Method for increasing vitamin D2 in edible mushrooms
A technology of edible mushrooms and vitamins, applied in the direction of food science, etc., can solve the problems of product quality and commerciality reduction, increase of fruit body browning degree, change of fruit body appearance and properties, etc., and achieve the effect of short operation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Choose shiitake mushrooms as raw materials, pack them in special food bags made of polyethylene materials, and irradiate them with ultraviolet light (irradiation energy 0.08mJ / cm 2 , irradiation time 25min, double-sided irradiation) and pulsed strong light treatment (single pulse energy is 2.2mJ / cm 2 , irradiation time is 50s, double-sided irradiation), and then vacuum freeze-dry the processed sample.
[0021] The results in Table 1 show that UV and pulsed strong light irradiation have significant effects on vitamin D in Lentinus edodes. 2 content is significantly affected. Vitamin D in blank control group 2 The content is low, 2.03μg / g, which may be related to the growth environment of shiitake mushrooms. Shiitake mushroom is a kind of saprophytic fungus that grows on wood. During the growth stage, it cannot receive direct light, and it is better to use scattered light. Therefore, the growth process of shiitake mushroom lacks sunlight, so that its ergosterol cannot ...
Embodiment 2
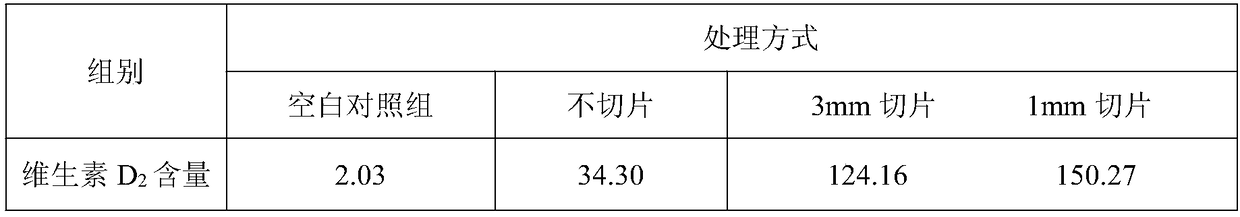
[0027] Choose shiitake mushrooms as raw materials, use special food bags made of polyethylene materials to pack unsliced edible fungi or edible fungi cut into 3mm and 1mm slices, and process the samples with pulsed strong light, with a single pulse energy of 2.2mJ / cm 2 , the irradiation time is 50s, double-sided irradiation. The treated samples were vacuum freeze-dried and ground.
[0028]It was found that the pretreatment of samples before pulsed intense light treatment had an effect on vitamin D in edible fungi 2 content has a great influence (see Table 2). Vitamin D content of sliced shiitake mushrooms before pulsed intense light treatment 2 The content is much higher than that of raw materials without any treatment before pulsed strong light treatment. Vitamin D in intact shiitake mushrooms treated with pulsed strong light 2 The content is 34.30μg / g, after cutting into slices of shiitake mushrooms with a thickness of 3mm, vitamin D 2 The content rose to 124.16μg / g...
Embodiment 3
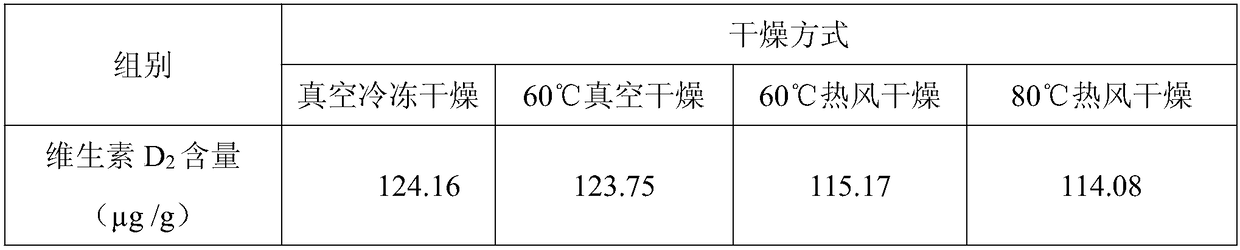
[0032] Choose shiitake mushrooms as raw materials, cut them into thin slices with a thickness of about 3mm, pack them in special food bags made of polyethylene materials, and irradiate them with strong pulsed light (single pulse energy is 2.2mJ / cm 2 , the irradiation time is 50s, double-sided irradiation). The treated shiitake mushrooms were dried in different ways, and it was found that after different drying methods, the vitamin D 2 The content changes less (see Table 3). Vacuum drying at a temperature below 60°C, the vitamin D in the shiitake mushrooms 2 The content is comparable to the vacuum freeze-dried sample, and the increase of drying temperature will destroy vitamin D 2 , leading to a decrease in its content, it should be carried out under low temperature and oxygen isolation conditions as much as possible.
[0033] Table 3 Effects of different drying methods on vitamin D in shiitake mushrooms 2 Effect of dry basis content (μg / g)
[0034]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com