Preparation method and application of thermosensitive macrolide antibiotics molecular-imprinting solid-phase-micro-extracted fibers
A macrolide and molecular imprinting technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry pretreatment, can solve the problems that have not yet been seen, and achieve the effects of improving repeatability and uniformity, easy control of thickness and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1. Preparation method of thermosensitive macrolide antibiotic molecularly imprinted solid-phase microextraction fiber
[0027] (1) A capillary with a length of about 4 cm and an outer diameter of 350 m is burned to remove the outer wall protective layer with a length of 2 cm, and the outer wall is sequentially soaked in 1M sodium hydroxide and 0.1M hydrochloric acid for 1 hour, washed with water until neutral, blown dry with nitrogen, and the volume Silanize the 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl acrylate / acetone solution at a ratio of 10%, and dry at 100°C; cut off a glass tube with a length of about 2cm and an inner diameter of 1mm, and dry it; (2) Weigh 0.1mmol of spiramycin, 0.4mmol of N-isopropylacrylamide, and 0.42mmol of methacrylic acid were dissolved in a mixed solvent consisting of 1mL of DMSO and 2mL of chloroform, and the mixed solution was sonicated at room temperature to make the template molecule and the functional unit The body is fully mixed; then add cr...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2. Verification of the effect of MIPs on the enrichment and concentration of macrolides
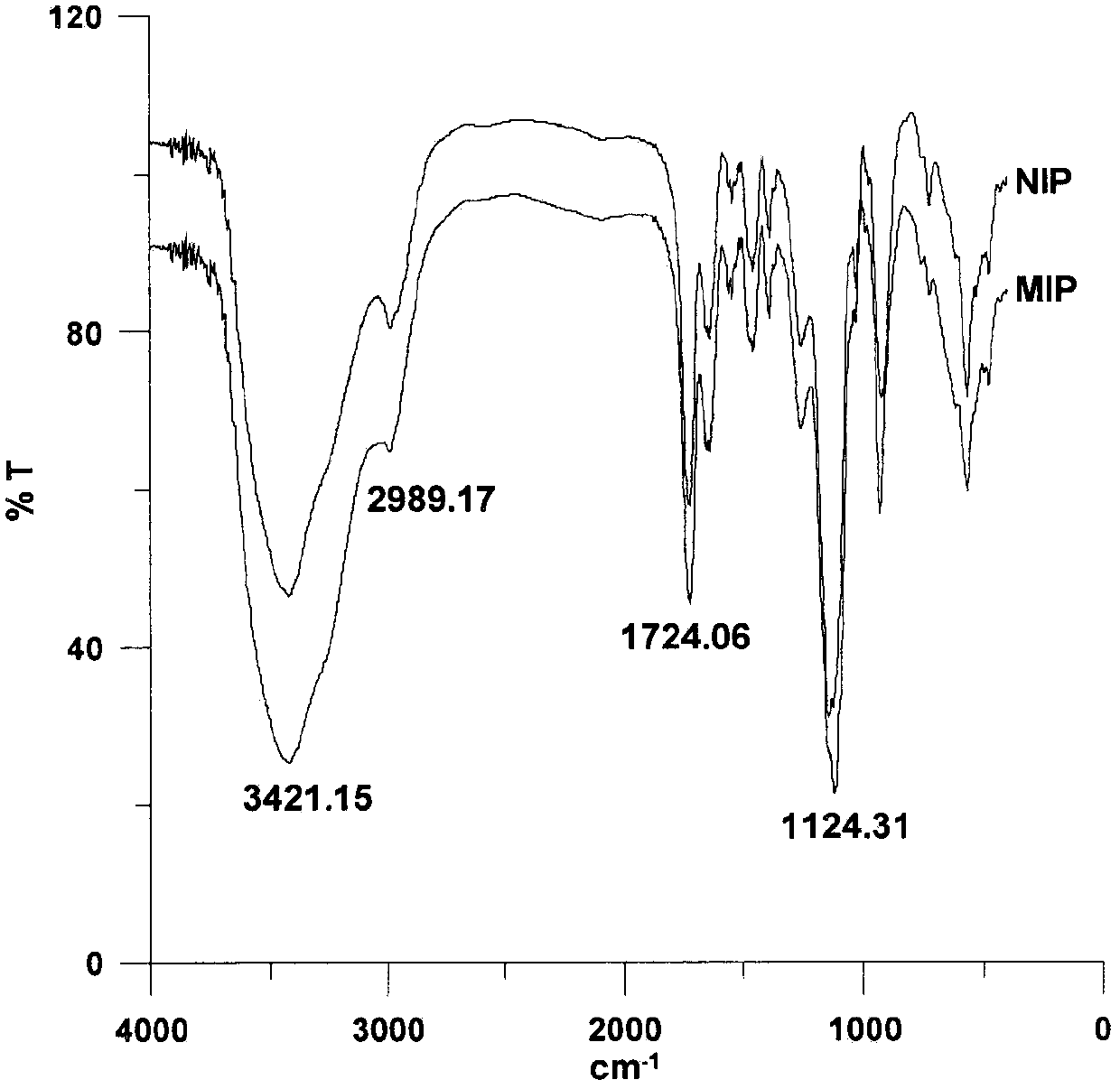
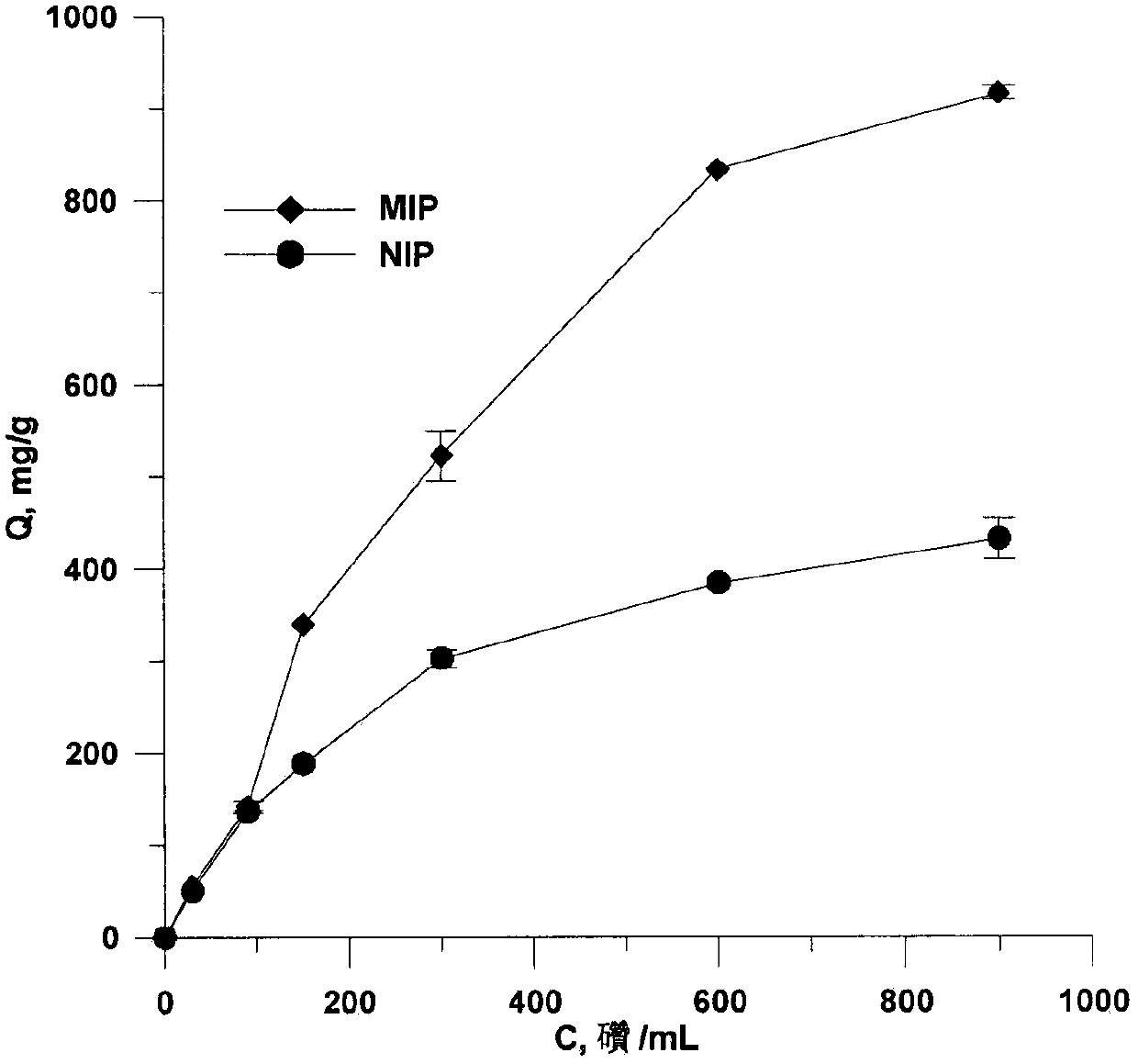
[0030] (1) The adsorption properties of molecularly imprinted polymers to template molecules were determined at different ratios, see Table 1. Finally established the optimal ratio of template molecule: thermosensitive functional monomer: non-thermosensitive functional monomer: crosslinking agent = 1: 3.5: 4.2: 20, wherein the non-thermosensitive functional monomer is methyl The enrichment effect is best when using acrylic acid. The resulting molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) were characterized by infrared spectroscopy, see figure 1 . It can be seen from the infrared spectrum that the MIPs material with eluted template molecules has the same wave number as that contained in non-template imprinted polymers (NIPs), indicating that the template molecules in the obtained MIPs material have been completely removed.
[0031] Table 1 The optimization of the type and ratio o...
example 3
[0037] Example 3. Temperature Sensitivity Characteristics of Thermally Sensitive Molecularly Imprinted Microextraction Fibers
[0038] (1) In order to verify the temperature sensitivity of heat-sensitive molecularly imprinted materials, heat-sensitive molecularly imprinted fibers were used as solid-phase microextraction materials, and spiramycin and tilmicol with a volume of 5 mL and a concentration of 20 μg / mL The solution samples of star and josamycin are the extraction solutions, and the parallel comparative experiments of the extraction amounts at different temperatures are carried out, as shown in Table 2. The results showed that the optimum extraction temperature for different target compounds was different for thermosensitive molecularly imprinted fibers.
[0039] Table 2 Temperature Sensitivity Experiments of Thermosensitive Molecularly Imprinted Fibers
[0040]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com