Joining material for joining silicon carbide ceramics and method for joining silicon carbide ceramics
A technology of silicon carbide ceramics and connecting materials, which is applied in the field of connecting silicon carbide ceramics by using the connecting materials, which can solve the problems of high cost and difficulty in industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
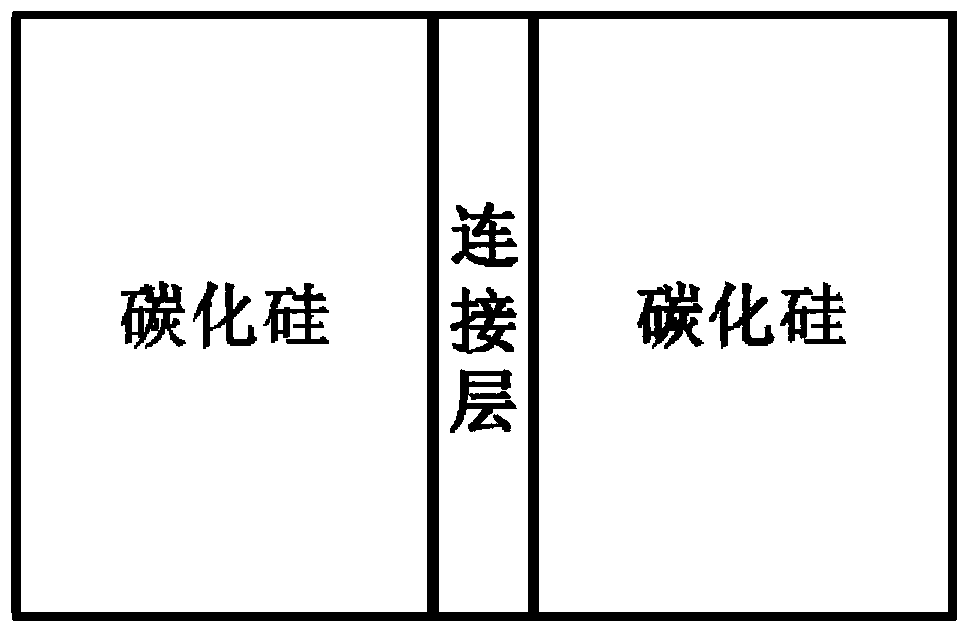
[0026] In this example, if figure 1 The silicon carbide ceramic materials to be joined are shown as being joined using the joining layer material. The material to be connected is two pieces of silicon carbide with a diameter of Ф20*20mm, and the material of the connection layer is pure titanium. The silicon carbide materials to be connected are connected together through the connection layer by heating and connecting with an external heat source. The method of external heat source heating connection is electric field assisted thermocompression connection. Specific steps are as follows:
[0027] (1) Polish the silicon carbide surface to be connected with 0.1 micron diamond polishing liquid to remove larger defects and impurities on the surface;
[0028] (2) Coating a 500nm Ti film on the surface of a piece of silicon carbide to be connected by PVD method, and then docking another piece of silicon carbide with its surface; then put the sample into a graphite mold, and then pla...
Embodiment 2
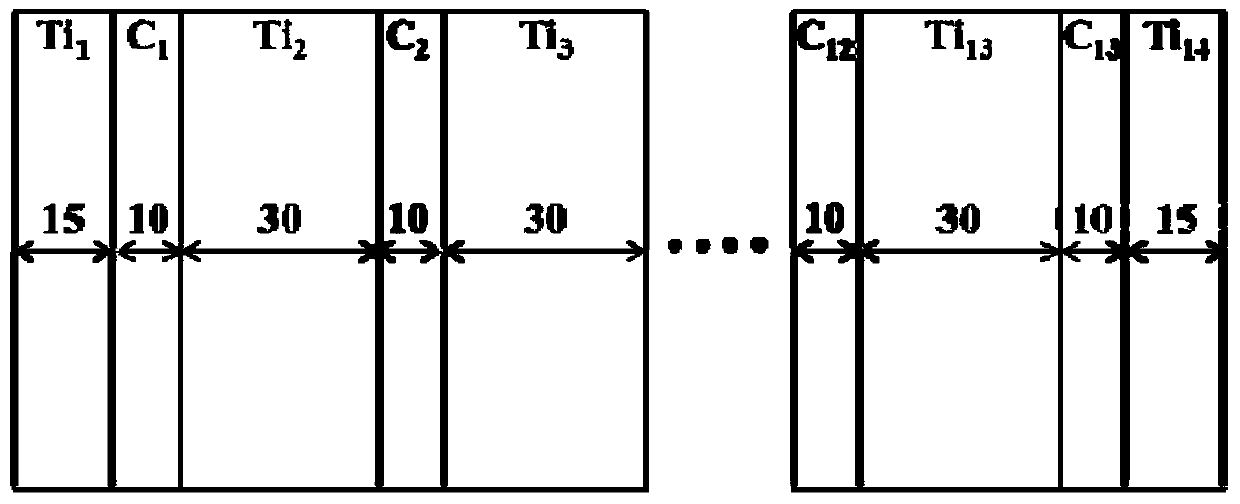
[0031] In this example, if figure 1 The silicon carbide ceramic materials to be joined are shown as being joined using the joining layer material. The material to be connected is exactly the same as that in Example 1. Connecting layer materials such as figure 2 As shown, it is a left and right stacked structure, including 14 layers of Ti films, and there is a carbon film between the adjacent titanium films. The thickness of the film is 10nm, the total thickness of the intermediate connection layer after lamination is 520nm, and the molar mass ratio of Ti to C is 1:0.6. The silicon carbide materials to be connected are connected together through the connection layer by using an external heat source to heat the connection. The method of heating connection with an external heat source is basically the same as that of Example 1, which is an electric field-assisted thermocompression connection, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0032] (1) Polish the silicon carbide surf...
Embodiment 3
[0036] In this example, if figure 1 The silicon carbide ceramic materials to be joined are shown as being joined using the joining layer material. The material to be connected is exactly the same as that in Example 1. The structure of the connection layer material is basically the same as that in Example 2, including 14 layers of Ti films, and a carbon film between adjacent titanium films. The only difference is that the thickness of the top and bottom titanium films is 2nm, the thickness of the rest of the titanium films is 4nm, the thickness of each carbon film is 2nm, and the total thickness of the intermediate connection layer after stacking is 78nm. The silicon carbide materials to be connected are connected together through the connection layer by using an external heat source to heat the connection. The method of heating connection with an external heat source is basically the same as that of Example 1, which is an electric field-assisted thermocompression connection,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com