Method for micropropagation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
A technology of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and inoculum amount, which is applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, planting substrates, etc., can solve the problems of high technical difficulty and high atomization cost, and achieves high mycorrhizal infection rate and operation. Simple and efficient multiplication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Mix zeolite, pumice, vermiculite and peat with a particle size of less than 2.5mm at a volume ratio of 12:3:3:1. After mixing, sterilize with high-temperature hot water (100°C) and keep warm at 60°C for 3 hours; spread clean water on the ground and set up an insect-proof net, place a perforated pot with a height of 80 cm and a diameter of 50 cm on the ground, and then place the sterilized matrix in the pot.
[0042]Inoculate Glomus intraradices in the matrix and mix evenly, the inoculation amount is 5% of the mass of the matrix; in the early spring season, the matrix is watered thoroughly, and corn, marigold and clover are sown successively in the matrix after inoculation; the density of the sowing 12 pieces / m 3 ; Cover a layer of white film on the top of the pot, and remove the film after emergence. After 1 week, remove the weak plants, leave 10 plants in the tank, and then apply 0.25 mg / m to the root zone 3 of spermidine. After 5 months of multiplication, remove ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The results of the G.i mycorrhizal mycorrhizal agents inoculated on different substrates were compared, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0051] Two kinds of cultivation substrates were used in the test: substrate 1 was mixed with zeolite, pumice, vermiculite and peat (particle size less than 2.5) in a volume ratio of 12:3:3:1, and substrate 2 was zeolite, vermiculite and peat (particle size was less than 2.5 ) were mixed at a volume ratio of 12:3:1 to inoculate arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in different cultivation substrates by means of multiplication, compare their infection rates, and obtain arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculants with good infection rates.
[0052] Table 1 Root infection rate of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus propagation
[0053]
[0054] It can be seen from Table 1 that the mycorrhizal rate of the bacterial agent propagated by substrate 1 is significantly higher than that of substrate 2, so zeolite, pumice, vermiculite and peat (particle s...
experiment example 3
[0056] Effects of Polyamines on Mycorrhizal Infection Rate and Root Vitality
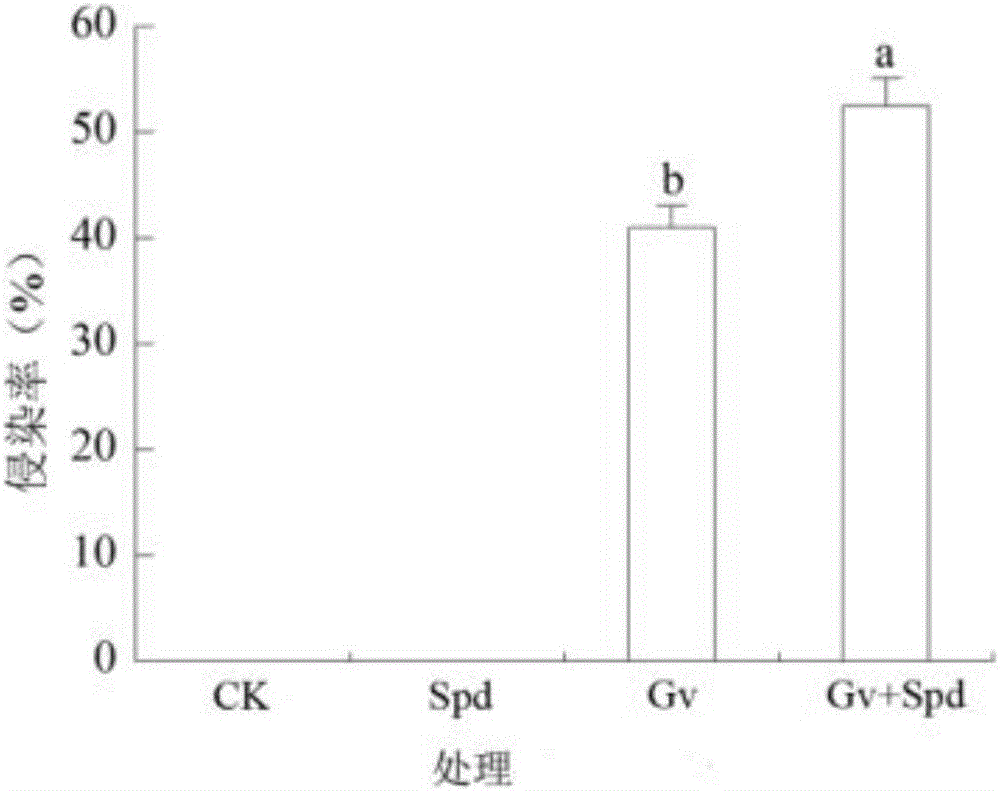
[0057] figure 1 It is a graph showing the effect of exogenous polyamines on AMF and root vigor of host plants, figure 2 It is the result graph of the effect of exogenous polyamines on the infection rate of AMF roots. As shown in the figure, adding AMF and Spd to the mixed matrix significantly increased the root activity of the host plant; adding Spd and AMF to the mixed matrix at the same time, compared with Gv, the root activity and infection rate of the host plant increased significantly . The above results indicated that Spd and AMF could increase the root activity of host plants, and Spd could significantly increase the mycorrhizal infection rate of AMF, thereby promoting the proliferation of the strain.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com