Culture medium for fermenting demeclocycline and fermentation method of demeclocycline
A demethylaureomycin and culture medium technology, which is applied in the field of fermentation medium for demethylaureomycin, can solve the problems of low fermentation titer and residual toxic substances, and achieve increased fermentation yield, stable chemical properties, and reduced costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
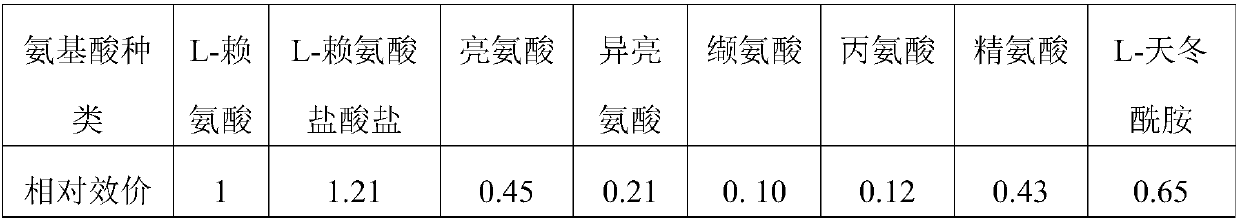
[0035]Under sterile conditions, a strain of Streptomyces aureofaciens NRRL3203 (purchased from the American Agricultural Research Culture Collection) was inoculated into the slant medium. After 2 days of slant culture at 28°C, light yellow-brown bacteria can be seen on the surface of the medium; after 3 or 4 days, the color of the medium deepens, and a small amount of white spores are formed; after 7-8 days, a large number of white spores can be seen on the surface of the medium, and the medium The matrix itself turns dark brown due to the production of Streptomyces aureomycin pigment. Under sterile conditions, use a sterilized inoculation shovel to gently scratch the sloping medium with spores, dig out as thin as possible a 0.8cm×1.5cm sloping medium full of spores, and inoculate the sterilized seeds In the culture medium, cultured on a rotary shaker at 28°C and 240rpm for 40-46h, it can be observed that the color of the culture in the shake flask changes from light yellow to...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Single carbon source determination experiment
[0039] Based on the formula of the basic fermentation medium, the nitrogen source, inorganic salt and other components and contents remained unchanged, and corn starch, glucose, sucrose, fructose, lactose, maltose, dextrin, mannitol, etc. were added to conduct single-factor carbon source experiments. The dosage is 8%. The fermented seeds prepared in Example 1 are inoculated in the fermentation medium with 10% (v / v) inoculum, pH7.0, loading 35mL / 250mL, at 30°C, 240rpm rotary shaker The bed culture was cultivated for 8 days, and the fermentation titer was measured by high performance liquid phase.
[0040] Basic fermentation medium composition: 8.0% corn starch, 3.0% soybean flour, 0.8% L-lysine, 0.3% sodium chloride, 0.2% ammonium sulfate, 1.0% calcium carbonate, 0.3% corn steep liquor, 0.6% soybean oil, α - Amylase 0.08%, deionized water 100 mL. The fermentation titer obtained by using the basic fermentation medium f...
Embodiment 3
[0049] (1) Nitrogen source determination experiment
[0050] According to the results of the above experiments, the 8% cornstarch in the basal medium was added to 11%, taking the optimized medium formula as a control, and under the condition of keeping other ingredients such as inorganic salts unchanged, fish meal, cottonseed meal, feather soybean flour, peanut flour, soybean meal powder or milk powder were all substituted for soybean flour, and the amount of replacement nitrogen source was 3%, and the shake flask was fermented for 8 days, and the fermentation titer was measured by high performance liquid phase. Experimental results show that: under the same culture conditions, compared with other nitrogen sources, when the nitrogen source is soybean flour, the titer of the fermented liquid is the highest.
[0051] Optimized medium: 11% corn starch, 3.0% soybean flour, 1.0% calcium carbonate, 0.8% L-lysine, 0.3% sodium chloride, 0.3% ammonium sulfate, 0.3% corn steep liquor, 0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com