Preparation and application of kapok fiber-based elastic foam material
A kapok fiber and elastic foam technology, applied in the fields of alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, inorganic chemistry, alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of complex preparation process requirements, weak organic solvent adsorption capacity, and inability to reuse again , to achieve significant adsorption effect, low price, and excellent superhydrophobic ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
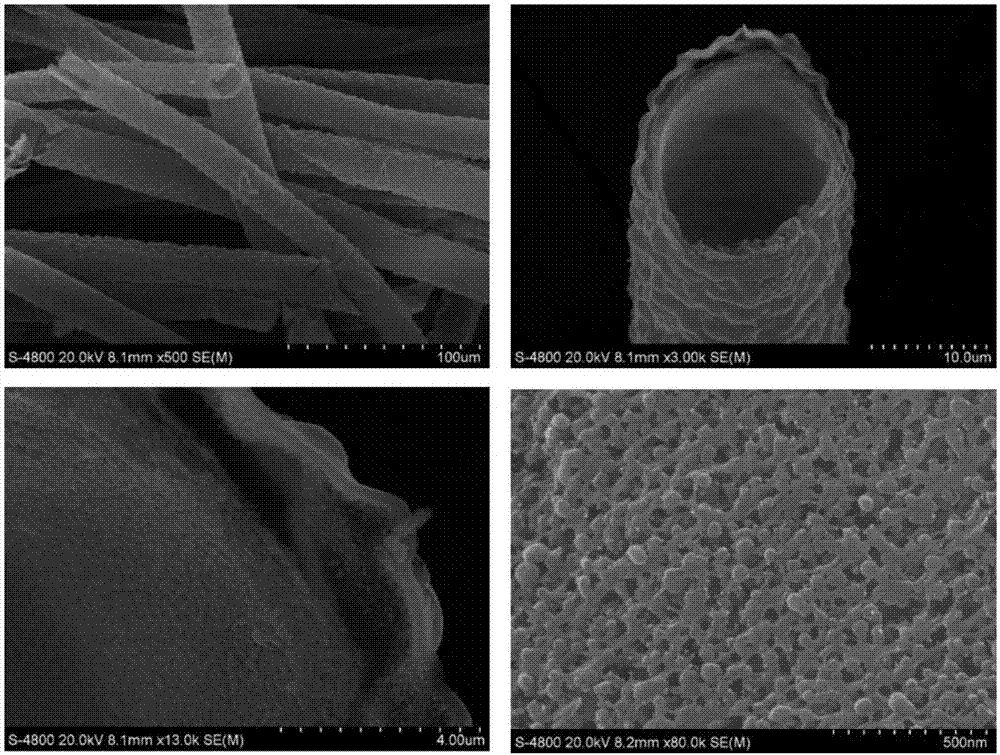
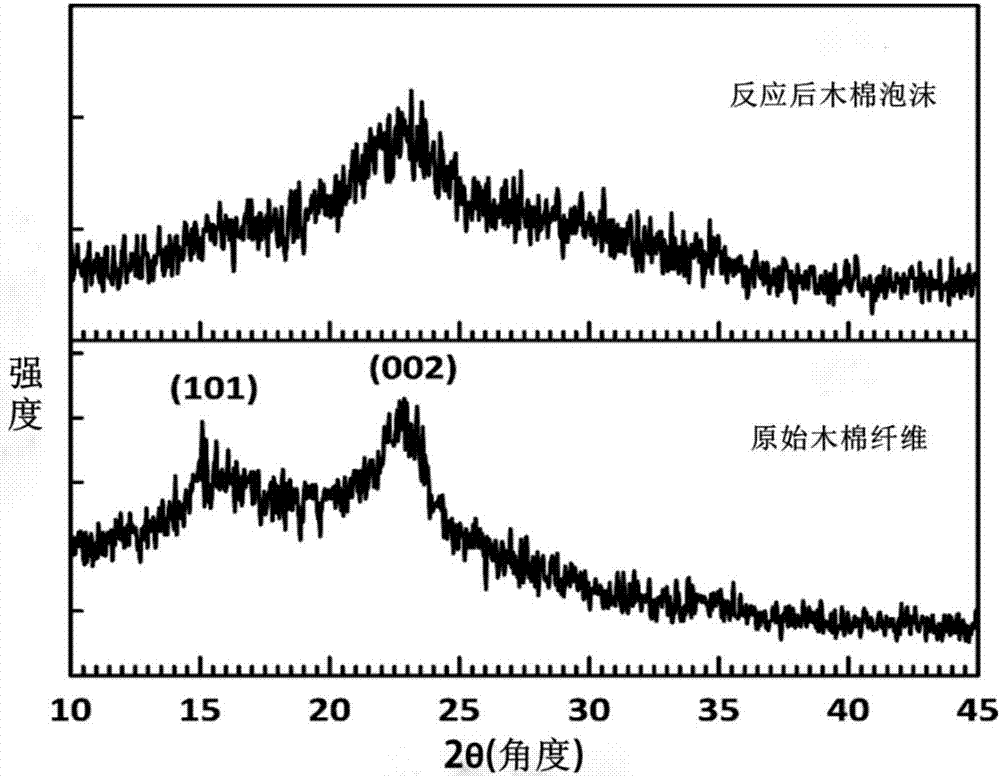
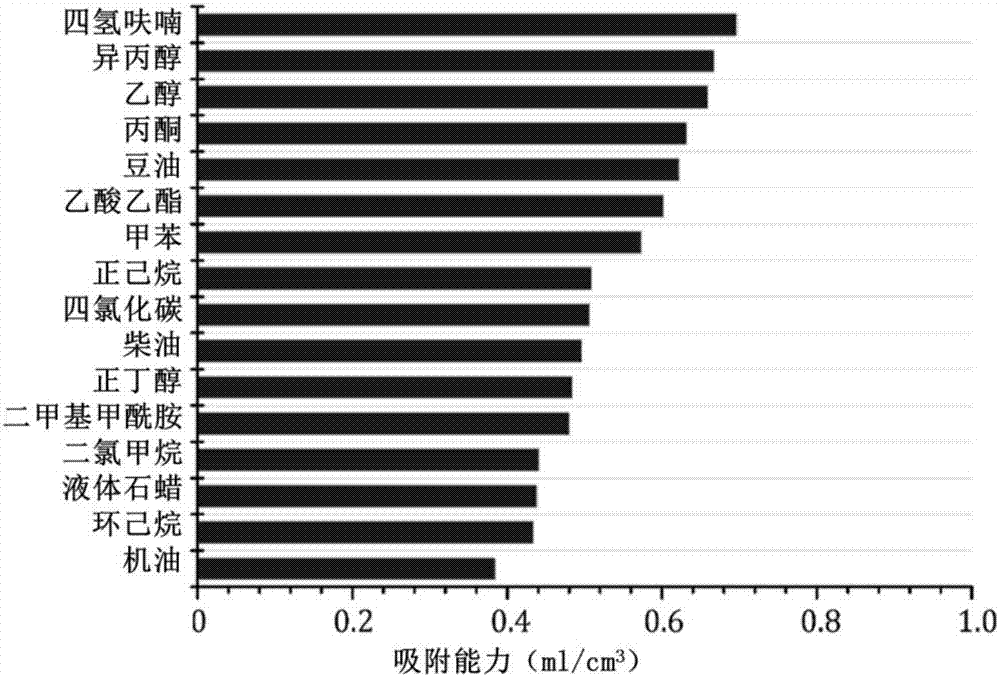
[0032] Weigh 0.8 g of kapok fiber and place it in a 25 ml polytetrafluoroethylene lined reactor, and add a 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution to soak for 12 hours. Then react at a constant temperature of 180°C for 24 hours, and the reaction product is first immersed in deionized water and then in absolute ethanol, rinsed, and dried naturally to obtain a cylindrical elastic foam with a diameter of 2 cm and a height of 2.5 cm.
Embodiment 2
[0034] This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that the reaction temperature in the step is 220°C. Others are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0036] This embodiment is different from embodiment 1 in that the concentration of glutaraldehyde in the steps is 4%. Others are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com