Recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and application thereof
A technology of Escherichia coli and phospholipase, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and protein engineering, can solve the problems of high culture cost, low production intensity, long enzyme production cycle, etc., and achieve the effect of high hydrolysis and transphosphatidylase activity and high vitality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1: Construction of recombinant phospholipase D genetically engineered bacteria
[0042] (1) Primers are designed, and the phospholipase D gene (shown in SEQ ID NO.2) derived from Streptomyces ambofaciens is subjected to PCR amplification by means of molecular biology with primers shown in SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4 : Add LA taq enzyme to the system, pre-denature at 94°C for 3min, denature at 94°C for 30s, anneal at 55°C for 30s, extend at 72°C for 1min, 30 cycles, and finally extend at 72°C for 10min;
[0043] (2) Digest the target fragment and expression vector pET28a(+) with restriction endonucleases HindIII and EcoR I at 37°C for 2h;
[0044] (3) Ligate the target gene with T4 ligase and plasmid pET28a(+) at 16°C for 10 hours after recovering the enzyme-cut gel;
[0045] (4) Introduce the ligation product into E.coli BL21 (DE3) competent, and culture it on a kanamycin-resistant LB plate for 12 hours;
[0046] (5) Perform PCR and enzyme digestion verificat...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2: Induced expression of genetically engineered bacteria
[0049] (1) Insert the constructed genetically engineered bacteria E.coli BL21-PLD1 into LB slant medium and culture for 12 hours; the strain without the expression vector was used as a control;
[0050] (2) Put a ring of slanted seeds into the LB medium and cultivate for 8 hours;
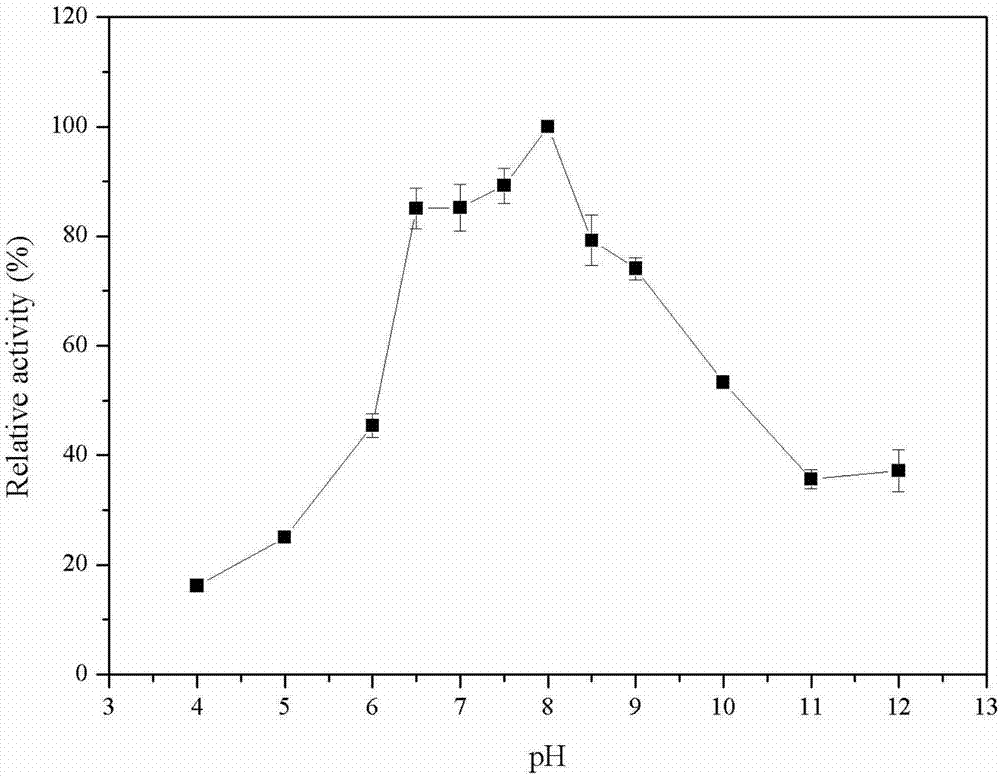
[0051] (3) Put the E.coli BL21-SaPLD seed solution into the LB medium and culture it to OD 600 was 0.6, using single factor optimization, adding IPTG with a final concentration of 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 mM for induction, respectively, and collecting the bacteria after induction at 16, 25, 30, and 37°C for 4, 8, 12, and 16 hours, and sterile The bacteria were washed with normal saline. Phospholipase D can be correctly expressed in the BL21 strain with a size of 55kDa (eg figure 1 shown), the optimal expression conditions are: IPTG concentration 0.1mM, induction temperature 25°C, induction time 12h, at this time the enzyme...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3: the purification of phospholipase D
[0054] Cultivate the genetically engineered bacterium constructed in Example 1, and induce its expression of phospholipase D according to Example 2, then collect the genetically engineered bacterium, and wash the thalline twice with sterile physiological saline; After 30 minutes, take the supernatant, which is the crude enzyme solution. Use affinity nickel column chromatography to purify phospholipase D, wash away impurity proteins with 10, 20, and 50 mM imidazole respectively, and then elute target protein with 300, 500 mM imidazole, and obtain phospholipase D with 10 kDa ultrafiltration concentration tube after dialysis and desalination Pure phospholipase D protein (as figure 2 shown). The purification results are shown in Table 1. The specific activity of the purified enzyme produced by the E.coli BL21-PLD1 strain can reach 0.27U / mg protein, while the specific activity of the pure enzyme from PLD2~PLD7 is 0.03, 0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific vitality | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com