Coupling technology for microelectrolysis-pressurized biofiltration treatment of industrial wastewater biochemical tail water
A technology for biological filtration and industrial wastewater, applied in filtration treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, sedimentation treatment, etc., can solve the problems of easy peeling off of the coating, uneven mud cake coating, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the improvement of microorganisms The effect of activity, small footprint and low operating cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
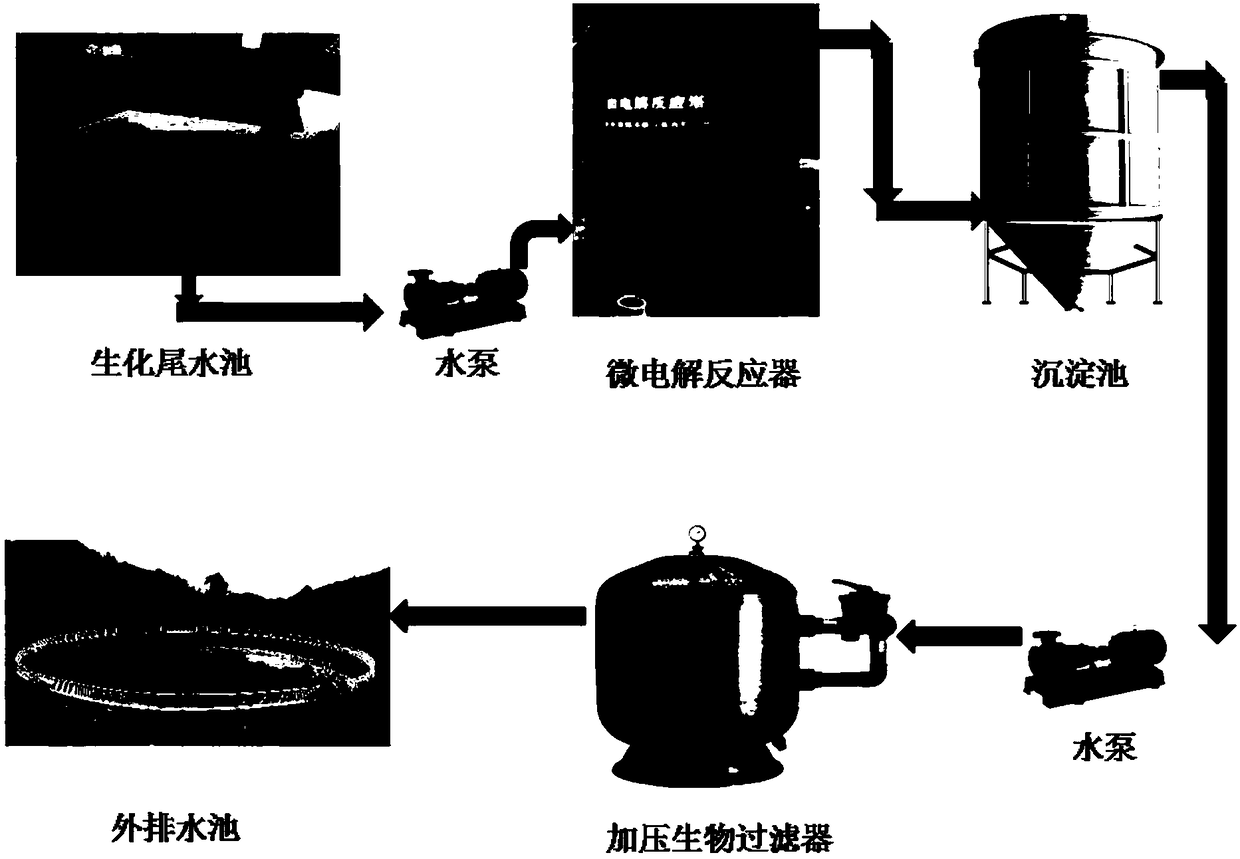
[0044] Example 1: Micro-electrolysis-pressurized biological filtration coupling technology deeply treats the biochemical tail water of printing and dyeing wastewater. Using the biochemical tail water of an industrial park as the treatment object, the specific steps are as follows:
[0045] (1) Pretreatment of micro-electrolysis reactor:
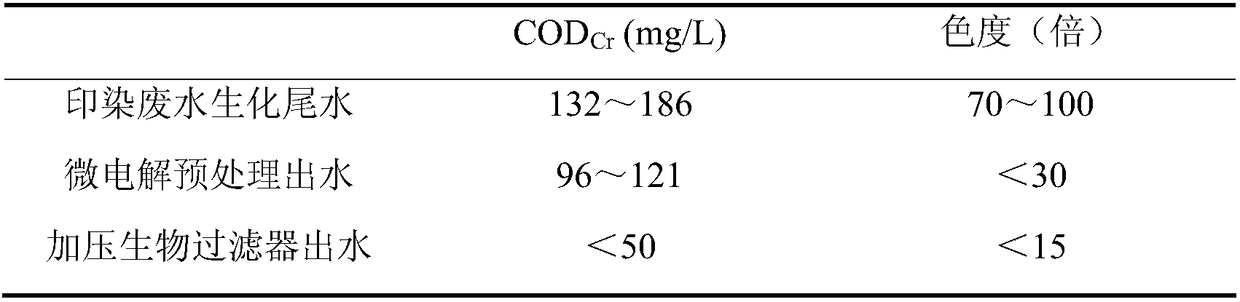
[0046] Adjust the pH of the printing and dyeing wastewater biochemical tail water (taken from a printing and dyeing wastewater plant in Zhongshan City, Guangdong) to 3.5, and then send it to a micro-electrolysis reactor filled with new micro-electrolysis fillers, and control the dissolved oxygen concentration in the reactor to 1.5~2.5 mg / L, the hydraulic retention time is 1 hour. The pH of the effluent is adjusted to 7.8. After precipitation, the effluent enters the subsequent pressurized biological filter for processing;
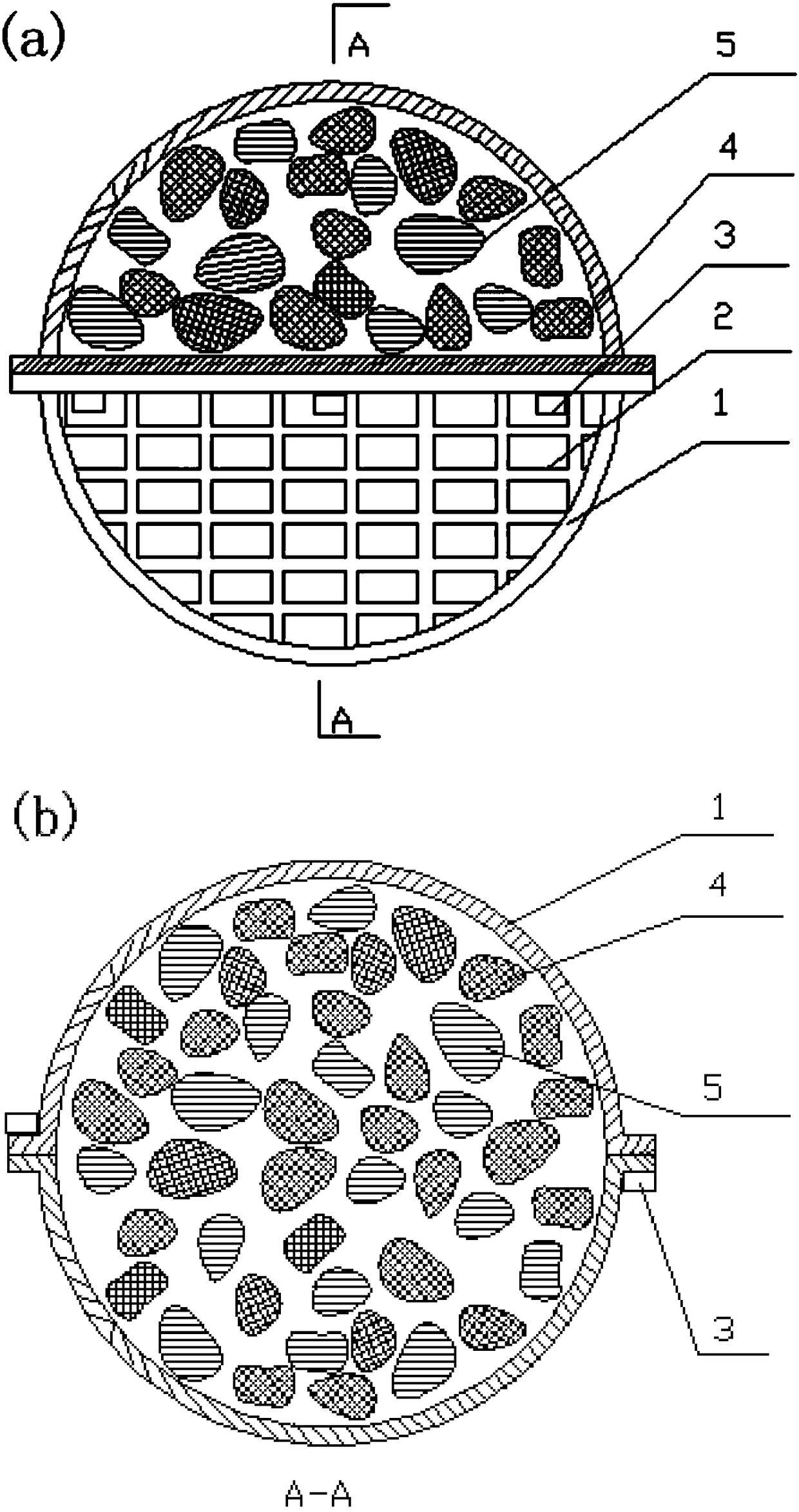
[0047] The new micro-electrolytic filler is composed of the following components in parts by weight: iron powder 45, activate...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2: Micro-electrolysis-pressurized biological filtration coupling technology deeply treats the biochemical tail water of the industrial park. Using the biochemical tail water of an industrial park as the treatment object, the specific steps are as follows:
[0057] (1) Pretreatment of micro-electrolysis reactor:
[0058] Adjust the pH of the biochemical tail water of the industrial park (taken from a sewage plant in an industrial park in Zhongshan, Guangdong) to 5.5 and send it to a micro-electrolysis reactor filled with new micro-electrolysis fillers, and control the dissolved oxygen concentration in the reactor to 2.5 mg / L, the hydraulic retention time is 2 hours. The pH of the effluent is adjusted to 8.8. After precipitation, the effluent enters the subsequent pressurized biological filter for treatment; among them:
[0059] The new micro-electrolytic filler is composed of the following components in parts by weight: iron powder 35, activated carbon 25, chalcopyri...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3: Micro-electrolysis-pressurized biological filtration coupling technology deeply treats the biochemical tail water of the industrial park. Using the biochemical tail water of an industrial park as the treatment object, the specific steps are as follows:
[0069] (1) Pretreatment of micro-electrolysis reactor:
[0070] Adjust the pH of the biochemical tail water of the industrial park (taken from a sewage plant in an industrial park in Zhongshan, Guangdong) to 4.0 and send it to a micro-electrolysis reactor filled with new micro-electrolysis fillers, and control the dissolved oxygen concentration in the reactor to 1.5~ 2.5mg / L, hydraulic retention time is 1.5 hours. The pH of the effluent is adjusted to 8.3, and after precipitation, the effluent enters the subsequent pressurized biological filter for treatment; among them:
[0071] The new micro-electrolytic filler is composed of the following components in parts by weight: iron powder 38, activated carbon 15, chalc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com