Interference sample eliminating method based on generalized inner-product arbitrary array
A generalized inner product and arbitrary array technology, applied in the field of space-time two-dimensional adaptive processing, can solve the problems of large amount of calculation, performance degradation of interference and pollution sample selection, and degradation of STAP target detection performance, etc., and achieve the effect of small calculation amount
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
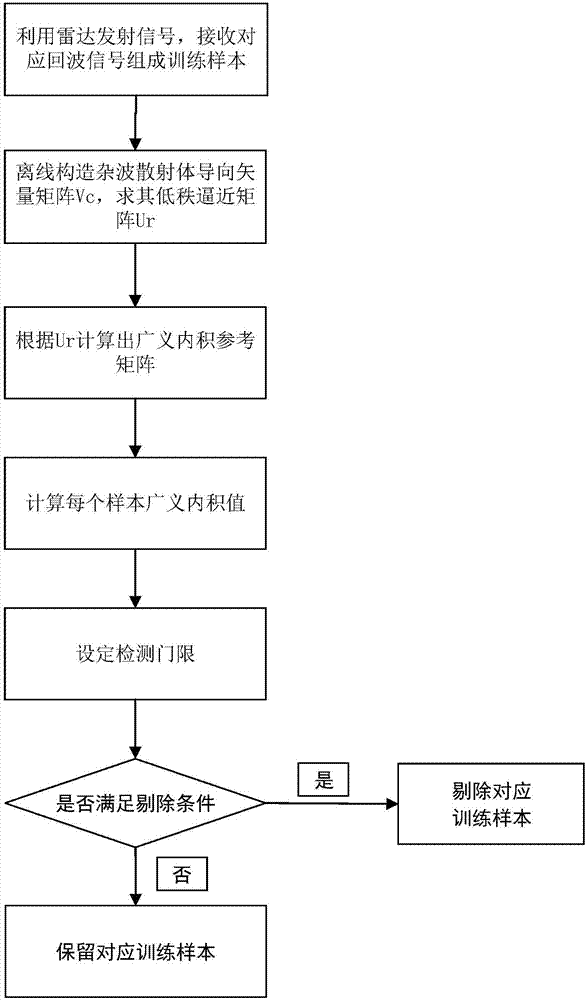
[0028] The present invention is a method for eliminating interference samples based on generalized inner product arbitrary arrays, and can also be said to be an improved space-time two-dimensional adaptive processing method based on generalized inner product, see figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0029] Step 1, get training samples: use the radar to transmit signals and receive the corresponding radar echo data; in the received radar echo data, select multiple distance units at the left and right ends of the distance unit where the target to be detected is located, that is, in There are a total of L distance units selected at the left and right ends of the distance unit where the target to be detected is located; the echo data of the selected L distance units are used as the corresponding L training samples, and the i-th training sample is expressed as X i , i ranges from 1 to L.
[0030] Step 2, Offline composition of the low-rank approximation matrix U of the clut...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The interference sample elimination method based on the generalized inner product arbitrary array is the same as that in embodiment 1, wherein in step 2, the low-rank approximation matrix U of the clutter subspace is formed off-line r The specific steps include:
[0038] (2.1) Divide each training sample evenly into N according to the orientation c sample blocks, N c is a natural number greater than 1, and the clutter scatterer steering vector matrix V c ; These two vectors, clutter airspace steering vector and clutter time domain steering vector, are only related to system parameters such as antenna element position, beam pointing angle, and flight speed, and have nothing to do with the received training sample data. A single scatterer corresponds to two steering vectors.
[0039] The time-domain steering vector V corresponding to the i-th clutter scatterer is constructed offline t and the original airspace steering vector S s , respectively:
[0040]
[0041]...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The interference sample elimination method based on the generalized inner product arbitrary array is the same as that in Embodiment 1-2, and in step 3, the inverse matrix of the target scatterer clutter noise covariance matrix is calculated offline According to the following formula:
[0060]
[0061] In the formula, [] H Represents the conjugate transpose of the matrix, and I is the identity matrix of order r.
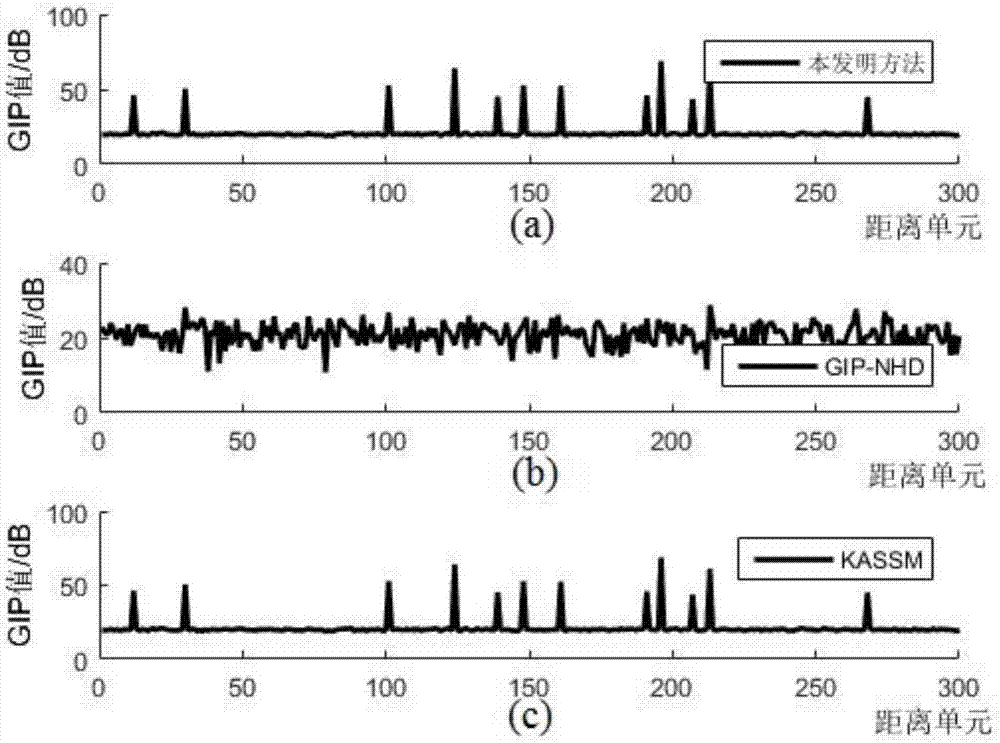
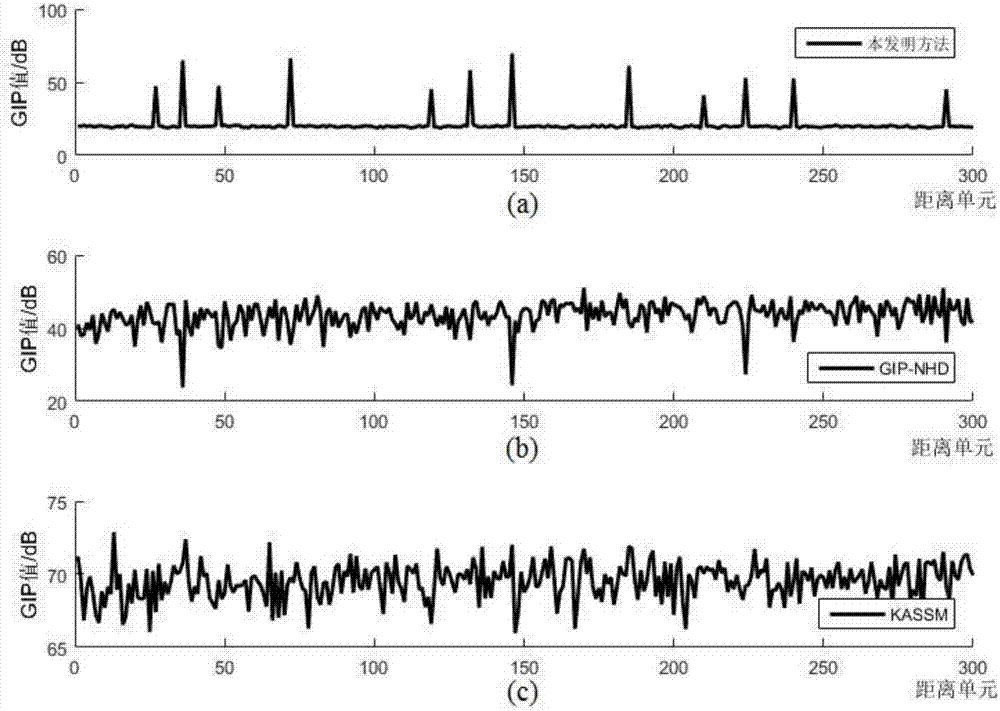
[0062] u r is the vector matrix V of the scatterer clutter c The eigenvectors corresponding to all non-zero eigenvalues of , most of the clutter signal energy has been constrained, so the low-rank approximation matrix U of the space-time steering vector matrix of clutter scatterers r It can approximate the characteristics of the real clutter subspace, and can approximate the inverse matrix of the covariance matrix without directly inverting the space-time clutter steering vector matrix The calculation amount of the present invention is greatly redu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com