nanoparticles, which is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0046] S1: Bake salmon or Spanish mackerel at 150~350℃ for 10~150min;
[0047] S2: The sample after baking is immersed in a polar organic solvent for extraction, and the mixed liquid after extraction is rotary evaporated to completely remove the polar organic solvent; wherein the mass to volume ratio of the sample and the polar organic solvent (g / ml) is 1:1~1:3, and the extraction time is 2~48h;
[0048] S3: Use water and non-polar organic solvent to reconstitute, separate and remove the non-polar organic solvent layer, then add non-polar organic solvent, and repeatedly extract and degrease until the water phase solution is clear and transparent; among them, water and each time are added The mass to volume ratio of the non-polar organic solvent is 1:1 to 1:3;
[0049] S4: Pass the above water-soluble extract through l...
Embodiment 1
[0064] 500g salmon (purchased from Dalian Changxing Aquatic Products Market) was roasted at 200°C for 60 minutes, and the roasted salmon was immersed in 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol for 10 hours, the supernatant was taken out, and rotary evaporated to completely remove the ethanol , Reconstitute the mixture with water: chloroform=1:1, then remove the chloroform, add chloroform for extraction and degreasing, until the aqueous phase solution is clear and transparent, the crude aqueous phase solution is concentrated and passed through D101 Porous adsorption resin column chromatography, collecting the fluorescent part, freeze-drying to obtain fluorescent nanoparticles.
[0065] TEM analysis of fluorescent nanoparticles ( figure 1 ), it can be seen that this method can successfully prepare spherical fluorescent nanoparticles with a particle size distribution of 1.6-3.6nm, an average particle size of 2.64±0.42nm, good crystallinity, and a lattice spacing of about 0.21nm . Th...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Take the fluorescent nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 and use the complete medium of liver cancer cells (Shanghai Institute of Cellular Cells, Chinese Academy of Sciences) as a solvent to prepare 10 mg / mL fluorescent nanoparticles, and use this fluorescent nanoparticle solution to culture liver cancer cells at 37°C for 5 hours , And then measure the distribution of fluorescent nanoparticles in the cell under a laser confocal microscope. The fluorescent nanoparticles are formulated into an aqueous solution and fed to model mice (SPF mice, Dalian Medical University) at a rate of 2 g / kg. After 6 hours, they are slaughtered and the intestines, brains, livers, lungs and kidneys are taken, and small animals are used. The fluorescence imager observes the distribution of fluorescent nanoparticles.
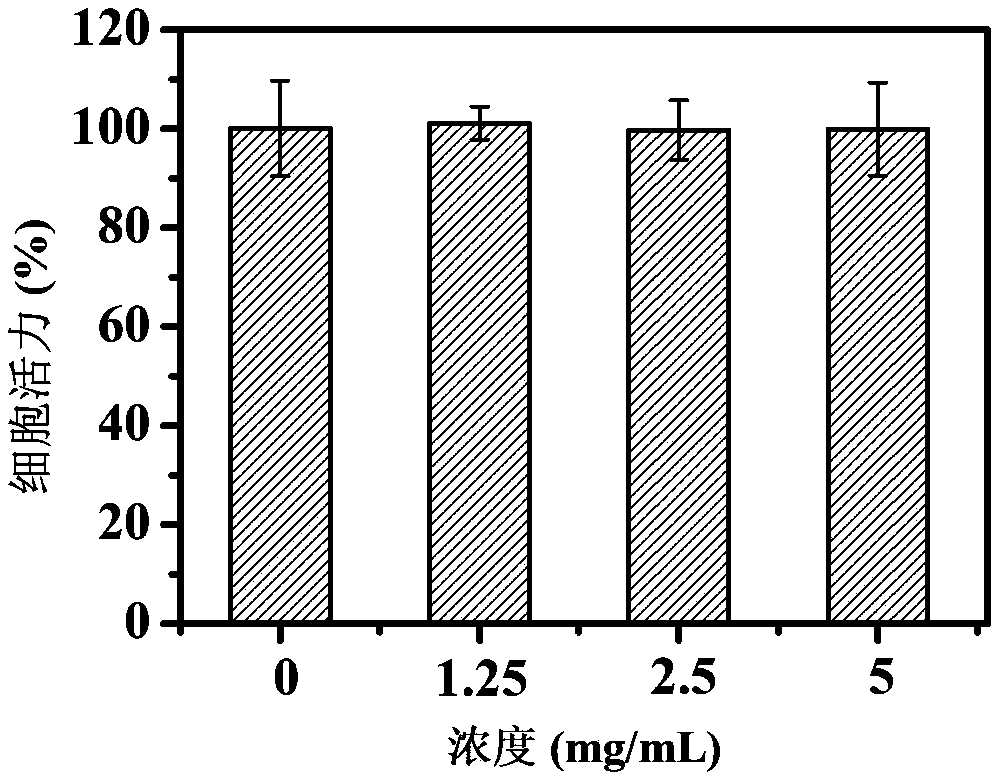
[0069] From Picture 9 It can be seen that fluorescent nanoparticles can enter the cell but not the nucleus, which indicates that the fluorescent nanoparticles have good cell compat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com