A Grouped Markov Superposition Coding Method Based on Double Recursion
A technology of superposition coding and double recursion, which is applied in the direction of using block codes for error correction/detection, coding, and error detection coding using multiple parity bits, and can solve non-recursive block Markov superposition coding Method, decoding complexity and high decoding delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
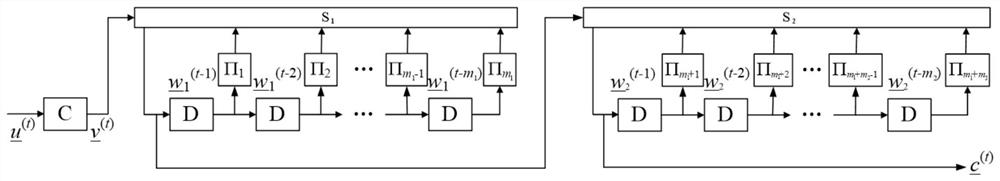
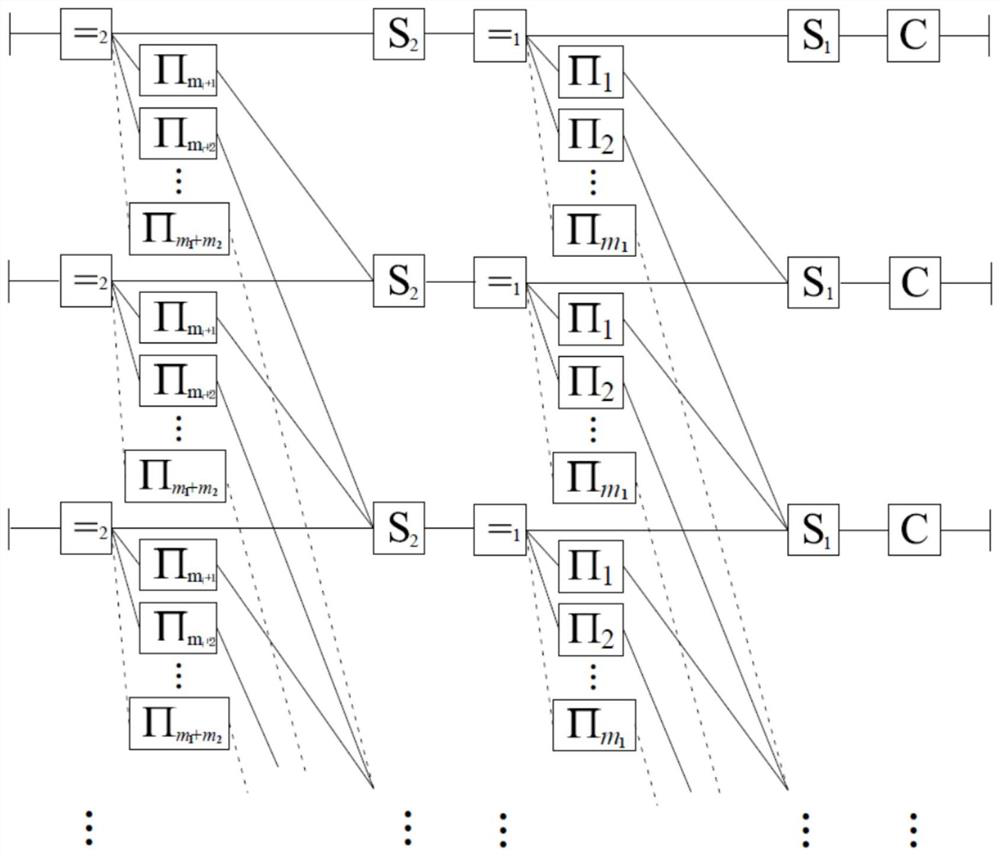
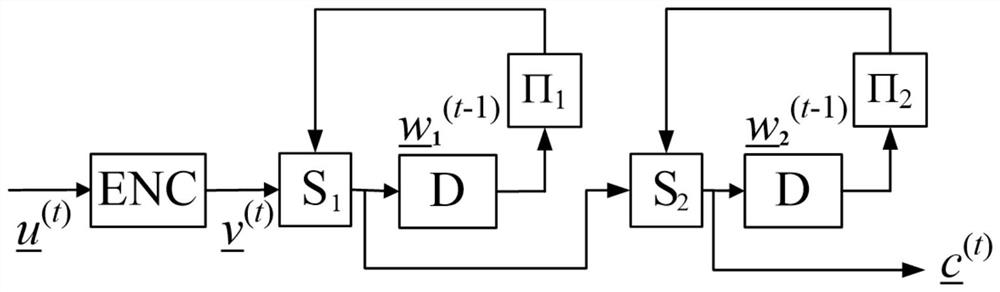
[0043] set m 1 =m 2 = 1, refer to figure 1 , and the corresponding coding diagram is as follows image 3 . refer to image 3 , a binary information sequence whose length is K=kL=1250×343 u Divided into L=343 equal-length groups u =(u (0) , u (1) ,…, u (342) ), the length of each packet is k=1250. The basic code encoder ENC uses a repetition code with code length n=2 and information bit length k=1. In this example, two random interleavers are used. The symbol-wise aliaser S uses a bit-wise binary field sum operator. The ending length T is set to be the same as the decoding delay d, ie T=d. refer to figure 1 , its encoding method includes the following steps:
[0044] Step 1. Put the information sequence u Divided into 343 equal-length groups u =( u (0) , u (1) ,…, u (342) ), the length of each packet is 1250; for t=-1, the sequence of length 2500 w 1 (t) with w 2 (t) The initialization is set as an all-zero sequence, that is, for t=-1, there is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com