Method for extracting ferric oxide from tailings
A technology of iron oxide and tailings, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of unrecycled titano-magnetite, complex properties, serious symbiosis, etc., and achieve the effect of strengthening environmental protection, less equipment investment, and expanding production capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
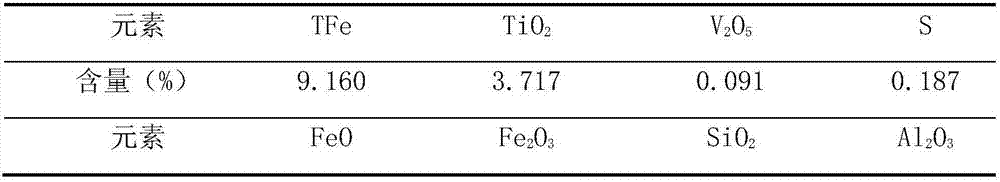
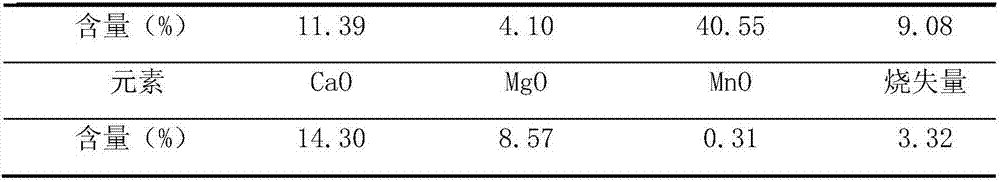
[0033] First, the chemical multi-element analysis of the tailings was carried out, and the analysis results are shown in Table 1.
[0034] Table 1 Results of tailings chemical multi-element analysis
[0035]
[0036]
[0037] Note: TFe---refers to FeO and Fe in tailings 2 o 3 The sum of the mass of ionic iron in the mass, the mass without oxygen, the reason is that it is generally difficult to combine FeO and Fe in chemical analysis 2 o 3 The amount of iron ions is measured separately, so only the total amount of iron ions can be measured.
[0038] It can be seen from the above table that the content of TFe in the tailings is 9.16%. Although most of the iron is removed, some iron still exists in the tailings.
[0039] First, take 1000g of the above-mentioned tailings and mix them with 620g of sodium hydroxide and place them in a reactor, control the melting reaction temperature to 480°C, and the melting reaction time to 50min, and obtain a mixed solid phase after mel...
Embodiment 2
[0052] First, take 1000g of the same tailings as in Example 1 and mix them with 620g of sodium hydroxide and place them in a reactor, control the melting reaction temperature to 480°C, and the melting reaction time to 50min, and obtain a mixed solid phase after melting and decomposition.
[0053] The mixed solid phase obtained in the above steps is fully washed with water at a temperature of 30° C., filtered to remove the dilute lye, and dried at room temperature to obtain the modified ore.
[0054] Step 1: Weigh 500g of the above-mentioned modified ore, and measure 275ml of water.
[0055] Step 2: Clean the grinder.
[0056] Step 3: Put 500g of tailings into the grinding machine, add 275ml of water at the same time, set the grinding time for grinding, and the grinding time is 3 minutes.
[0057] Step 4: Take out all the pulp in the grinding machine, use a 200-mesh (0.074mm) sieve to carry out wet sieving in a basin filled with clean water, and obtain the on-sieve product and...
Embodiment 3
[0065] First, take 1000g of the same tailings as in Example 1 and mix them with 620g of sodium hydroxide and place them in a reactor, control the melting reaction temperature to 480°C, and the melting reaction time to 50min, and obtain a mixed solid phase after melting and decomposition.
[0066] The mixed solid phase obtained in the above steps is fully washed with water at a temperature of 30° C., filtered to remove the dilute lye, and dried at room temperature to obtain the modified ore.
[0067] Step 1: Weigh a portion of 500g of modified ore that has been ground for 3 minutes, and measure 750ml of water.
[0068] Step 2: Mix one part of modified ore with one part of 750ml water to prepare a slurry with a concentration of 40%.
[0069] Step 3: Clean the magnetic separator, start the drum, set the current of the magnetic field strength to 4.5A, and feed the ore pulp into the ore feeding port of the magnetic separator at a uniform speed. After feeding the ore, turn off the p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com