Power flow transfer identification algorithm based on multi-branch removal and deviation paths
A technology of power flow transfer and identification algorithm, which is applied in the direction of AC network, calculation, circuit device with different sources of the same frequency, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the chain trip of transmission lines, complicated verification calculation, lack of power grid, etc., so as to avoid modification. , improve the efficiency of the algorithm, reduce the effect of the amount of matrix operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The technical solution of the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
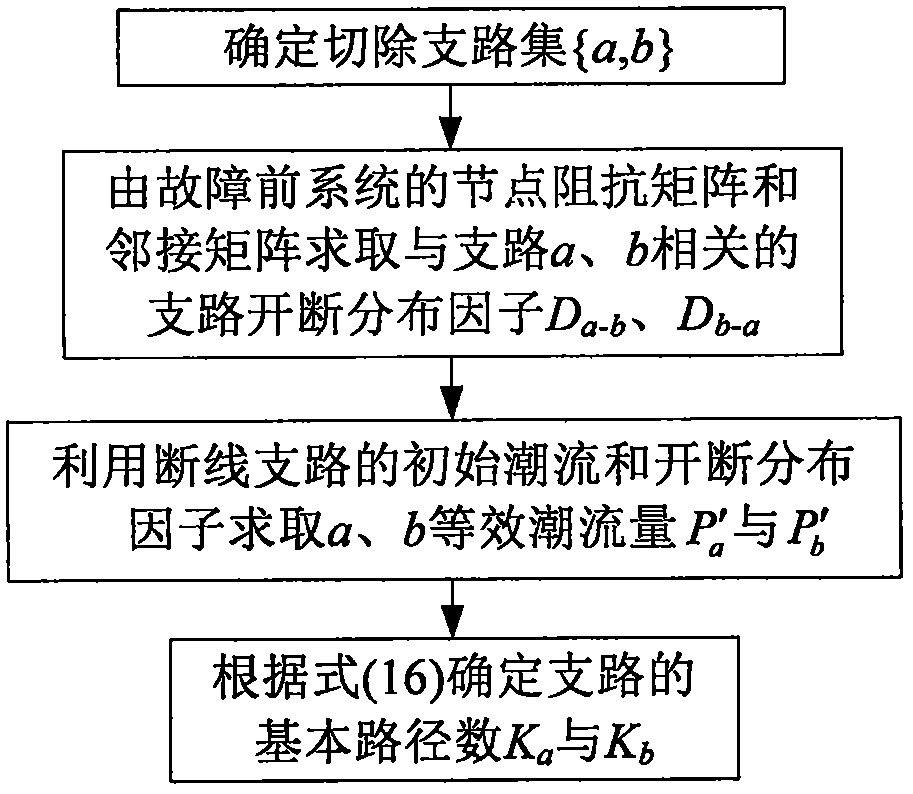
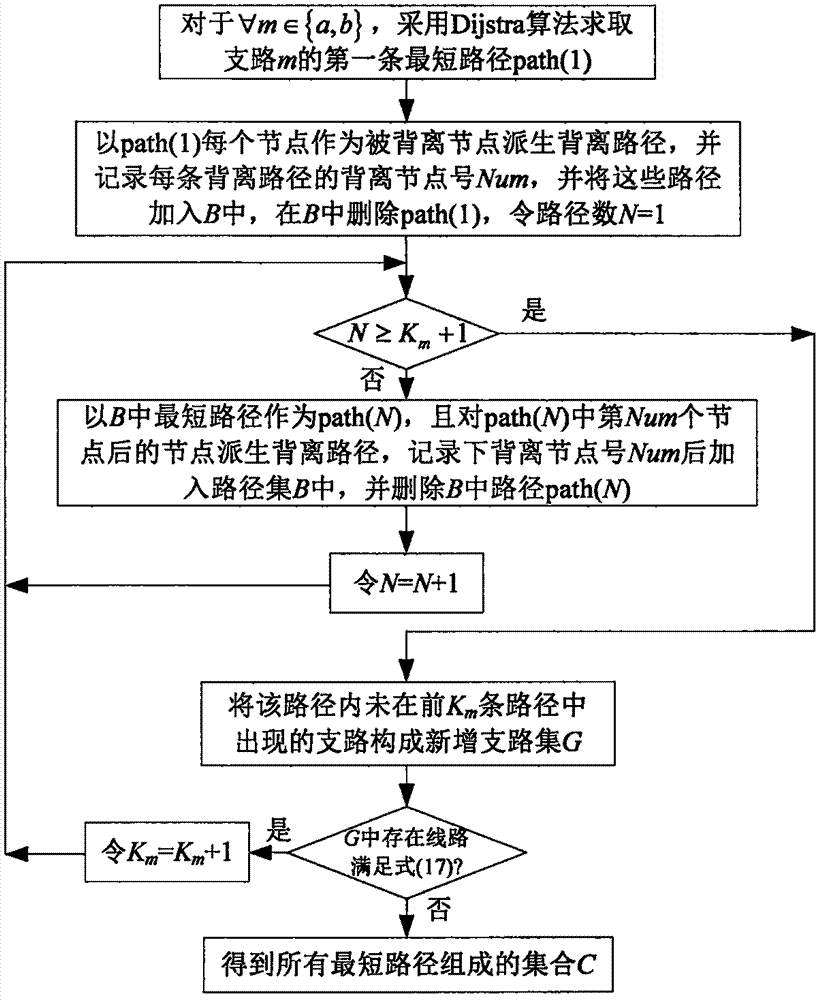
[0026] A power flow transfer recognition algorithm based on multi-branch cutting and deviation paths described in the present invention includes the following steps:
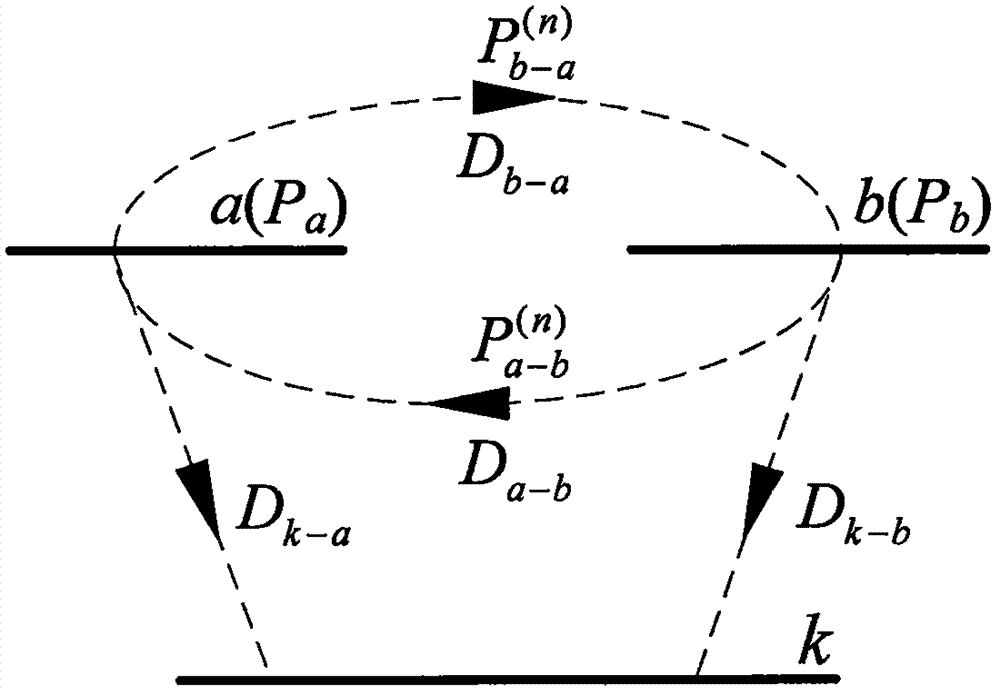
[0027] Step 1: Analyze the composition of the power flow transferred to the non-faulty branch. When multi-branch cutting occurs, the transferred power flow on branch k can be regarded as multiple branches with equivalent power flow as the initial power flow and then transferred to The superposition of the power flow on branch k simplifies the cutting of multiple branches into the case of cutting off multiple single branches, avoiding a large number of correction calculations for the node impedance matrix in the DC method, and realizing the rapid estimation of the power flow transfer;
[0028] Assume that the initial power flows are P a with P b Branches...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com