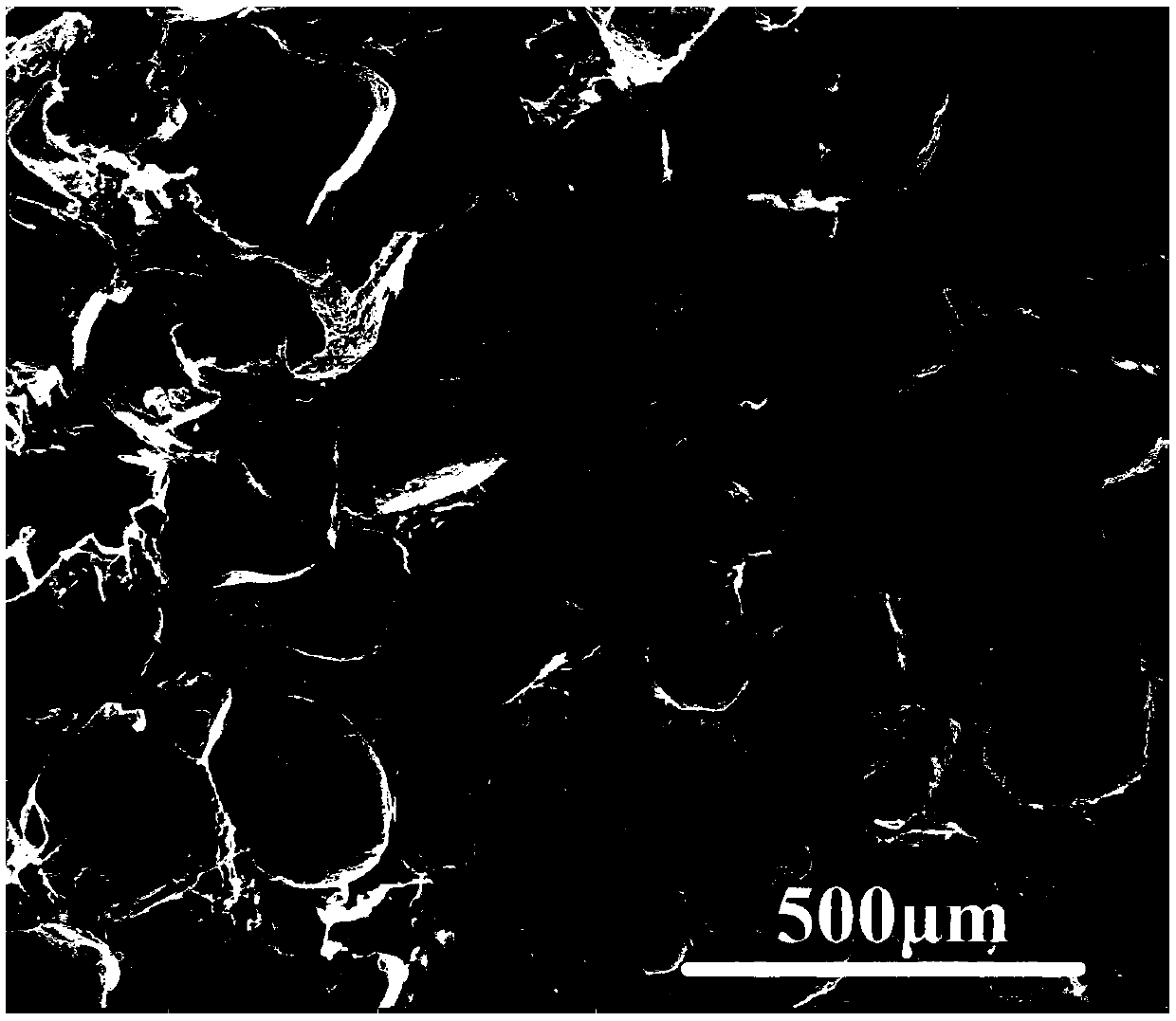
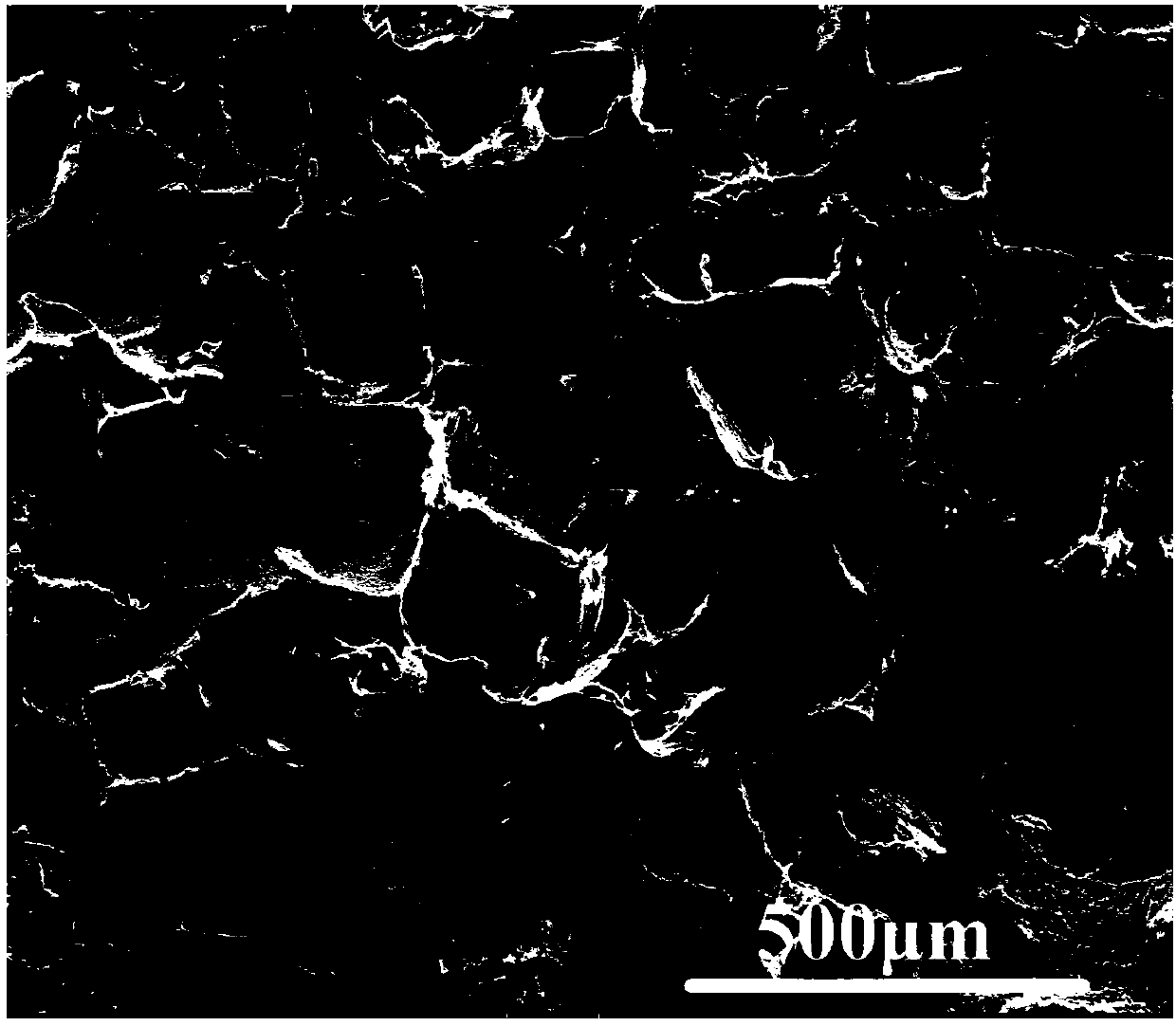
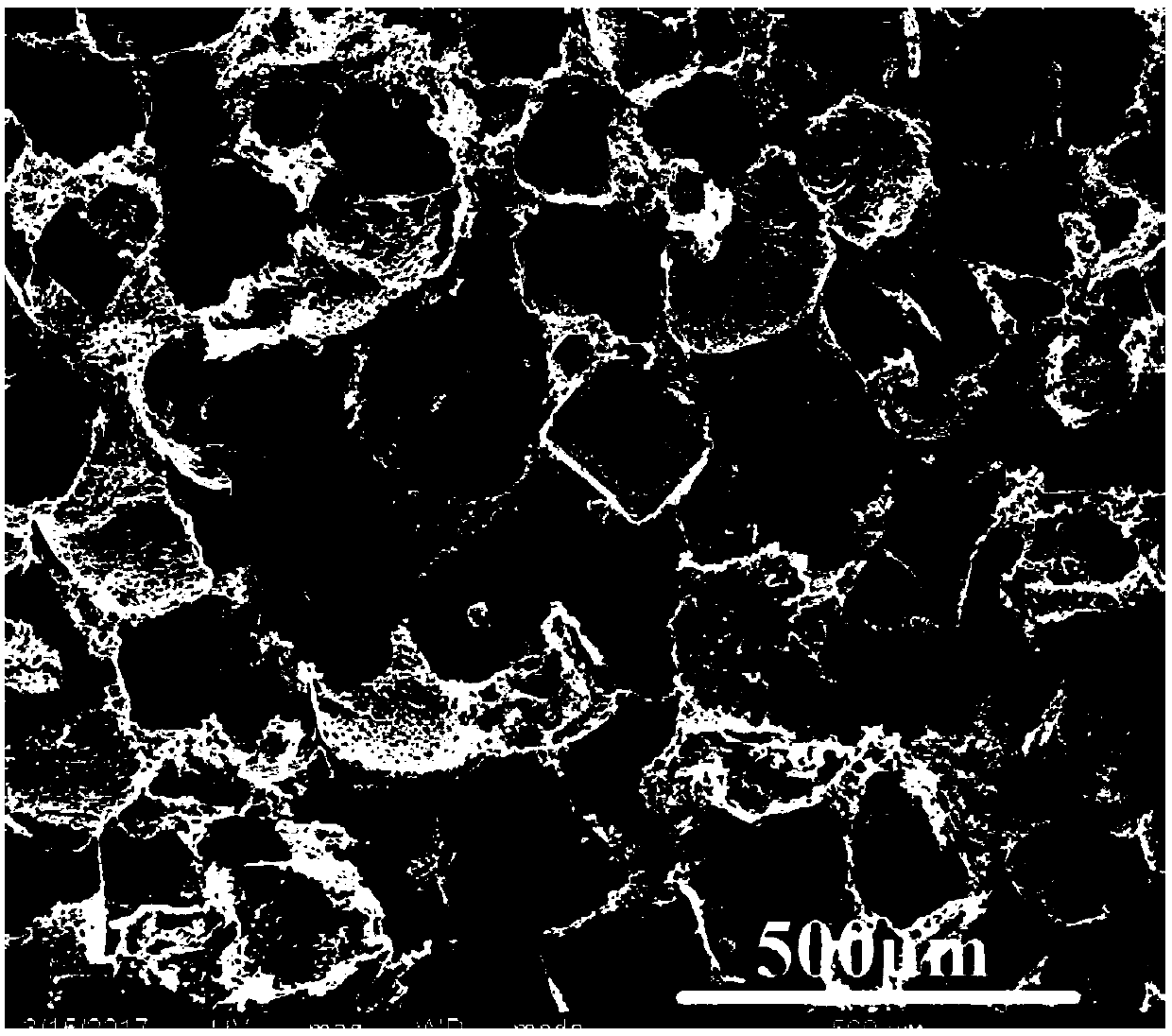
Porous polylactic acid material for scaffold for tissue engineering and preparation method thereof
A tissue engineering scaffold and porous material technology, applied in the fields of polymer material processing and biomedicine, can solve problems such as poor biocompatibility and complex process, and achieve good hydrolysis resistance, excellent mechanical properties, and good dimensional stability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] The invention provides a preparation method of a polylactic acid porous material for a tissue engineering scaffold, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0034] 1) Dissolve the dried and weighed L-polylactic acid (PLLA) and D-polylactic acid (PDLA) in the solvent respectively to form the corresponding polylactic acid solution, then mix the L-polylactic acid solution and the D-polylactic acid solution, and then add Adding a porogen into the mixed solution, and then performing solution casting; waiting for the solvent to volatilize to obtain a polylactic acid stereoblend;
[0035] 2) Put the obtained polylactic acid stereoblend into deionized water to leach the porogen, and replace the deionized water every 1 to 24 hours, and the dissolution time is 1 to 14 days;
[0036] 3) Dry the leached sample under the condition of 40-150° C. to obtain a highly heat-resistant polylactic acid porous scaffold material.
[0037]In step 1) of the present invention, th...
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Preparation of Polylactic Acid Porous Materials for Engineering Supports
[0041] (1) Using the solution casting method, dissolve 3g of dry and weighed polylactic acid (PLLA) and 3g of polylactic acid (PDLA) in 45ml of dichloromethane solvent respectively, stir for 2h, and then mix the polylactic acid solution and D-polylactic acid solution, stirred for 24 hours, added 24g of sodium chloride particles with a size of 100-180 μm, stirred until the viscosity of the solution was large enough, and the sodium chloride particles no longer sank to the bottom, and then the solution was cast; at room temperature Stand for 7 days, and the polylactic acid stereoblend is obtained after the solvent volatilizes;
[0042] (2) The obtained blend is put into deionized water and the sodium chloride is leached, and the deionized water is changed every 12 hours, and the dissolving time is 3 days;
[0043] (3) Dry the leached sample in a vacuum oven at 40° C. to obtain a highly he...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Preparation of Polylactic Acid Porous Materials for Engineering Supports
[0049] (1) Using the solution casting method, dissolve 3.6g of dry and weighed L-polylactic acid (PLLA) and 2.4g of D-polylactic acid (PDLA) in 45ml of dichloromethane solvent respectively, stir for 2 hours, and then mix the L-polylactic acid (PDLA) Lactic acid solution and D-polylactic acid solution, stirred for 24 hours, added 24g of sodium chloride particles with a size of 100-180 μm, stirred until the viscosity of the solution was large enough, and the sodium chloride particles no longer sank to the bottom, and then the solution was cast; at room temperature Place under the condition for 7 days, and the polylactic acid stereoblend is obtained after the solvent volatilizes;
[0050] (2) The obtained blend is put into deionized water and the sodium chloride is leached, and the deionized water is changed every 12 hours, and the dissolving time is 3 days;
[0051] (3) Dry the leached s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com