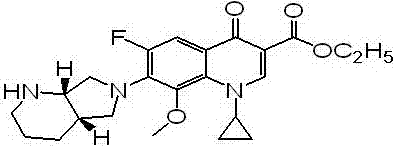
Moxifloxacin analogue as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of analogues and products, applied in the field of moxifloxacin analogues and their preparation and use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Preparation of moxifloxacin analogue Y.
[0026] Add 2.00g of moxifloxacin, 20.00ml of dichloromethane, 0.61g of triethylamine to a 100ml flask, (Boc) 2 O1.31g, stirred at room temperature for 3h, distilled off the solvent, and purified by column chromatography; the product was dissolved in 20ml of fresh dichloromethane, and 1 drop of DMF was added dropwise into SOCl 2 0.5ml, reflux reaction for 1h, spin dry the solvent; dissolve the residue with 15ml fresh dichloromethane, slowly drop the solution into a solution of 5ml dichloromethane+2ml absolute ethanol, reflux reaction for 1h, spin dry the solvent; The residue was added to 10ml of a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid: dichloromethane = 1:1, reacted at room temperature for 2 hours, separated by column chromatography, and the target product moxifloxacin analog Y was collected to obtain 0.89g.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2 Preparation of moxifloxacin analogue Y.
[0028] Add moxifloxacin 2.00g, dichloromethane 20.00ml, triethylamine 0.70g, (Boc) to a 100ml flask 2 O1.31g, stirred at room temperature for 5h, evaporated the solvent under reduced pressure; dissolved the residue with 20ml of fresh dichloromethane, added 2 drops of DMF, the temperature dropped to 0°C, slowly added 1.00g of oxalyl chloride dropwise, and the dropwise To room temperature, stirred for 3h. The solvent was spin-dried under reduced pressure; the residue was dissolved with 15ml of fresh dichloromethane, the solution was slowly dropped into a solution of 5ml dichloromethane+2ml absolute ethanol, the reaction was refluxed for 1h, and the solvent was spin-dried; the residue was added to Add 2ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid dropwise to 10ml of methanol, heat up to 70°C for 4 hours, cool and filter, refine the wet product with 4ml of ethanol, filter for crystallization, and dry to obtain 0.71g of moxifloxac...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3 HPLC separation of moxifloxacin analogues and moxifloxacin.
[0030] Chromatographic conditions.
[0031] project parameter project parameter chromatography Shimadzu HPLC chromatography system, LC-2010AHT, equipped with Class-VP workstation Column model Phenyl column, 250×4.6mm, 5μm flow rate 1.3ml / min pre-column Phenyl column Detection wavelength 293nm Column temperature 45℃ mobile phase Aqueous solution (0.5g / L tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate, 1.0g / L potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 3.4g / L phosphoric acid)-methanol (72:28) Solvent A Aqueous solution of 0.5g / L tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate, 1.0g / L potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.050g / L anhydrous sodium sulfite, 2ml / L phosphoric acid
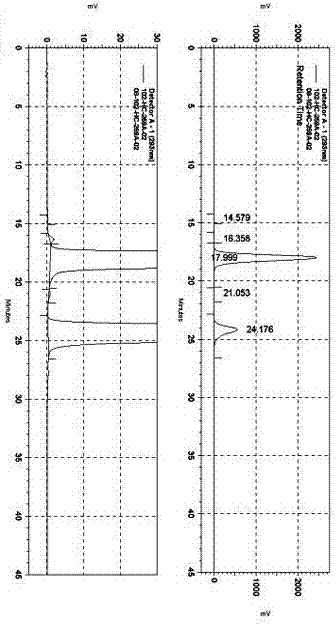
[0032] Use solvent A to prepare samples of the test solution containing about 1 mg of moxifloxacin hydrochloride and 0.3 mg of moxifloxacin analogue Y per 1 ml, as attached figure 1 , the retention time of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com