Method in UE supporting synchronization signals, method in base station supporting synchronization signals and devices
A technology for synchronizing signals and signals, applied in radio transmission systems, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as narrow beams, achieve the effect of improving transmission efficiency and saving signaling overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
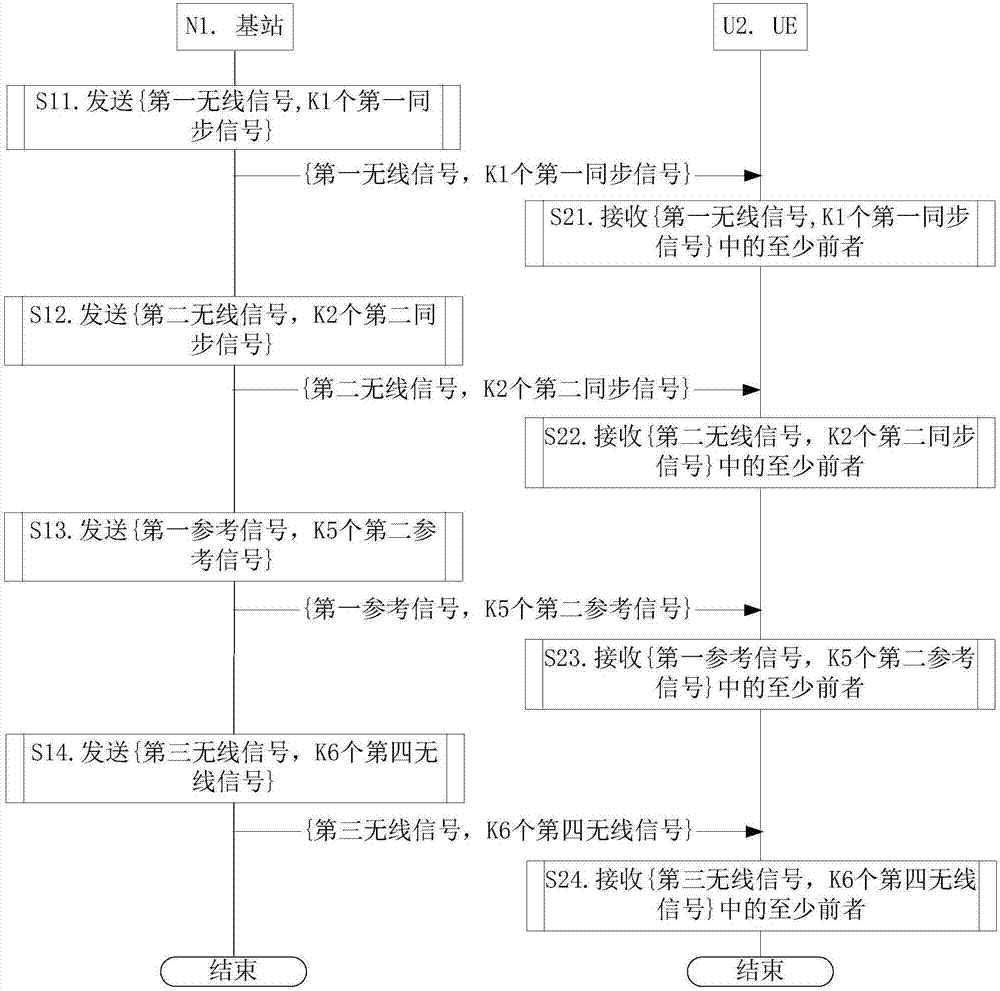
[0287] Embodiment 1 illustrates the flow chart of wireless transmission, as attached figure 1 shown. attached figure 1 In , the base station N1 is the serving cell maintenance base station of the UE U2.
[0288] For N1, send {first wireless signal, K1 first synchronization signals} in step S11; send {second wireless signal, K2 second synchronization signals} in step S12; send {first reference signal, K5 second reference signals}; send {third wireless signal, K6 fourth wireless signal} in step S14.
[0289] For U2, at least the former of {first wireless signal, K1 first synchronization signals} is received in step S21; at least the former of {second wireless signal, K2 second synchronization signals} is received in step S22; At least the former of {first reference signal, K5 second reference signals} is received in step S23; and at least the former of {third wireless signal, K6 fourth wireless signal} is received in step S24.
[0290] In Embodiment 1, the second time-freque...
Embodiment 2
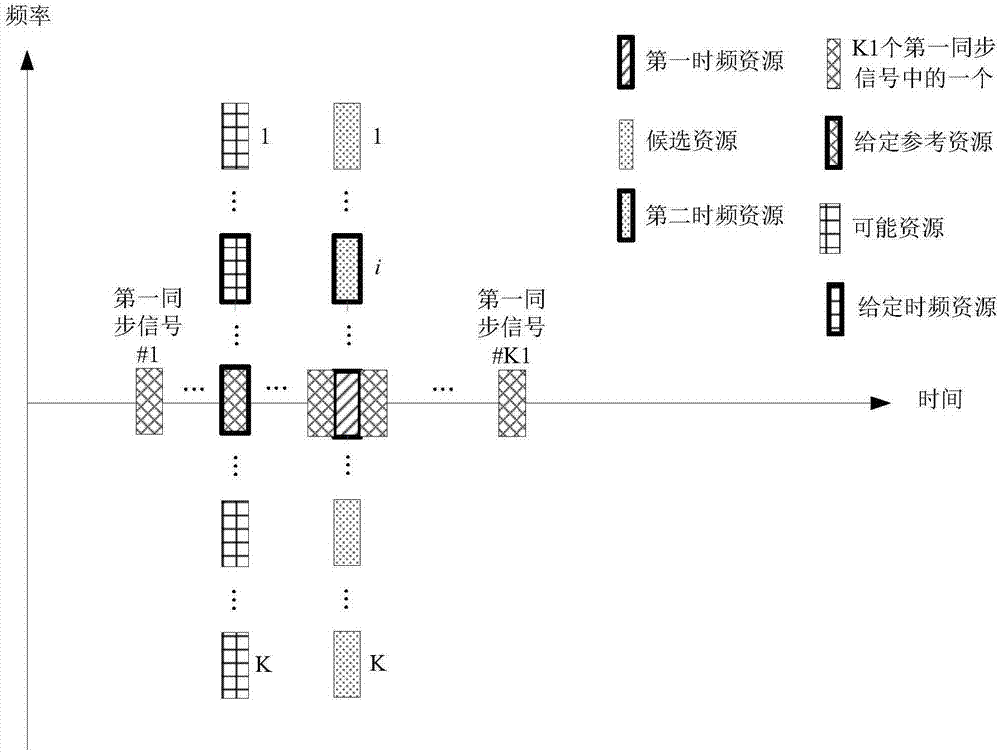
[0312] Embodiment 2 illustrates {first time-frequency resource, second time-frequency resource, K candidate resources, resource mapping of K1 first synchronization signals, given time-frequency resource, K possible resources, given reference resource} , and the schematic diagram of the association between the position of the second time-frequency resource in the K candidate resources and {the first time length, R1 antenna ports}, as shown in the attached figure 2 mentioned.
[0313]In Embodiment 2, the first synchronization signal in the first wireless signal and the K1 first synchronization signals form K3 first synchronization signals, and K3 is the sum of K1 and 1. The time domain resources occupied by the K3 first synchronization signals are orthogonal. The K candidate resources completely overlap in the time domain and are orthogonal in the frequency domain. The first time-frequency resource and the K candidate resources occupy the same time resource in the time domain...
Embodiment 3
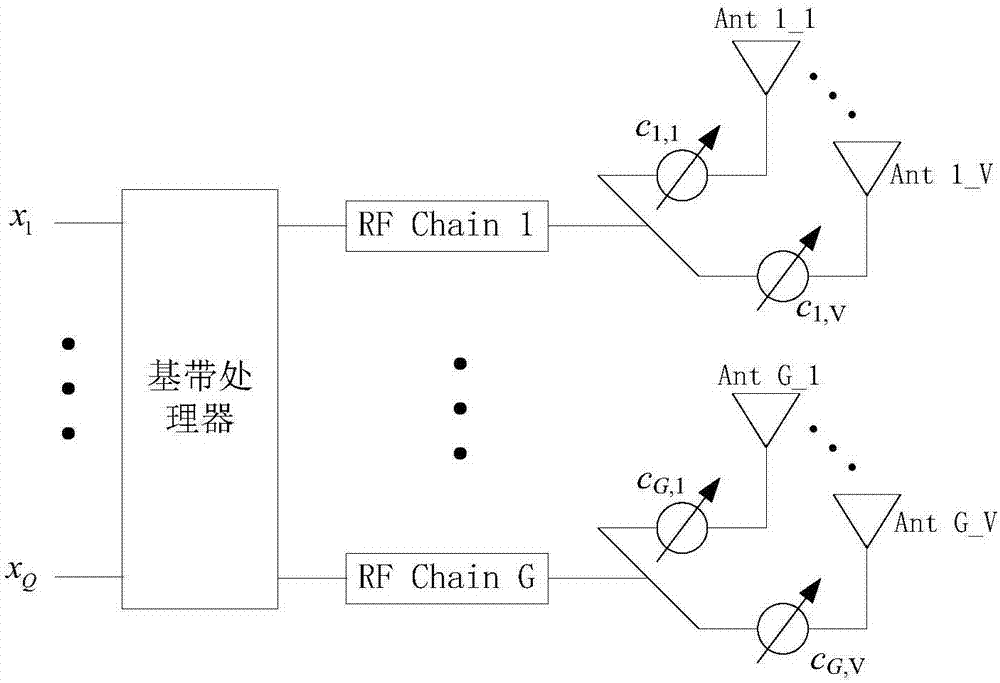
[0331] Embodiment 3 illustrates the schematic diagram of the antenna structure, as attached image 3 shown.
[0332] attached image 3 , the communication node is equipped with G antenna groups, and the G antenna groups correspond to G RF (Radio Frequency, radio frequency) chains (chains) respectively. One antenna group includes V antennas, G is a positive integer, and V is a positive integer. For 1≤g≤G, the antennas in antenna group #g include the attached image 3 In {Ant g_1, Ant g_2, ..., Ant g_V}, the antennas in the antenna group #g pass the analog beamforming vector c g Perform analog beamforming, where c g is a V×1-dimensional vector, and the analog beamforming vector corresponding to one antenna group is composed of the weighting coefficients on the V antennas included in the antenna group, that is, c g =[c g,1 ... c g,v ].
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com