Method, reagent and kit for detecting minimal residual disease
A kit and reagent technology, applied in the field of cancer diagnosis, can solve problems such as hindering low-frequency malignant cell detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
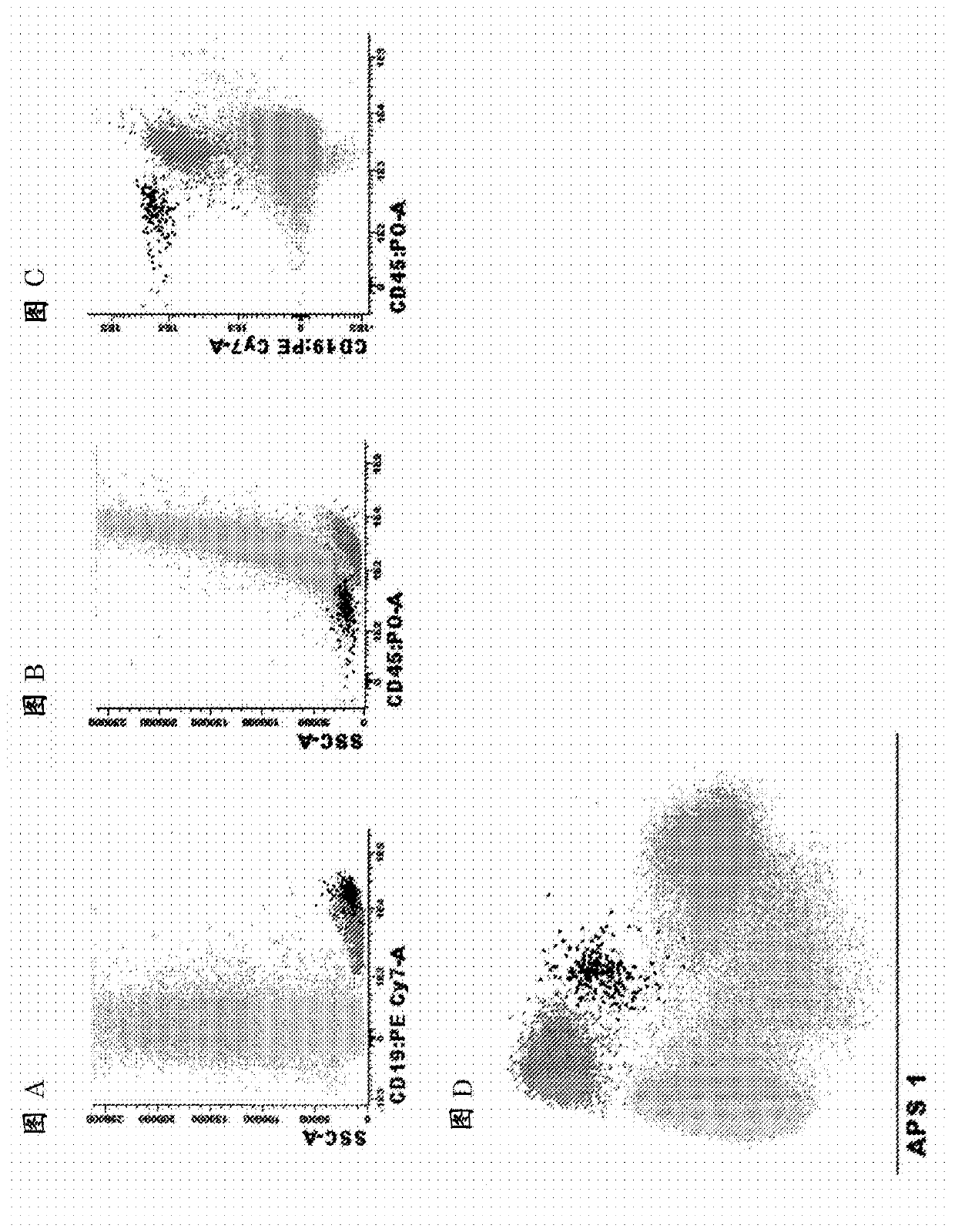
[0096] Example 1. Antibody panel and diagnostic method for MRD detection in BCP-ALL patients
[0097] Markers used to identify total B cells and B cell precursors in bone marrow
[0098] List of relevant identification markers : CD19, CD45
[0099] How to use them : The use of CD19 markers to preset gates is necessary to identify pure B cell populations. To focus on normal B cell precursors (BCP), CD45 negative or weakly positive can be used to distinguish CD45 positive mature B cells from BCP. In the case of CD19 treatment, CD22 can be used instead of CD19. These markers can also be used in combination with side light scattering (SSC) or forward light scattering (FSC) or both FSC and SSC to identify peripheral blood or bone marrow or other types of samples (e.g. bone marrow, tissue biopsy, spinal fluid) B cells in. It is worth noting that other markers used to distinguish between normal BCP cells and BCP-ALL cells (such as CD10, CD20, CD38, and CD34) (see below) can also help...
Embodiment 2
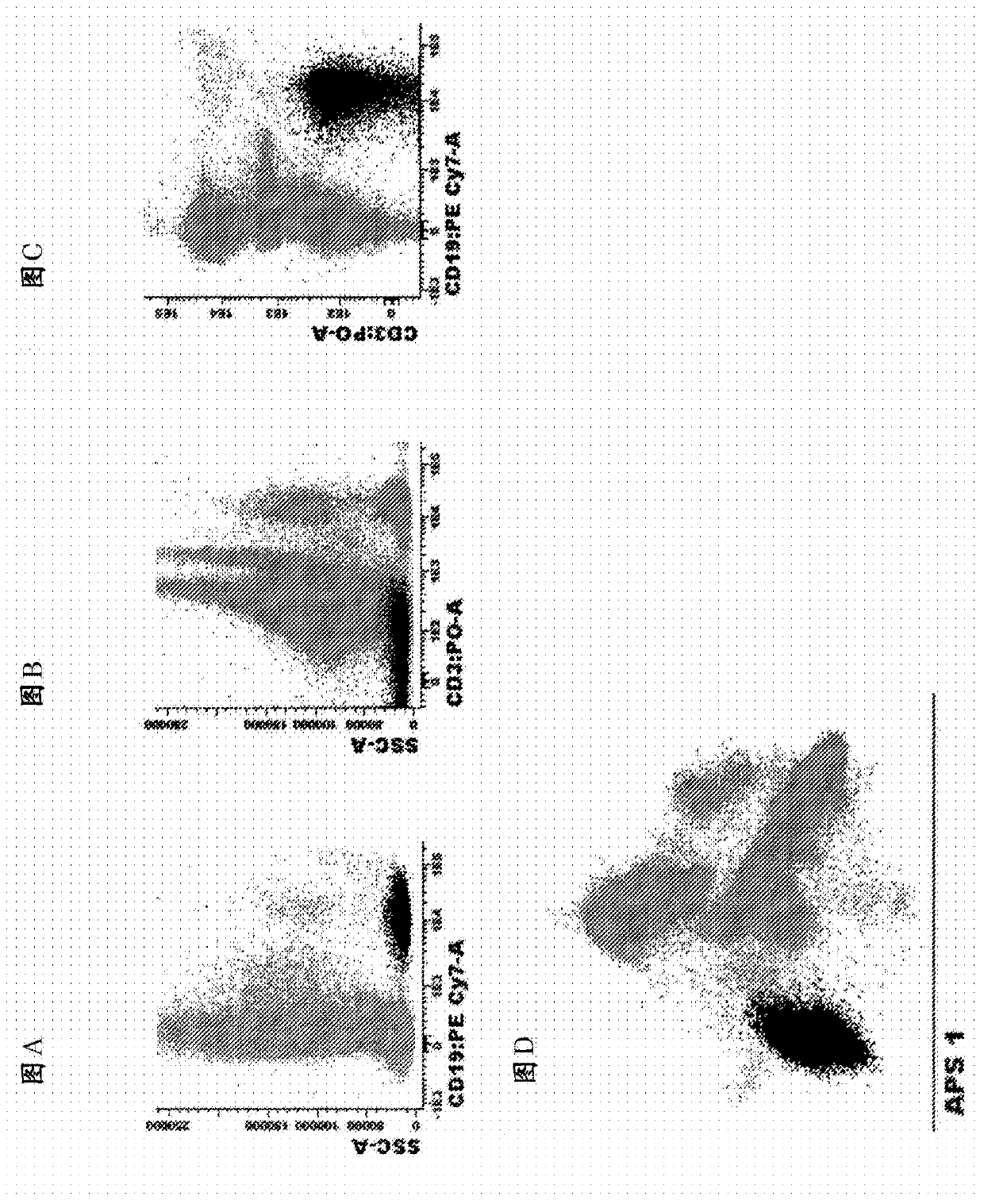
[0114] Example 2. Antibody panel and diagnostic method for MRD detection in CLL patients
[0115] Markers used to identify total B cells in peripheral blood and bone marrow:
[0116] List of identification markers :CD19, CD3 (exclude markers)
[0117] How to use them : Using this combination of markers to preset gates is necessary to identify pure B cell populations and remove T cell / B cell doublets. These markers can also be used in combination with side light scattering (SSC) or forward light scattering (FSC) or both FSC and SSC to identify peripheral blood or bone marrow or other types of samples (e.g., tissue biopsy, spinal fluid) B cells. For finer gating to better enrich CLL cells, both CD5 and CD27 can be used. Markers used to distinguish between normal B cells and CLL cells:
[0118] List of markers and the most common phenotypic aberrations :
[0119] CD27 : Positive on CLL cells and a small part of normal B cells
[0120] CD5 : Positive on CLL cells and a small part o...
Embodiment 3
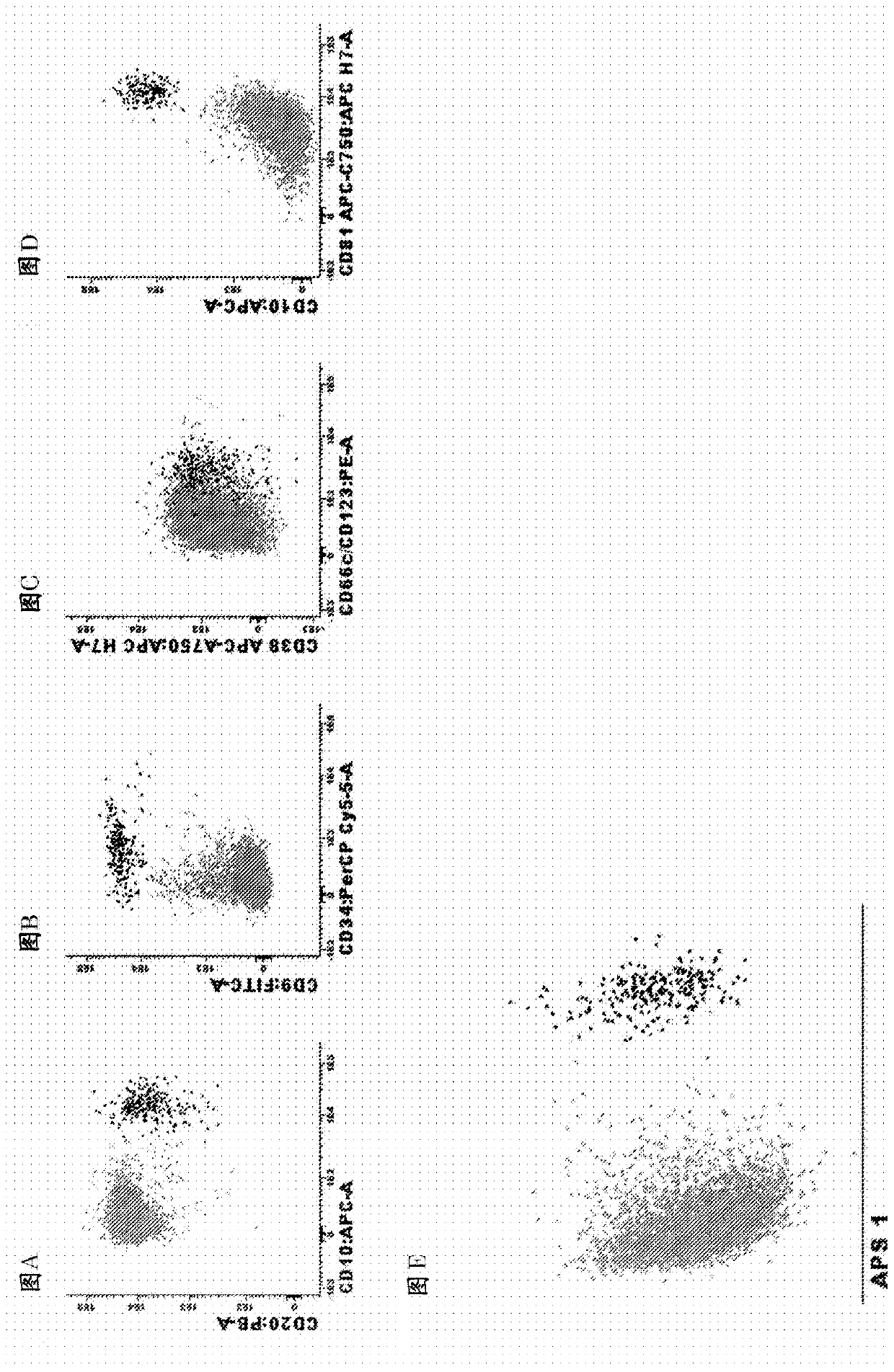
[0129] Example 3. Antibody panel and diagnostic method for MRD detection in MM / PCD patients
[0130] Markers used to identify total plasma cells in bone marrow:
[0131] List of identification markers : CD38, CD138 and CD229
[0132] How to use them: Any combination of the three markers works at any fluorescent dye position; any combination of two of the three markers can also be used or even one of the three markers alone can be used in some cases (not all). It is preferably combined in the following order: 1) CD138 / CD38 / CD229; 2) CD138 / CD38, 3) CD138 / CD229; 4) CD38 / CD229; 5) CD138; 6) CD38); 7) CD229. It should be noted that any of these markers, alone and in combination, can also be used in combination with side light scattering (SSC) or forward light scattering (FSC) or both FSC and SSC to identify bone marrow or other types of samples (e.g., peripheral blood, Tissue biopsy, spinal fluid) in plasma cells.
[0133] Markers used to distinguish between normal and clonal / malignan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com