Surface functionalization modification method for metal organic framework (MOF) material based on liposome membrane
A metal-organic framework and surface functionalization technology, which is applied in the field of surface functionalization modification of metal-organic framework materials, can solve the problems of early release of MOFs materials that cannot be improved, poor biological stability, etc., and achieves improved biological stability and biological safety. Simple operation, high biosafety effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0057] The synthetic method of MOFs material of the present invention specifically comprises:
[0058] (1) Synthesize UiO series and ZIF series by solvothermal synthesis. The specific steps are to weigh an appropriate amount of metal ions and organic ligands, ultrasonically disperse them in the corresponding solvent, add an appropriate amount of regulator, and transfer them to a hydrothermal kettle , react at a certain temperature for a period of time, centrifuge and ultrasonically redisperse at a certain speed, and wash with a suitable solvent several times to obtain the final product.
[0059] When UiO-66 is synthesized in the above steps, the metal ion is anhydrous zirconium chloride, and the amount weighed is 10-30 mg, specifically 25 mg; the organic ligand is terephthalic acid, and the amount weighed is 30-80 mg, specifically It can be 40mg; the reaction solvent is N,N-dimethylformamide, the measured amount is 3-6mL, specifically 4mL; the regulator is glacial acetic acid,...
Embodiment 1
[0076] Preparation of liposomes
[0077] Preparation of DOPA liposomes
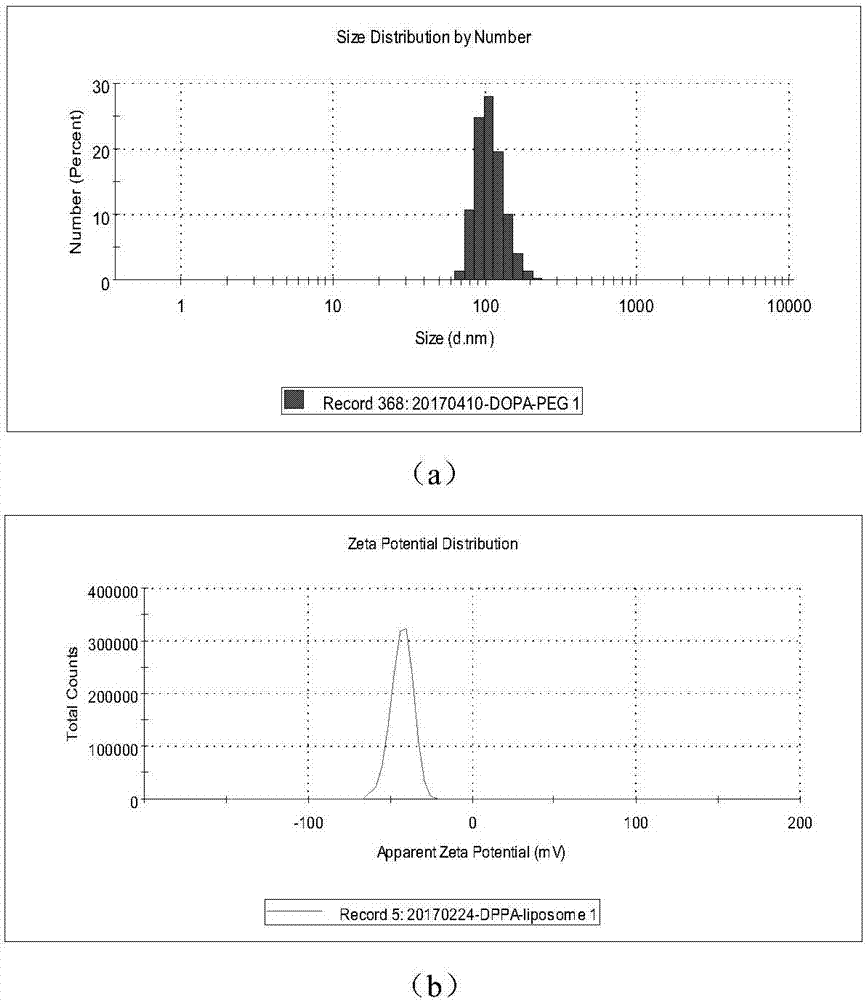
[0078] Take by weighing 5mg lipid, wherein the mass ratio of various lipid components is DOPA / chol / 18:1PEG-2000PE=15:6:1, be dissolved in the mixed solution of 2mL chloroform and methanol (volume ratio is 4:1 ), dissolved and mixed evenly, the organic solvent was sucked dry with a rotary evaporator under the condition of a water bath at 35°C, and dried under vacuum at room temperature overnight. Add 4ml of HEPES buffer (100mMNaCl, 10Mm HEPES, pH 7.4) to hydrate at room temperature for 1-2h, and then extrude 21 times with a liposome extruder to obtain DOPA liposomes with a size of 120-130nm. like figure 2 (a) shows the hydrodynamic diameter diagram of DOPA liposome, such as figure 2 (b) shows the potential diagram of DOPA liposomes.
[0079] Preparation of DOPC liposomes
[0080] Take by weighing 5mg lipid, wherein the mass ratio of various lipid components is DOPC / chol / 18:1PEG-2000PE=15:6:1, be dis...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Preparation of MOFs materials
[0085] Preparation of UiO-66
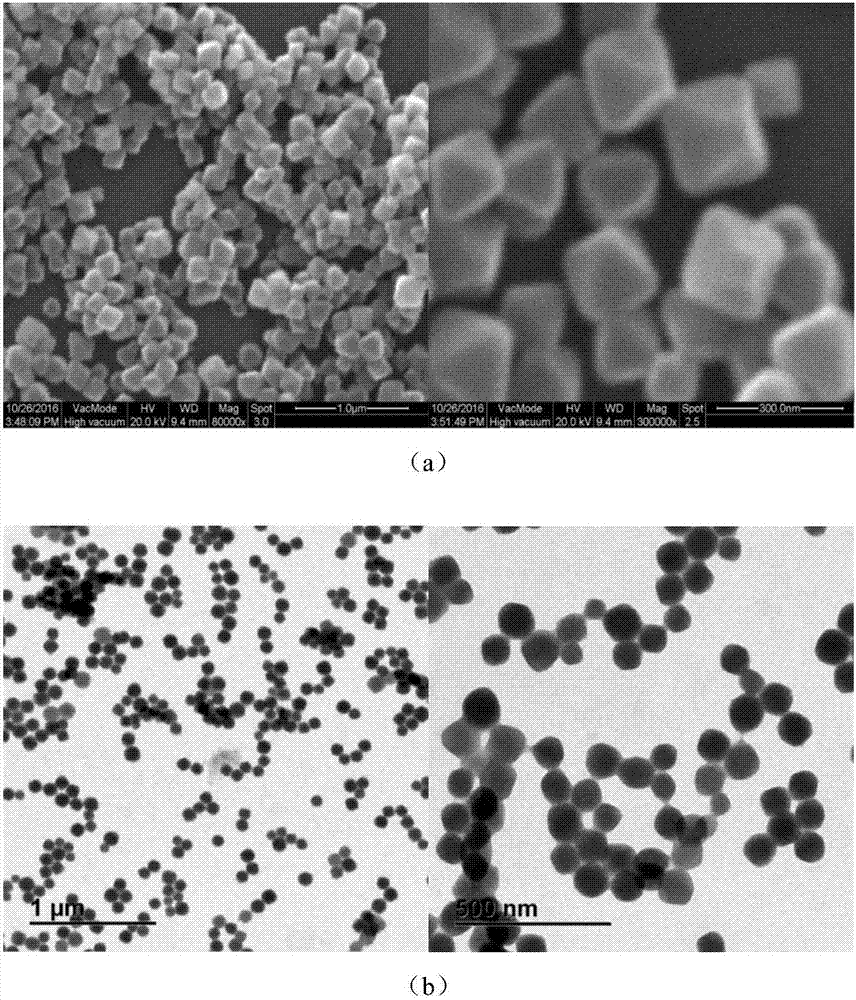
[0086] Weigh 15.5mg zirconium chloride (ZrCl 4 ), 50mg terephthalic acid (H 2 BDC), dissolved in 4ml of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), dissolved completely, added 0.3-0.9ml of acetic acid, transferred to a hydrothermal reaction kettle, reacted at 90-100°C for 18h, and the obtained solution Centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10min, and wash twice with ethanol and water respectively by ultrasonic dispersion and centrifugation to obtain UiO-66, whose hydrodynamic size is 140-900nm. like image 3 (a) shows the SEM image of UiO-66 with a hydrodynamic diameter of 230 nm, as image 3 (b) shows the TEM image of UiO-66 with a hydrodynamic diameter of 150 nm.
[0087] Preparation of MIL-100
[0088] Weigh 486mg of ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O), 140 mg of isophthalic acid (H 3 BTC), dissolved in the mixed solution of 5ml water and ethanol, wherein the volume ratio of water and ethanol is 1:0.25~4, complet...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com