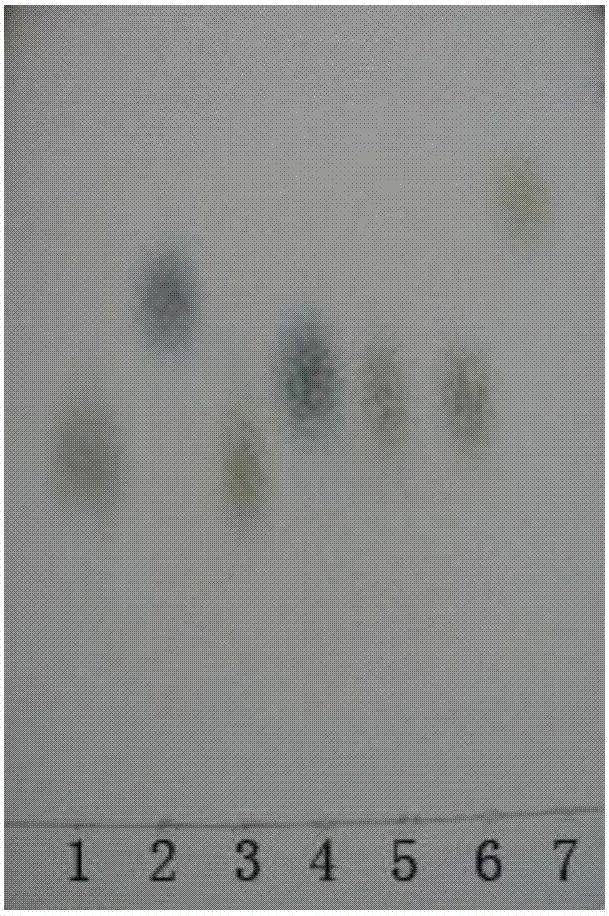Botrytis crust fungi strain and method for rapidly and artificially promoting biological crust culturing by adopting exopolysaccharides of botrytis crust fungi strain
A botrytis and exopolysaccharide technology, which is applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of low survival rate, high cost, and strong evaporation of afforestation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
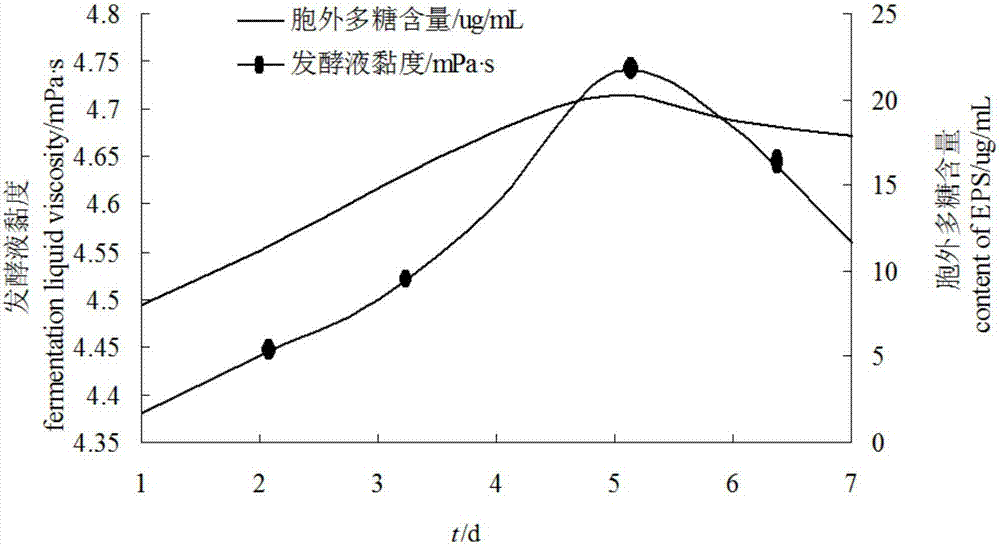
[0037] Relational model of embodiment 1 bacterial strain exopolysaccharide content and fermentation broth viscosity
[0038] (1) Strain screening and identification
[0039] Strains were screened using the high-fold dilution method.
[0040] Observation and identification of strain colony morphology: single colony was cultivated on PDA medium by single hyphae picking method, and the density, surface shape, size, color, texture, growth speed, edge shape, etc. of the aerial hyphae of the colony were recorded. Using insert culture method, observe the microscopic morphological characteristics and classify and identify the isolated fungi, and classify and identify according to the Ainsworth classification system, and identify the genus.
[0041] (2) Extraction, purification and identification of polysaccharides
[0042] Take the activated strain, put it into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 200ml of liquid fermentation medium, culture it with shaking at 28°C for 3 days, measur...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2 thin-layer chromatography (TLC) detects
[0046] (1) Strain screening and identification
[0047] Strains were screened using the high-fold dilution method.
[0048] Observation and identification of strain colony morphology: single colony was cultivated on PDA medium by single hyphae picking method, and the density, surface shape, size, color, texture, growth speed, edge shape, etc. of the aerial hyphae of the colony were recorded. Using insert culture method, observe the microscopic morphological characteristics and classify and identify the isolated fungi, and classify and identify according to the Ainsworth classification system, and identify the genus.
[0049] (2) Extraction, purification and identification of polysaccharides
[0050] Take the activated strain, put it into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 200ml of liquid fermentation medium, culture it with shaking at 28°C for 3 days, measure the viscosity with a NDJ-79 rotary viscometer, and use...
Embodiment 3
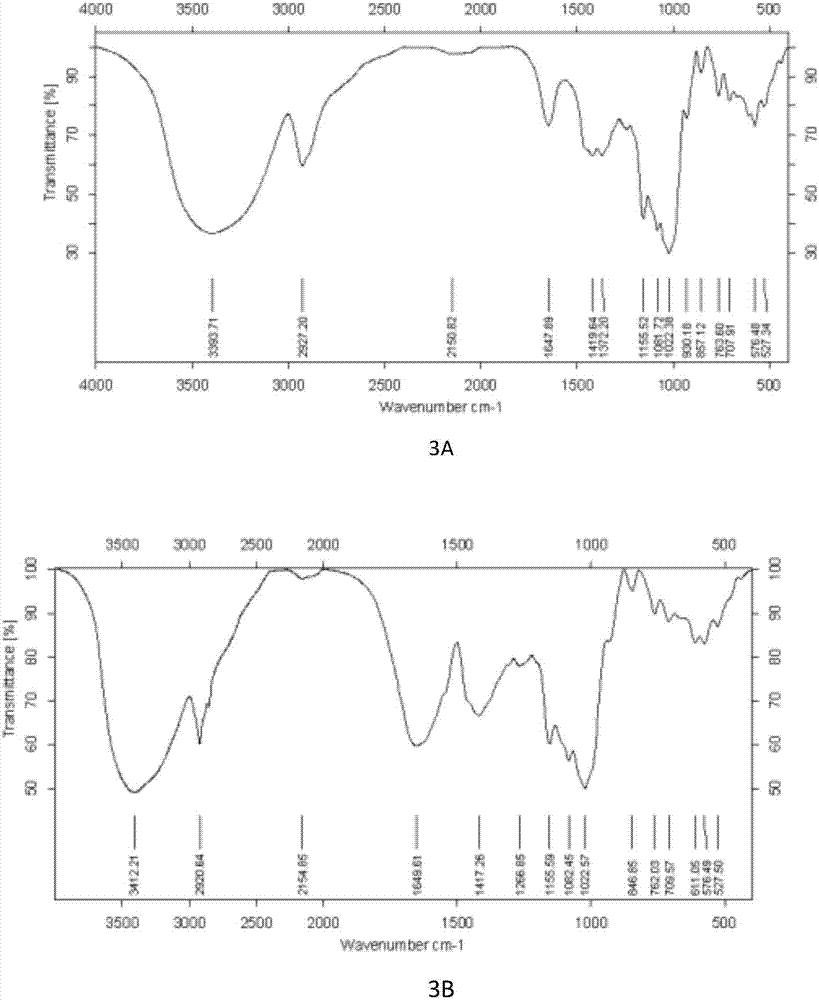
[0057] Infrared spectrum analysis of embodiment 3 exopolysaccharide
[0058] (1) Strain screening and identification
[0059] Strains were screened using the high-fold dilution method.
[0060] Observation and identification of strain colony morphology: single colony was cultivated on PDA medium by single hyphae picking method, and the density, surface shape, size, color, texture, growth speed, edge shape, etc. of the aerial hyphae of the colony were recorded. Using insert culture method, observe the microscopic morphological characteristics and classify and identify the isolated fungi, and classify and identify according to the Ainsworth classification system, and identify the genus.
[0061] (2) Extraction, purification and identification of polysaccharides
[0062] Take the activated strain, put it into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 200ml of liquid fermentation medium, culture it with shaking at 28°C for 3 days, measure the viscosity with a NDJ-79 rotary viscometer,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com