Colorectal cancer biomarker
A biomarker and colorectal cancer technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as genome instability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
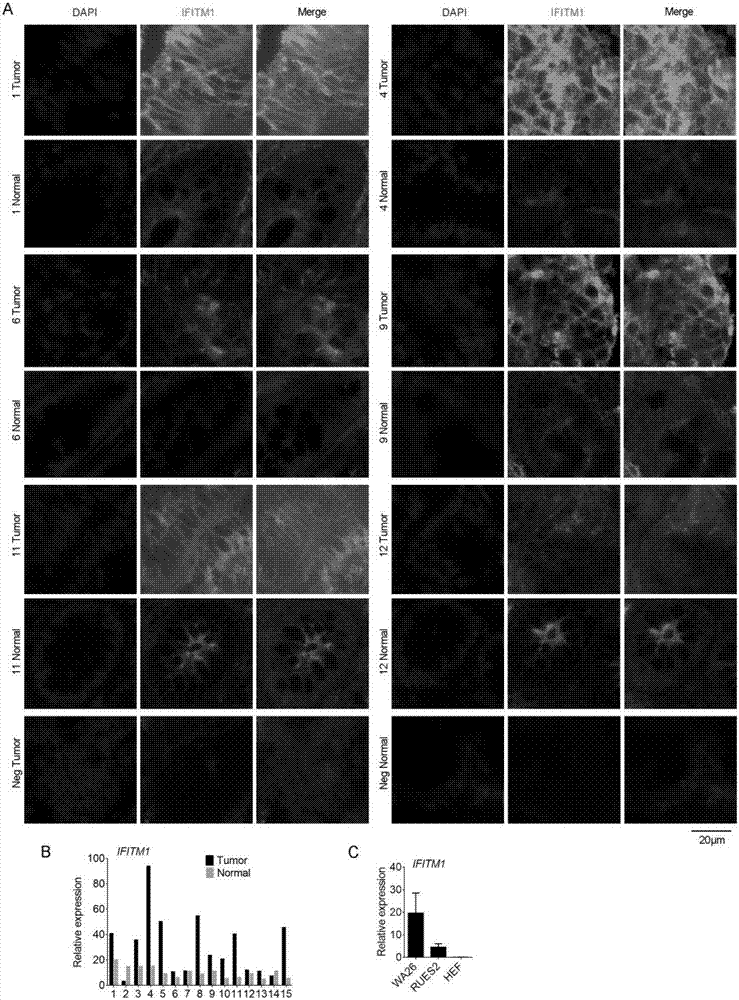
[0028] Detection of IFITM1 expression in colorectal cancer and hESCs ( figure 1 )
[0029] Materials and Methods:
[0030] 1. Randomly select patients with colorectal cancer, and take frozen tissue sections (including tumor and normal parts) from patients with colorectal cancer for immunofluorescence staining.
[0031] 2. Randomly select patients with colorectal cancer, extract RNA, and detect the mRNA level of IFITM1 by quantitative PCR; and take RNA from hESCs cell lines (WA26 and RUES2) to detect the expression level of IFITM1.
[0032]3. Results: The expression of IFITM1 in the tumor site of colorectal cancer was significantly higher than that in normal tissues, and its expression was high in hESCs cell lines (with HEF cells as the control).
Embodiment 2
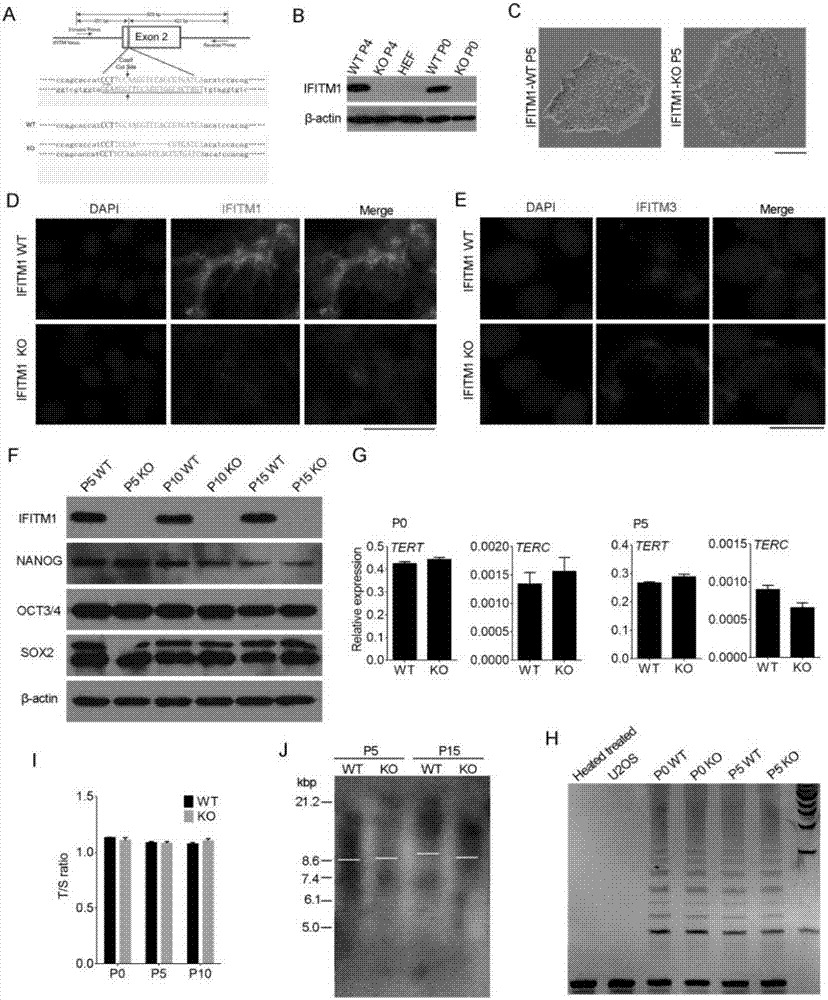
[0034] Using CRISPR / Cas9 technology to construct IFITM1 knockout hESCs cell line ( figure 2 )
[0035] 1. Cell culture: using Essential 8 (invitrogen) culture medium at 37°C, 5% CO 2 To culture hESCs cells under certain conditions, the medium needs to be changed every day.
[0036] 2. Plasmid construction: Design primers according to the CDS region sequence of the IFITM1 protein published by NCBI, and insert it into the px459 plasmid through amplification and ligation. After positive clone PCR identification, sequencing, and BLAST comparison, the results showed that px459-IFITM1 was successfully constructed .
[0037] 3. Cell transfection and identification: hESCs cell lines were stored in Essential 8 medium at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator. The plasmid is transferred into cells by nuclear transfer technology, and then the cells are cultured. IFITM1 knockout cells were obtained through drug screening and monoclonal cell selection, and then verified by sequencing...
Embodiment 3
[0039] To verify the effect of IFITM1 knockout on hESCs ( figure 2 ,3,4)
[0040] 1. There was no change in cell pluripotency after IFITM1 knockout was detected by western blot; telomerase was not changed after IFITM1 knockout was detected by quantitative PCR and TRAP experiments; detected by quantitative PCR (T / S ratio) There was no change in cellular telomere length.
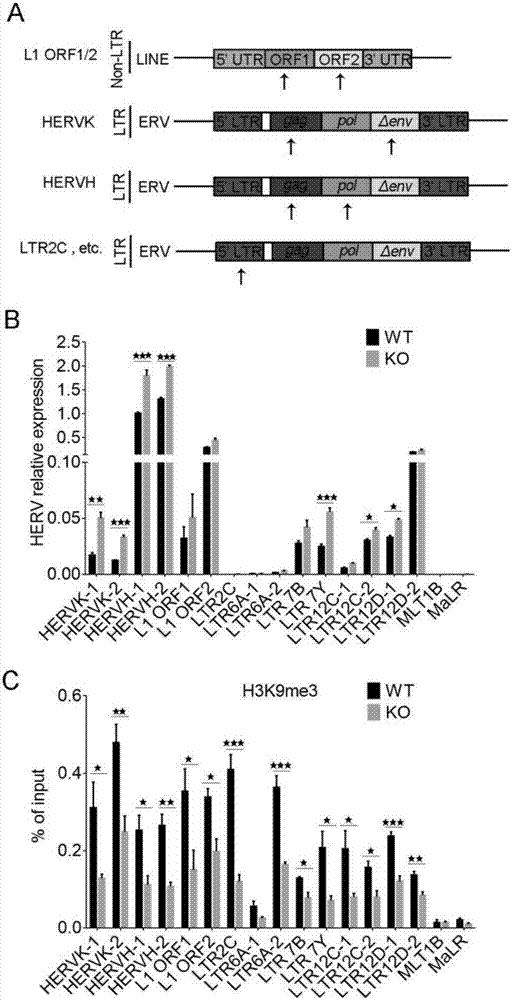
[0041] 2. Through PCR experiments, we detected that after IFITM1 was knocked out, the cells were harvested to extract RNA, and the detection showed that HERVs in the cells increased. The primers used for detection are as follows:
[0042]
[0043]
[0044] 3. Through ChIP-qPCR experiments (using 2 primers), we found that after IFITM1 was knocked out, the enrichment of H3K9me3 at HERVs sites decreased, because H3K9me3 can inhibit the expression of HERVs, thus leading to an increase in the expression of HERVs.
[0045] 4. Collect the cells of the same generation in 3 for immunofluorescence (5mC and 5hm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com