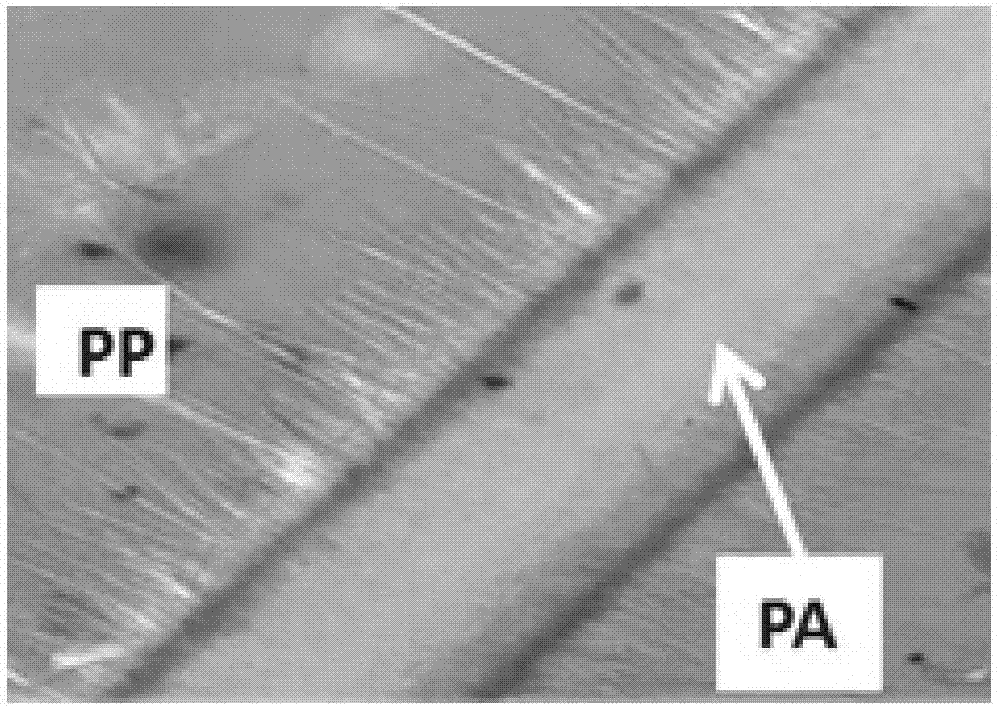
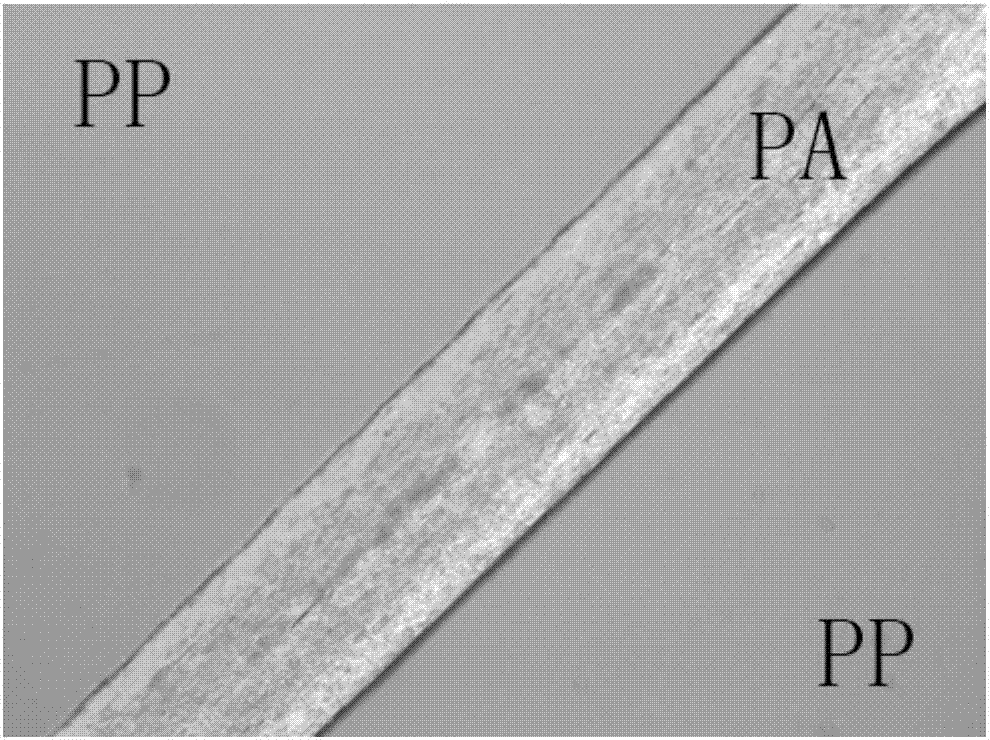
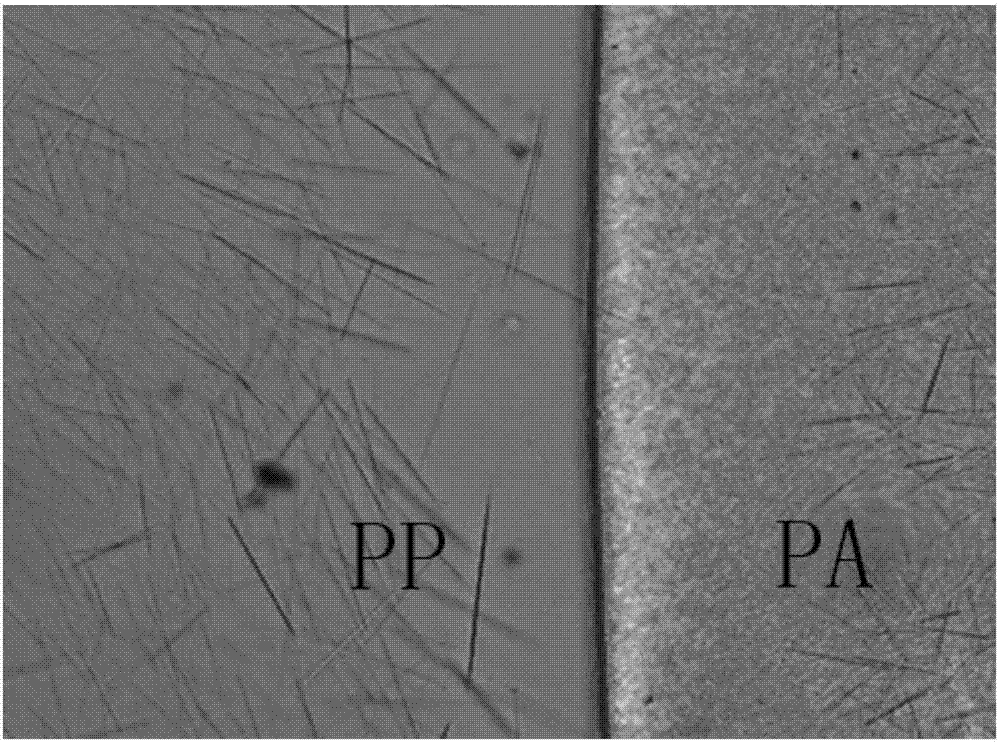
Preparation method of interface interlocked polyphase polypropylene-based polymer blending composite material
A technology of heterogeneous polypropylene and polymer materials, which is applied in melt spinning, textile and papermaking, and filament forming treatment to achieve the effects of improving mechanical strength, interfacial compatibility, and interfacial properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The raw materials in this example are aromatic beta nucleating agent (TMB-5), homopolypropylene (T30S) and nylon 66 (PA66), the mass ratio of which is 0.1:95:5.
[0034] First, TMB-5 and nylon 66 are melted and pre-mixed and extruded at 270 °C, and then the pre-mixed material is mixed with homopolypropylene and put into a screw extruder through a controlled multi-phase melt blending extrusion process. (The temperature of the melting section of the extruder is 270 °C), the self-assembly temperature of the second stage (ie the die section) is 180 °C, and the extrusion speed is 100 r / min. The prepared homopolymer polypropylene / nylon 66 composite material not only has The interface interlocking structure, and because TMB-5 can self-assemble at the interface of homopolypropylene and nylon 66 to form an interlocking structure with an incompatible interface, the mechanical properties test results show that the interface interlocking structure makes the composite material Compa...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The raw materials in this example are sorbitol alpha nucleating agent (DBS), block copolymerized polypropylene (EPS30R) and polylactic acid (PLA), and the mass ratio is 0.5:60:40.
[0037] First, melt premix and extrude DBS and polylactic acid at 190 °C, then mix the premix with block copolymerized polypropylene and put it into the injection molding machine. The temperature of the second stage is 230 °C), the self-assembly temperature of the second stage (ie the die section) is 170 °C, and the injection speed is 80 r / min. The prepared block copolymer polypropylene / polylactic acid blend composite material not only has interface interlocking structure, and because DBS can self-assemble at the interface of block copolymerized polypropylene and polylactic acid to form an interlocking structure of an incompatible interface, the mechanical property test results show that the interlocking structure of the interface increases the tensile strength of the composite material. and ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The raw materials in this example are rare earth beta nucleating agent (WBG-II), random copolymerized polypropylene (R200P) and polyethylene terephthalate (FR515), the mass ratio of which is 1:90:10.
[0040] First melt premix and extrude WBG-II and polyethylene terephthalate at 260°C, then mix the premix with the random copolymer and put it into a vulcanizer through a controlled multiphase melt blending The molding process (the temperature of the vulcanizer is 260°C and the pressure is maintained for 5mins) is moved into the second stage (ie, another vulcanizer), and the self-assembly temperature of the other vulcanizer is set to 160°C and the pressure is maintained for 5mins. The prepared random copolymer polypropylene / polyethylene terephthalate blend composite not only has an interfacial interlocking structure, but also because WBG-II can be used at the interface between random copolymer polypropylene and polyethylene terephthalate. The interlocking structure of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com