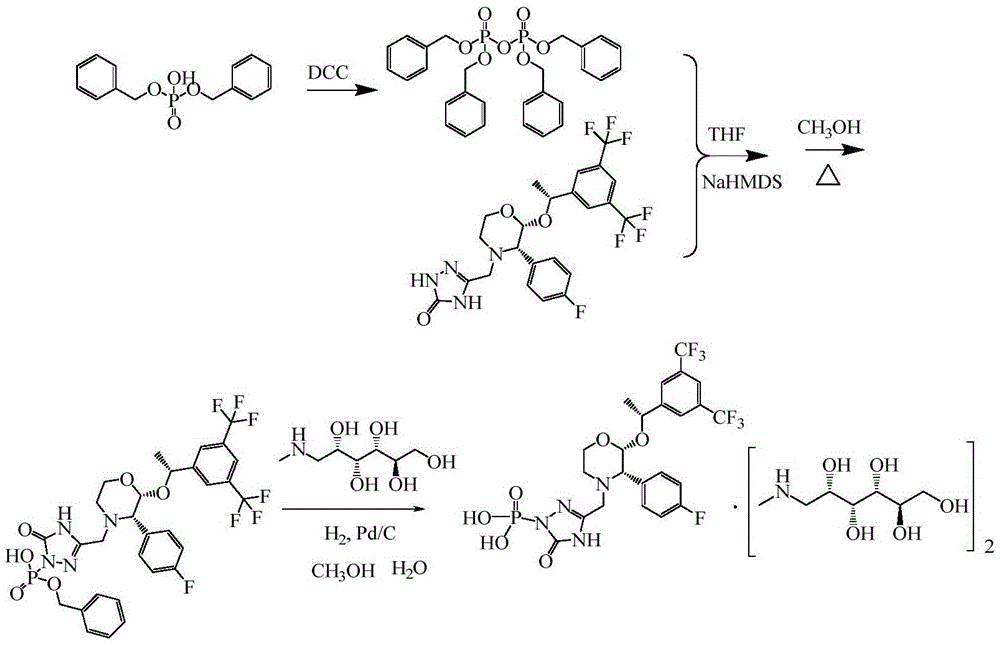
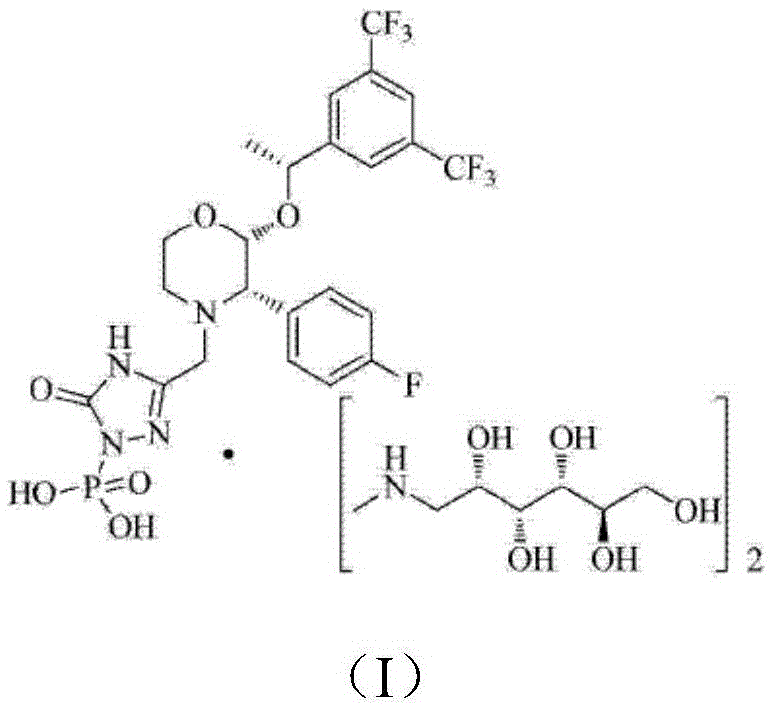
Refined palladium removing process for fosaprepitant
A fosaprepitant dimeglumine and solvent technology, applied in the field of medicinal chemistry, can solve problems such as potential safety hazards, and achieve the effects of low adsorption, low price, and simple removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The preparation of embodiment 1 fosaprepitant dimeglumine
[0035] Put 15.0g of fosaprepitant dibenzyl ester, 9.2g of meglumine, 4.7g of 10% Pd / C, 24mL of Mili-Q water, and 300mL of methanol into the hydrogenation kettle, and hydrogenate at 0.38-0.42Mpa at 18-22°C 2 hours. After the reaction, the hydrogenation solution was filtered through a 0.22 μm polytetrafluoroethylene filter membrane, 15 g of JYG-01-II (purchased from Suboco Energy Co., Ltd.) was added, and stirred at 25° C. for 18 hours. After palladium removal is completed, the palladium removal solution is filtered through a 0.22 μm polytetrafluoroethylene filter membrane and washed with an appropriate amount of methanol. Methanol and water were distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain a concentrated solution, which was then dissolved in 80 mL of methanol, added dropwise to 400 mL of acetone under nitrogen protection, separated from solid and liquid, and dried in vacuum to obtain 16.0 g of fosaprepitant d...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The preparation of embodiment 2 fosaprepitant dimeglumine
[0052] Add 15.0g fosaprepitant dibenzyl ester, 9.2g meglumine, 4.7g 10% Pd / C, 24mL Mili-Q water, 300mL methanol into the hydrogenation kettle, 0.38~0.42Mpa, 18~22℃ Hydrogenate for 2 hours. After the reaction, the hydrogenation solution was filtered through a 0.22 μm polytetrafluoroethylene filter membrane, 15 g of JYG-01-II was added, and stirred at 25° C. for 24 hours. After palladium removal is completed, the palladium removal solution is filtered through a 0.22 μm polytetrafluoroethylene filter membrane and washed with an appropriate amount of methanol. Methanol and water were distilled off under reduced pressure, then dissolved in 80 mL of methanol, added dropwise to 400 mL of acetone under nitrogen protection, separated from solid and liquid, and dried in vacuum to obtain 16.0 g of fosaprepitant dimeglumine finished product. Take an appropriate amount of fosaprepitant dimeglumine sample, and determine th...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The preparation of embodiment 3 fosaprepitant dimeglumine
[0054] Add 15.0g fosaprepitant dibenzyl ester, 9.2g meglumine, 4.7g 10% Pd / C, 24mL Mili-Q water, 300mL methanol into the hydrogenation kettle, 0.38~0.42Mpa, 18~22℃ Hydrogenate for 2 hours. After the reaction, the hydrogenation solution was filtered through a 0.22 μm polytetrafluoroethylene filter membrane, 15 g of JYG-01-II was added, and stirred at 30° C. for 18 hours. After palladium removal is completed, the palladium removal solution is filtered through a 0.22 μm polytetrafluoroethylene filter membrane and washed with an appropriate amount of methanol. Methanol and water were distilled off under reduced pressure, then dissolved in 80 mL of methanol, added dropwise to 400 mL of acetone under nitrogen protection, separated from solid and liquid, and dried in vacuum to obtain 16.0 g of fosaprepitant dimeglumine finished product. Take an appropriate amount of fosaprepitant dimeglumine sample, and determine th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com