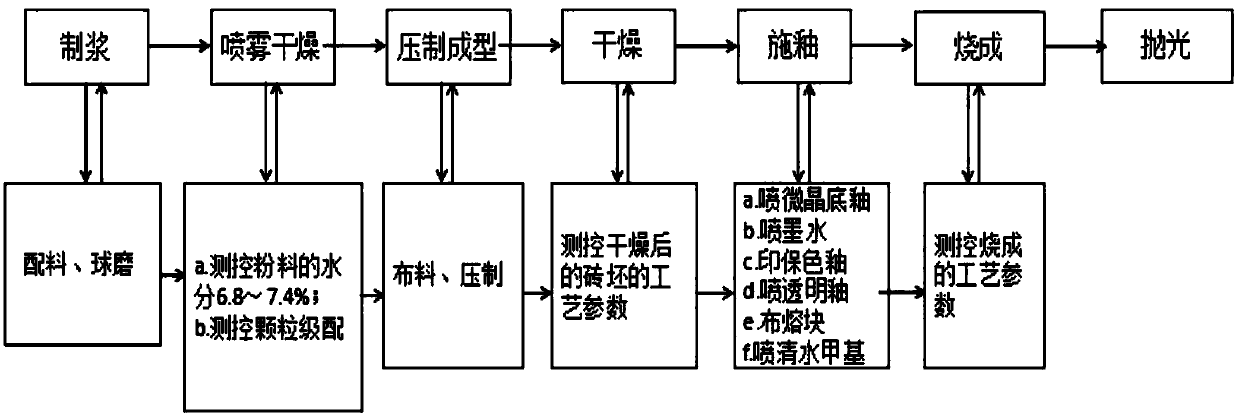
Production process of microcrystalline tile
A production process and microcrystalline technology, applied in the field of architectural ceramics processing, can solve the problems of high rejection rate, unreasonable operation, waste, etc., and achieve the effects of stable product performance, improved overall strength, and improved production quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1-a kind of production technology of microcrystalline brick, comprises the steps:
[0042] (1) Pulping: select the mineral raw materials used to prepare microcrystalline bricks for batching, and add them into a ball mill for ball milling to obtain slurry;
[0043] (2) Spray drying: The slurry is spray-dried to obtain powder, and the moisture content of the powder is measured and controlled at the discharge conveyor belt under the spray tower to be 6.8-7.4%, and the particle gradation is 0.5% for 20 mesh and 35% for 40 mesh , 62% for 80 mesh, 2.5% for below 100 mesh;
[0044] (3) Compression molding: the powder is transported to the press for distribution, and compression molding is performed to obtain bricks;
[0045] (4) drying: dry the adobe, and measure and control the drying temperature of the adobe after drying to be 85°C, and the drying strength is 1.5MPa;
[0046] (5) Glazing:
[0047] a. Spray the microcrystalline bottom glaze on the surface of the...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2-a kind of production technology of microcrystalline brick, comprises the steps:
[0056] (1) Pulping: select the mineral raw materials used to prepare microcrystalline bricks for batching, and add them into a ball mill for ball milling to obtain slurry;
[0057] (2) Spray drying: The slurry is spray-dried to obtain powder, and the moisture content of the powder is measured and controlled at the discharge conveyor belt under the spray tower to be 6.8-7.4%, and the particle gradation is 0.2% for 20 mesh and 47% for 40 mesh , 50% for 80 mesh, 2.8% for below 100 mesh;
[0058] (3) Compression molding: the powder is transported to the press for distribution, and compression molding is performed to obtain bricks;
[0059] (4) Drying: dry the adobe, and measure and control the drying temperature of the adobe after drying to be 90°C, and the drying strength is 1.5MPa;
[0060] (5) Glazing:
[0061] a. Spray microcrystalline bottom glaze on the surface of the bri...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Embodiment 3-a kind of production technology of microcrystalline brick, comprises the steps:
[0070] (1) Pulping: select the mineral raw materials used to prepare microcrystalline bricks for batching, and add them into a ball mill for ball milling to obtain slurry;
[0071] Before the ball mill discharges, measure and control the process parameters of the slurry at the ball mill outlet, put the slurry into the transfer pool, ground pool or transfer tank, and perform sampling to detect the process parameters of the slurry; the slurry The process parameters of the material include moisture, fineness, flow rate and specific gravity;
[0072] The moisture content of the slurry discharged from the pulp outlet of the ball mill is controlled to be 32-35%, the fineness is controlled to be 250 mesh, the sieve residue is 1.1%, the flow rate is controlled to be 70s; the specific gravity is controlled to be 1.69g / ml;
[0073] The moisture content of the slurry in the transfer poo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com