Electric chemical method for accelerated corrosion on stainless steel welding seam region
A technology to accelerate corrosion and stainless steel, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of accelerated corrosion of stainless steel, and achieve the effect of accelerating the corrosion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1 Preparation of working electrode
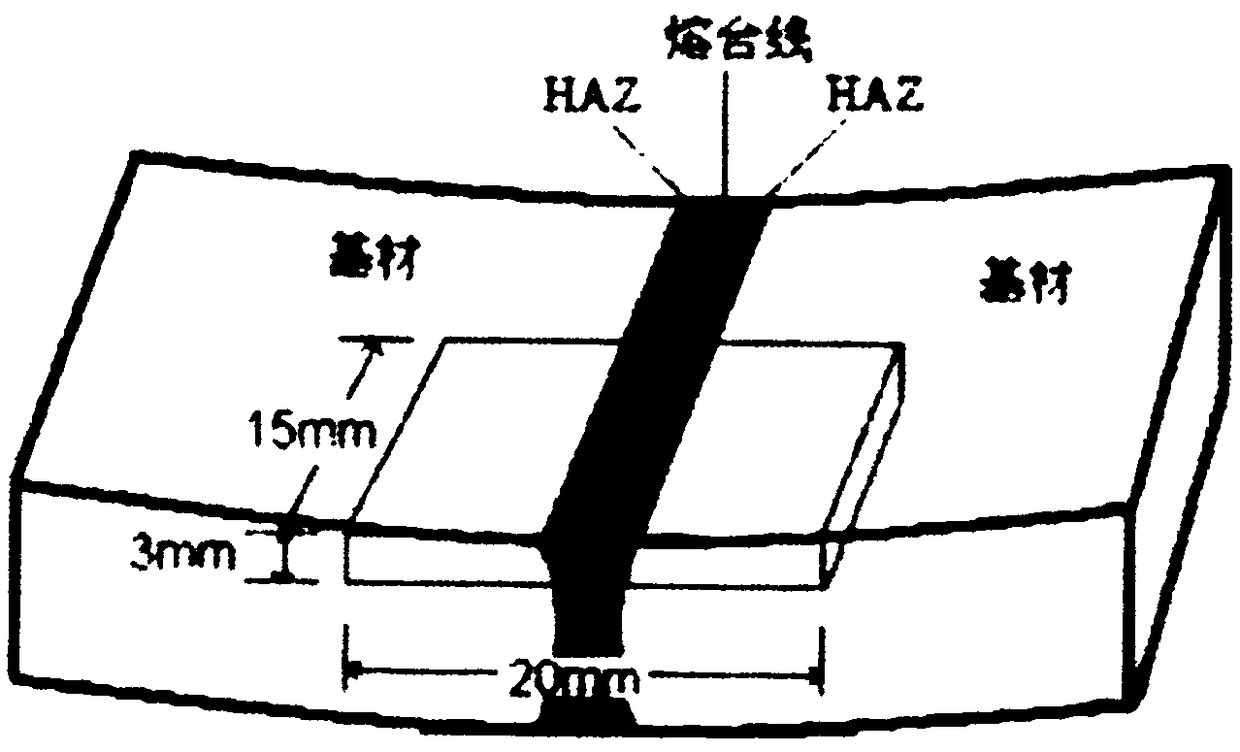
[0040] 1.1 Use wire cutting to cut T4003 to the required size, and its working surface should include fusion zone, heat-affected zone, and base metal zone. Among them, the welding line should be located in the center of the sample.
[0041] 1.2 Perform passivation treatment on the stainless steel weld sample, using a phosphoric acid aqueous solution with a mass volume ratio of 3% (phosphoric acid mass: aqueous solution volume = 3%) and a potassium dichromate aqueous solution with a mass volume ratio of 5% (dichromic acid mass : aqueous solution volume=5%) in a water bath at 85 degrees for 15 minutes.
[0042] 1.3 The back of the stainless steel weld is welded with copper wire, and the copper wire is used as the connection wiring with the electrochemical device.
[0043] 1.4 Use epoxy resin and PVC pipe to encapsulate the sample.
[0044] 1.5 After the epoxy resin is completely cured, use water sandpaper to polish to 2000 mesh, use a...
Embodiment 2
[0065] 1 Preparation of working electrode
[0066] 1.1 Use wire cutting to cut T4003 to the required size. The working surface should include the fusion zone, heat-affected zone, and base metal zone. The welding line should be located in the center of the sample.
[0067] 1.2 Perform passivation treatment on the stainless steel weld sample, using a phosphoric acid aqueous solution with a volume ratio of 3% and an aqueous solution of potassium dichromate with a mass volume ratio of 5% in a water bath at 85 degrees for 15 minutes.
[0068] 1.3 The back of the stainless steel weld is welded with copper wire, and the copper wire is used as the connection wiring with the electrochemical device.
[0069] 1.4 Use epoxy resin and PVC pipe to encapsulate the sample.
[0070] 1.5 After the epoxy resin is completely cured, use water sandpaper to polish to 2000 mesh, use alcohol to dehydrate and degrease, dry it with cold wind, and place it in a drying tank for use.
[0071] 1.6 After d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com