Application of heat-sensitive materials in the preparation of injections for protecting the surrounding structures of organs during thermal ablation
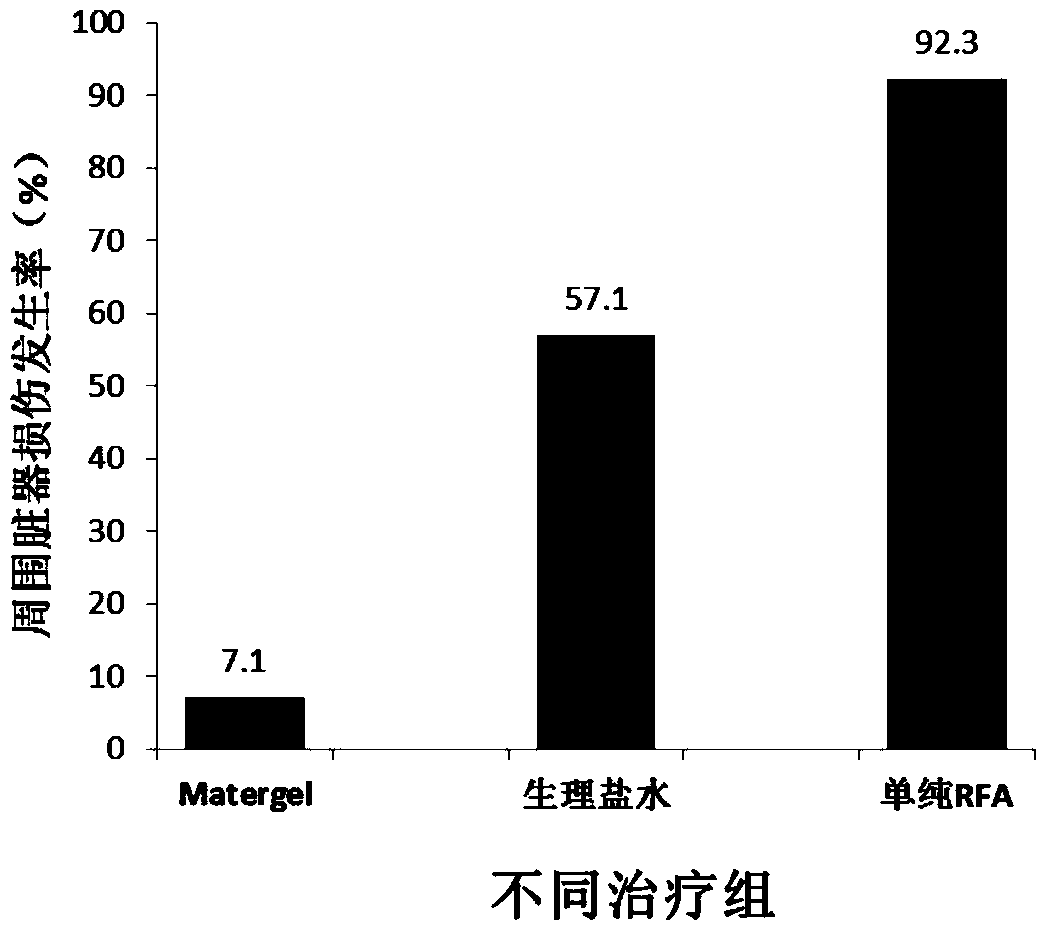
A heat-sensitive material and thermal ablation technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of easy tearing of perihepatic structures, human injury, bleeding or tearing of the intestinal wall.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] The heat-sensitive injection uses Matrigel basement membrane matrix (BD Company, USA), which was previously used in cell culture experiments. Its main components are composed of laminin, type IV collagen, nestin, heparan sulfate glycoprotein, etc., and also contain a temperature-sensitive hydrogel. Matrigel gels quickly at a temperature of 22-35°C, so it should be frozen and thawed overnight on ice at 0-4°C when dissolving (it will partially gel as the temperature rises above 4°C). All supplies should be placed in an ice bath prior to use, and Matrigel must be administered with a pre-cooled syringe or catheter. BD Matrigel basement membrane matrix can form a semi-solid gel within 1min at 37°C, and polymerize to form a three-dimensional matrix with biological activity, which simulates the structure, composition, physical properties and functions of cell basement membranes in vivo, which is beneficial to the growth of cells in vitro Culture and differentiation, and studi...
Embodiment 2
[0078] The heat-sensitive injection uses a temperature-sensitive poloxamer aqueous solution, of which 15.4% is poloxamer P407. This polymer hydrogel is a mixed system of a three-dimensional space cross-linked network composed of polymers and water. The traditional Used in non-ionic surfactants, in recent years, it has been widely used in the fields of drug control release. This hydrogel is in a low-viscosity liquid state at 14-20°C (room temperature), and turns into a gel at 34-37°C (close to body temperature), with the highest viscosity at 40°C. We put the aqueous solution of poloxamer produced by Sigma company at room temperature to maintain a liquid state.
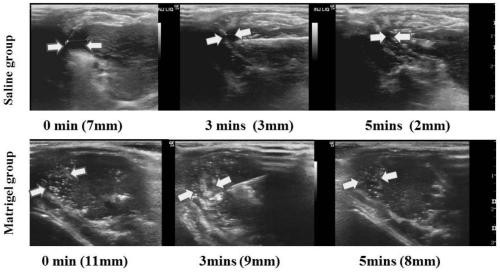
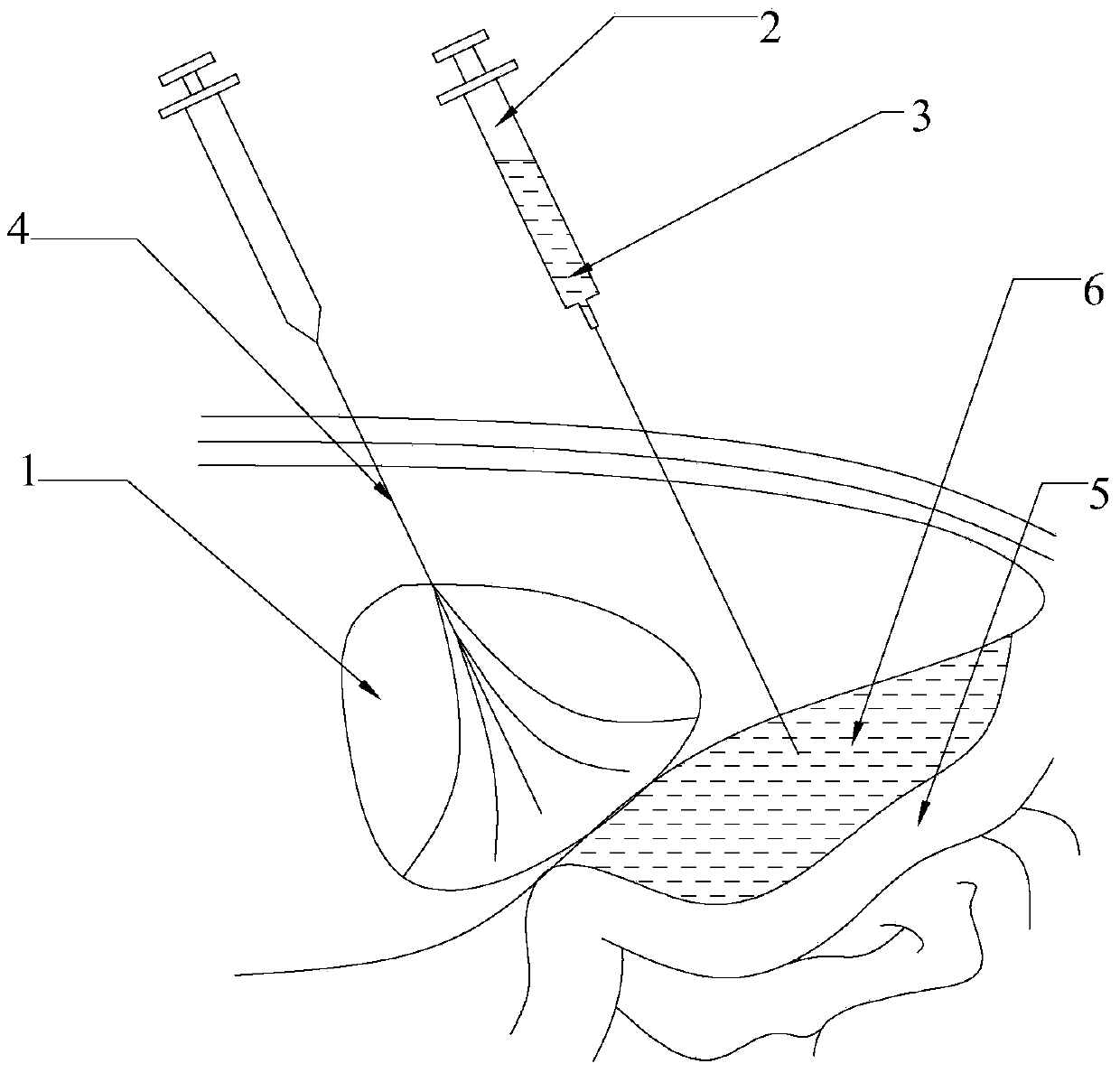
[0079] Using the Sprague Dawley rat experiment, radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors adjacent to the diaphragm, ultrasound-guided injection of an appropriate amount (10ml) of poloxamer aqueous solution in the gap between the liver ablation area and the diaphragm before treatment to form a 5-10mm thick isolation zone ....
Embodiment 3
[0081] The temperature-sensitive injection uses a temperature-sensitive temperature-sensitive nano-polyhydrogel (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylamide) (referred to as temperature-sensitive nanogel) (Institute of Materia Medica, School of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology development). This is a smart nanomaterial that can produce structural and performance changes in response to small changes in temperature. It is currently used in the field of vascular embolization. Studies have shown that temperature-sensitive nanogels have low sol viscosity and high gel strength, and have rapid temperature response and significant thixotropy. At a normal temperature of about 20°C, the temperature-sensitive nanogel is in a liquid state with good fluidity. When the temperature rises to 34-37°C, it will completely lose its fluidity within 12 seconds and become a gel state.
[0082] Using the Sprague Dawley SD rat experiment, radiofrequency ablation of l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com