Spinal muscular atrophy related gene copy number detecting kit and method based on gene trapping and second-generation sequencing technique
A next-generation sequencing technology, a technology for spinal muscular atrophy, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of uneven sequencing depth, poor stability, and high error rate, achieve high throughput, improve detection sensitivity, and good robustness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1 Sequencing of samples (obtaining sequence information of polynucleotide fragments from samples)
[0063] Samples are sequenced through the following steps:
[0064] 1) DNA extraction and fragmentation. The sample used can be either blood or saliva. DNA is extracted and purified, and the extracted DNA is interrupted by ultrasonic waves, the ends are filled and phosphorylated, and adapters are added on both sides.
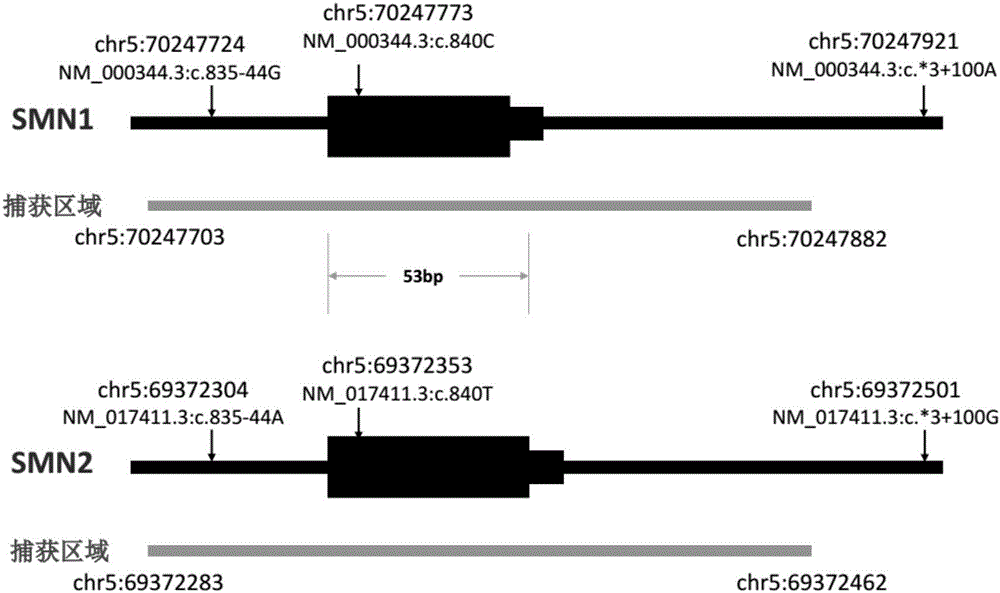
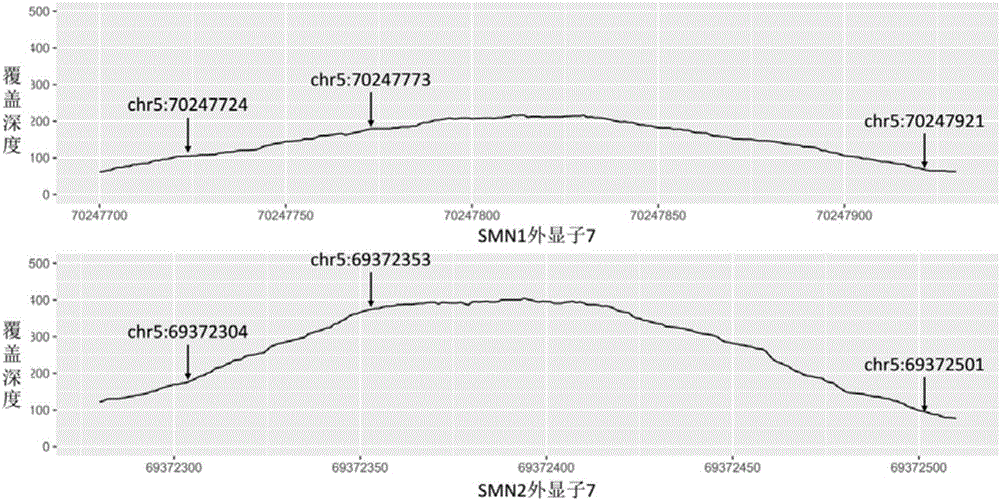
[0065] 2) Target area capture. In this method, a specially designed capture probe is used to capture the target region, magnetic beads are separated and enriched, PCR is amplified, and a sequencing library is constructed. Here, the target region includes the exons of SMN1 / 2 and some other genes and bases within a certain range upstream and downstream. Wherein, the target capture region and the corresponding probe sequence of SMN1 / 2 exon 7 are as described in Table 1, figure 1 The exon 7 of the SMN1 gene and the SMN2 gene and the three different ...
Embodiment 2
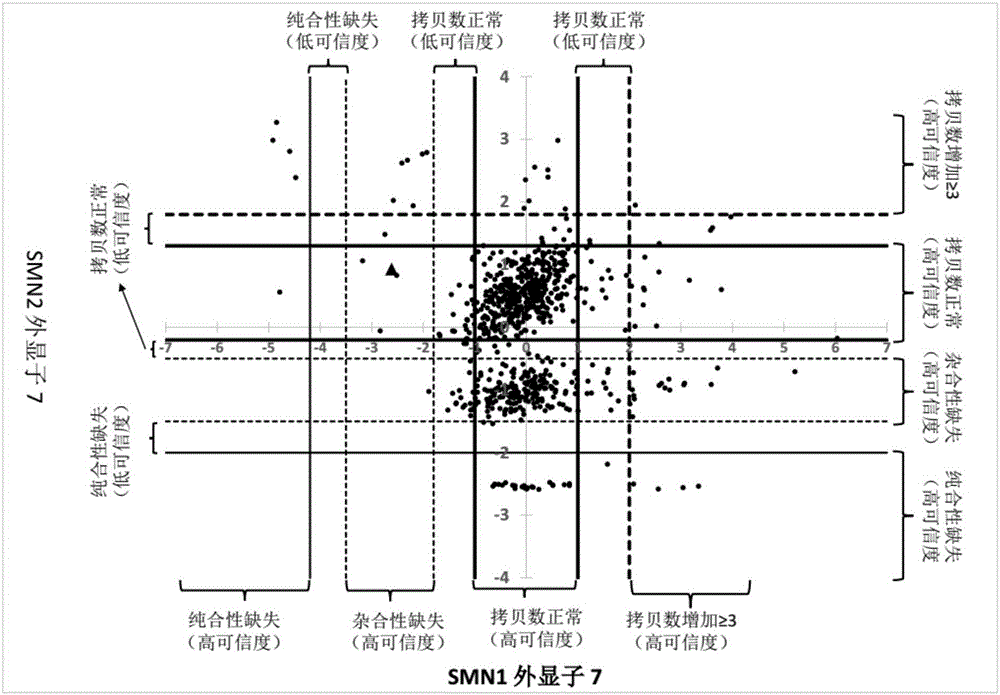
[0076] Example 2 Estimating the copy number of genes related to spinal muscular atrophy through data analysis.
[0077] The data analysis of the present invention involves the following steps:
[0078] Step A, aligning the sequencing reads (reads) to the human reference genome (hg19) using alignment software (BWA software, version: 0.7.12).
[0079] Step B, removing repetitive sequences. Use Picard (a basic sequence processing tool, version 2.8) to remove repetitive sequences (PCR duplicate reads) generated during PCR amplification.
[0080] Step C, removing reads whose alignment results are not credible. Here, the unreliable alignment result means that because SMN1 and SMN2 are highly homologous, although the alignment software assigns a read to exon 7 of one of the genes, in fact the read can be assigned to SMN1 , can also be assigned to SMN2. For the reads assigned to SMN1 / 2 exon 7, the present invention eliminated those reads that did not cover any of the sites describ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com