Metabolomics profiling of central nervous system injury
A technology of central nervous system and metabolomics, applied in omics, analytical materials, biostatistics, etc., can solve problems such as lack of sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Materials and methods
[0097] The Western University Human Research Ethics Committee approved this study. Informed consent was obtained from the legal guardian, and consent was obtained from the adolescent subjects.
[0098] Target recruitment:
[0099] Male youth ice hockey players (bantamweight, age 12-14 years) from southwestern Ontario, Canada were recruited for this study. To aid in recruitment, informational posters of the study were presented in the ice hockey city of Arenas along with consent forms from Arenas officials, and oral presentations have been made to several area hockey boards and coaches. Juvenile hockey players with suspected concussion injuries were screened and consent was obtained at the primary physician at the Fowler Kennedy Sports Medicine Clinic at Western University. A sports concussion injury is diagnosed when the mechanism of injury is observed after the onset of typical concussion symptoms and in the absence of structural damage. C...
Embodiment 2
[0170] Example 2 - Primary Impact Traumatic Brain Injury
[0171] Materials and methods
[0172] shock exposure
[0173] In performing this study, the authors followed the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the Ethics of Animal Experimentation published by the Canadian Society for the Care of Animals. Adult male Sprague-Dürer rats were obtained from Charles River Laboratories (St. Constant, Que, Canada) and acclimatized for at least one week prior to exposure. A total of 15 control samples and 15 impact-injured samples. On the day of use, anesthetize the animal (~280-330 g) with 3% isoflurane in oxygen, place it in a restraint consisting of a clear plastic cylindrical sleeve, with the neck comfortably enclosed in a plastic ring, And the head protrudes through an opening at one end which is concave so that it conforms to the curvature of the inside of the blast tube. Use end caps fitted with pistons to support the rear legs. On the left side of the...
Embodiment 3
[0196] Example 3 - Prognosis
[0197] Metabolomics
[0198] Plasma from participants in three groups was analyzed: (1) participants with a first concussion injury, (2) participants with two or more reported concussion injuries, and (3) no history of concussion injury comparison participants. All concussion-injured and non-concussion-injured controls were clinically evaluated to determine concussion symptoms and severity. Participants were also assessed according to accepted standard diagnostic criteria. Plasma was analyzed for metabolites by DI / LC-MS / MS and MR.
[0199] PCA
[0200] Using PCA, it was demonstrated that the top 10 components, each weighted to a number of underlying metabolites, explained the majority of the variance in the data.
[0201] t-SNE
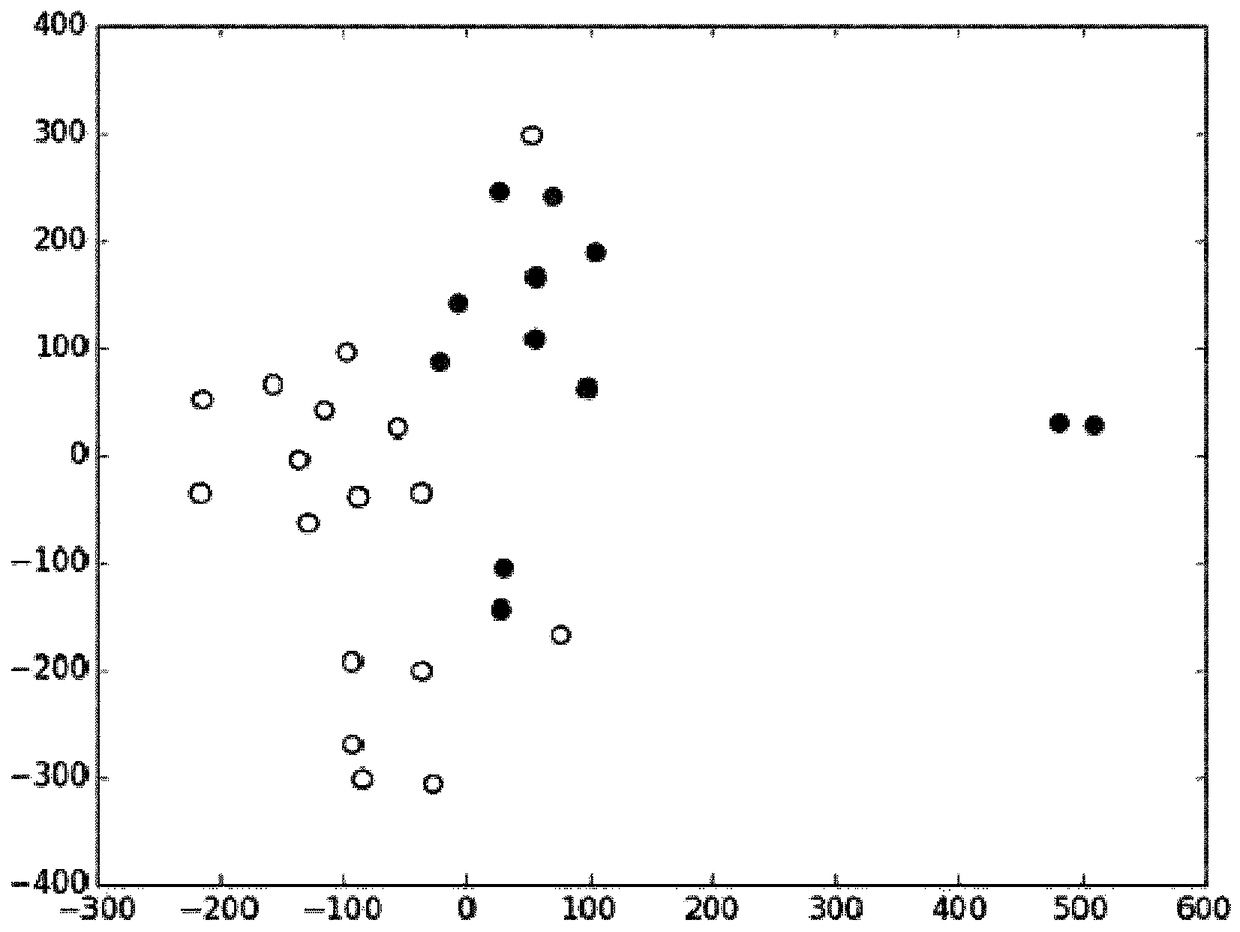
[0202] Using t-SNE, the entire metabolic dataset was reduced to two dimensions, since the inherent dimensionality of this data is significantly lower than the number of metabolites. After this dimensionality...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com