Surface plasma-based quantum dot random laser and preparation method thereof
A surface plasmon and random laser technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of fluorescence quenching, random laser emission efficiency reduction, etc., to enhance local field strength, prevent fluorescence quenching, increase stimulated absorption and stimulated The effect of radiation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
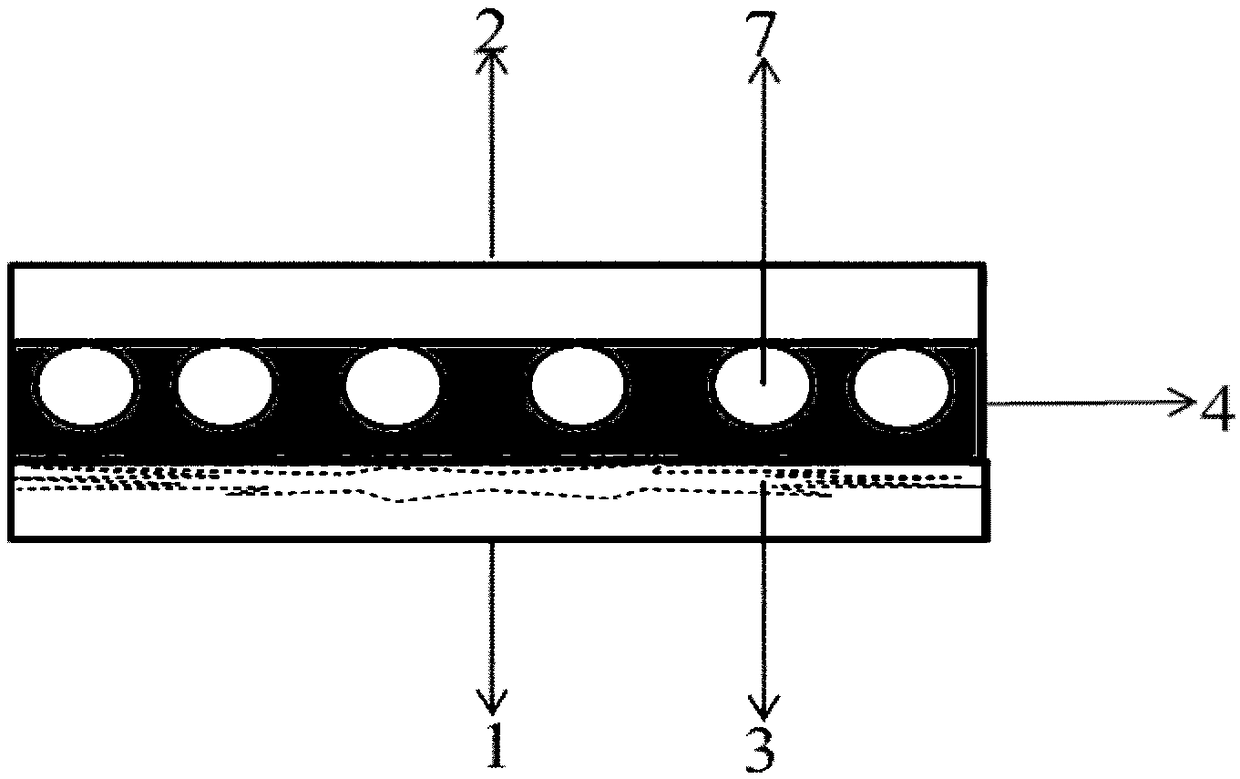
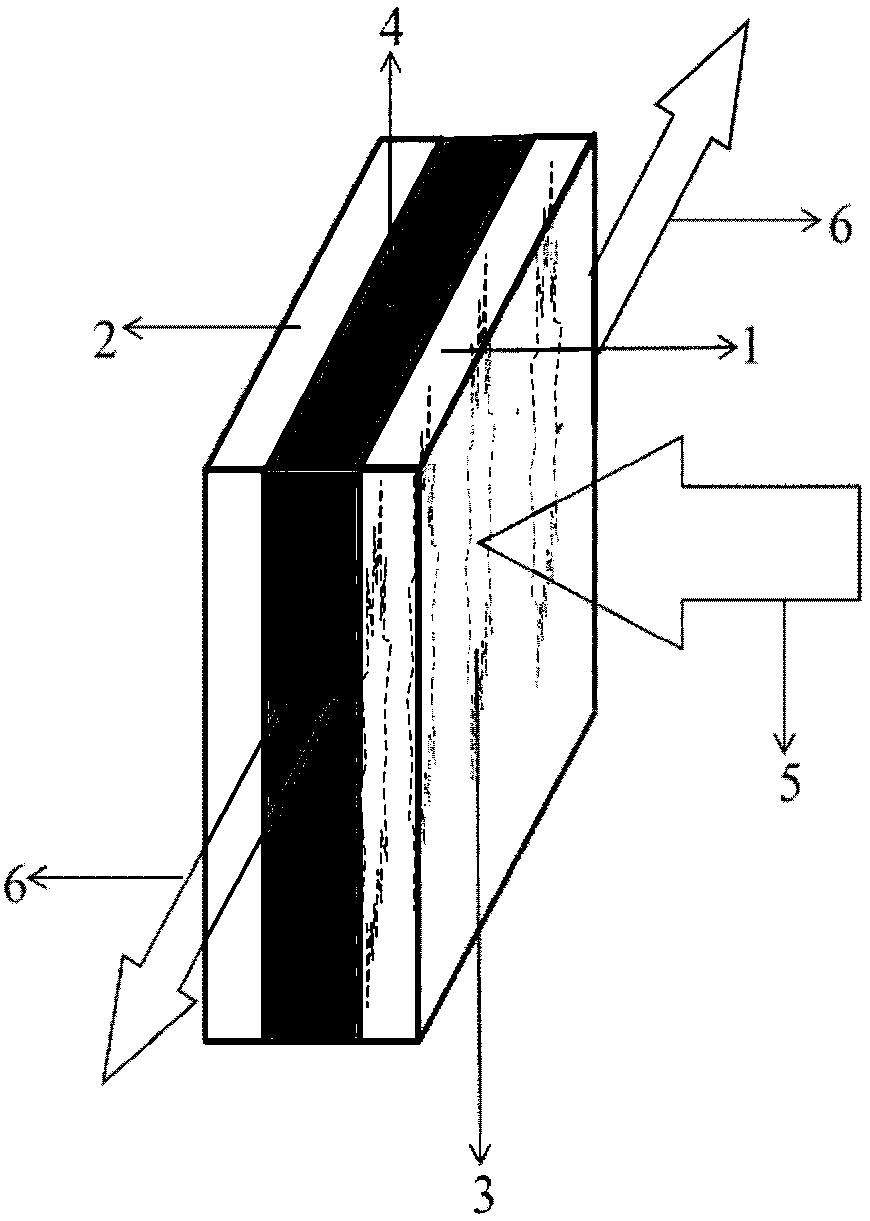
[0021] Embodiment 1: a kind of quantum dot random laser based on surface plasmon, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a first glass substrate 1 , a PVA spacer layer 4 , Ag nanoparticles 7 and a second glass substrate 2 stacked in sequence.
[0022] Several parallel micron-scale grooves 3 are arranged on the inner surface of the first glass substrate 1. CdSe / SnS quantum dots are deposited in these grooves 3. The width of the grooves 3 is 80 μm, the depth is 45 μm, and the interval is 1 mm.
[0023] Ag nanoparticles 7 are fixed on the inner surface of the second glass substrate 2, and the PVA spacer layer 4 is located between the Ag nanoparticles 7 and the CdSe / SnS quantum dots, with a thickness of 40nm.
[0024] The specific operation of the preparation method of the above-mentioned laser is as follows:
[0025] (1) On the first glass substrate 1, micron-scale grooves 3 are etched with diamond, and CdSe / SnS quantum dots are deposited in the grooves 3 by spin coating, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: roughly the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that the quantum dots are selected from CdSe / CdS quantum dots, the metal nanoparticles are Au nanoparticles, the width of the groove 3 is 40 μm, the depth is 30 μm, the interval is 2mm, and the spacer layer 4 The material is PMMA, the thickness is 15nm. During the preparation process, the spin-coating speed of the quantum dots 4 was 200rpm / 120s, the second glass substrate 2 was silanized with APTMS for 2h, rinsed and dried, then immersed in the colloidal suspension of Au nanoparticles 7 for 1h, the PMMA spacer layer 4 The spin coating speed was 5000 rpm.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3: roughly the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that the quantum dots are selected from CdSe / SnS quantum dots, the metal nanoparticles are Ag nanoparticles, the width of the groove 3 is 120 μm, the depth is 60 μm, the interval is 3mm, and the spacer layer 4 The material is PMMA, and the thickness is 70nm. During the preparation process, the spin-coating speed of the quantum dots 4 was 400rpm / l20s, the second glass substrate 2 was silanized with APTMS for 4h, rinsed and dried, then immersed in the colloidal suspension of Ag nanoparticles 7 for 4h, the PMMA spacer layer 4 The spin coating speed was 2000 rpm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com