Molecular marker of brown planthopper resistance major gene qBph4(t) of paddy rice and application of molecular marker
A technology of anti-BPH and main gene, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve problems such as difficult to effectively introduce and aggregate insect-resistant genes, complex insect resistance identification, etc., and achieve the effects of shortening the breeding cycle, convenient identification, and clear selection targets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
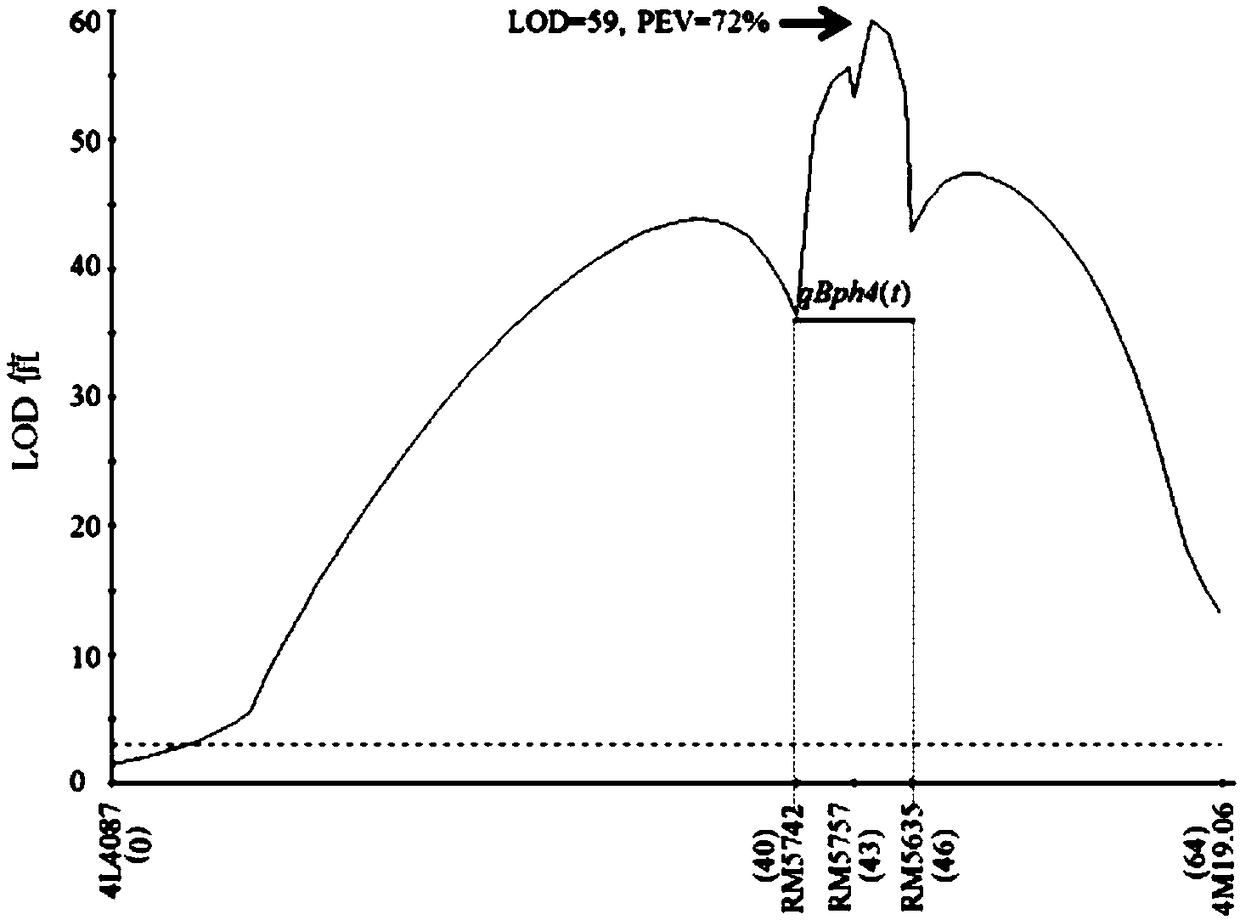
[0032] Example 1 Acquisition of Molecular Markers
[0033] (1) 9311 / ARC5984F2 population construction and phenotypic identification
[0034] (1) The previous insect resistance identification experiments showed that the farm variety ARC5984 had high resistance to the brown planthopper population collected from the paddy fields in the suburbs of Nanning. In order to find simple and effective molecular markers that are closely linked to qBph4(t), the present invention crossed the insect-susceptible variety 9311 as the female parent and the brown planthopper-resistant rice variety ARC5984 as the male parent, and then selfed the obtained F1 to construct F2 Segregated populations; each F2 individual plant obtained the corresponding F2:3 family by selfing.
[0035] (2) Insect resistance identification of parents and F2:3 families was carried out by inoculation treatment at seedling stage. In order to ensure the consistent growth of each family in the parent and F2:3 populations, al...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 Verification of Molecular Markers
[0053] 1. Materials and methods
[0054] 1.1 Materials
[0055] Negative varieties: 4 copies, susceptible varieties 9311, Nipponbare, Taichung Local No. 1, and Hebai R54, all of which are conventional rice materials preserved in our laboratory; 20 susceptible families in the offspring of the 9311×ARC5984 hybrid combination.
[0056] Positive varieties: A total of 30 insect-resistant families in the offspring of the high insect-resistant varieties ARC5984 and 9311×ARC5984 hybrids.
[0057] Molecular marker primers: RM5635; RM5742; RM5757.
[0058] 1.2 Method
[0059] Genomic DNA was extracted from leaves of rice samples by CTAB extraction, the sample DNA was amplified with primer RM5635, the amplified products were separated by 6% non-denaturing PAGE gel, and the amplified DNA bands were recorded by silver staining. (method is with embodiment 1)
[0060] 2. Results:
[0061] Using the above method, the genomic DNA of 54...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com