Method for preparing cellulose nano-fibers based on biomass material
A biomass raw material and nanofiber technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of cellulose nanofibers, can solve the problems of difficult recovery of acid waste liquid, unsatisfactory cellulose purity, harmful ecological environment safety, etc., so as to avoid environmental problems and reduce chemical The generation of polluting waste and the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
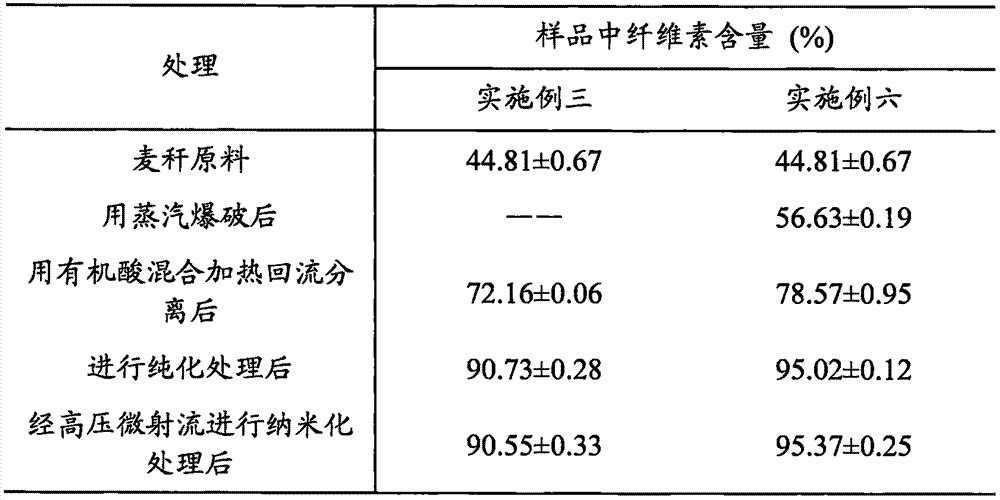
[0050] Dry the bagasse waste at 45°C and knead it into velvet; take 1000 g of the bagasse powder, carry out steam explosion and centrifugation under a pressure of 2.0 MPa, wash the product 5 times with distilled water, and freeze-dry it for later use; weigh the frozen 15g (dry weight) of the dried product was mixed with a formic acid-acetic acid aqueous solution mixed reagent (formic acid / acetic acid / water volume ratio 10 / 70 / 20) mixed with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:30, and heated to reflux at 100°C for 3h , while stirring at a speed of 400rpm; the reaction is stopped, the product is cooled to room temperature, and filtered with No. 4 (aperture is 5-15 μm) sand core funnel and washed to neutrality with distilled water; the resulting product is mixed with 1.5% hydrogen peroxide ( pH=10.0) mixed at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:30, reacted at 55°C for 3 hours, and then washed the reaction product with distilled water until neutral; made a 0.15% suspension of the product sample a...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The rice straw was air-dried under natural conditions, crushed through a 1mm sieve; 2000 g of the rice straw powder sample was subjected to steam explosion and centrifugal treatment under a pressure of 2.8 MPa, and the product was washed 5 times with distilled water, and freeze-dried for later use; 20g (dry weight) of the product was mixed with the mixed reagent of formic acid and acetic acid aqueous solution (formic acid / acetic acid / water volume ratio 5 / 80 / 15) with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20, heated and refluxed at 90°C for 4h, and simultaneously Stir at a speed of 350rpm; when the reaction stops, the product is cooled to room temperature, then centrifuged at 4500rpm, and washed with distilled water until neutral; the resulting product is mixed with 3% NaOH solution at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:50 and heated Heat and stir for 2 hours; prepare the resultant sample into a 0.20% suspension, make it uniformly pass through a high-pressure homogeneous microfluidizer, ...
Embodiment 3
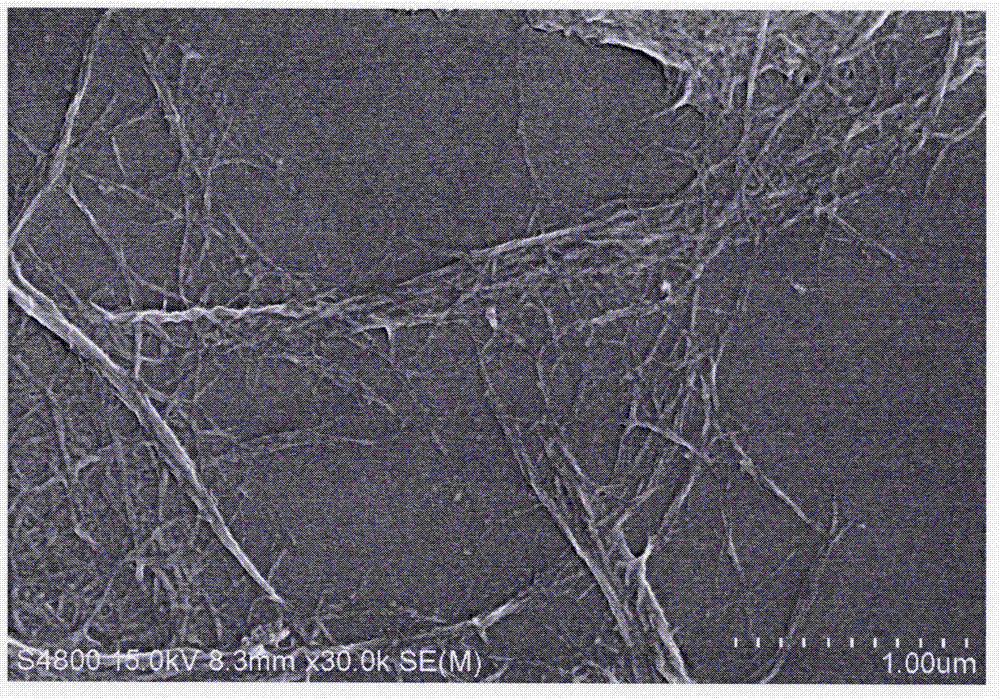
[0054] The wheat straw was air-dried under natural conditions and crushed through a 1mm sieve; 10 g (dry weight) of the wheat straw powder was weighed and mixed with a formic acid-acetic acid aqueous solution (formic acid / acetic acid / water volume ratio 30 / 50 / 20) to solidify Mix the liquid at a ratio of 1:25, heat and reflux at 107°C for 3 hours while stirring at a speed of 400rpm; after the reaction stops, cool the product to room temperature, and then filter it with a No. 3 (pore size of 15-40μm) sand core funnel and washed with distilled water until neutral; the resulting product was mixed with 1.8% hydrogen peroxide-0.18% cyanamide solution (pH=10.0) at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:30, reacted at 50°C for 4 hours, and then washed with distilled water until neutral The resultant sample is made into a 0.10% suspension, and it is uniformly passed through a high-pressure homogeneous micro-fluidizer, and processed 5 times under a pressure of 150MPa to obtain a dispersion of wheat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com