Preparation method for heat-resistant microcrystalline glass capable of being molten at low temperature
A glass-ceramic and melting technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of heat-resistant glass-ceramics, can solve the problems of high melting temperature, short material properties, and high viscosity of glass liquid, and achieves strong practicability and efficiency. The effect of popularization, low production cost and resource saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
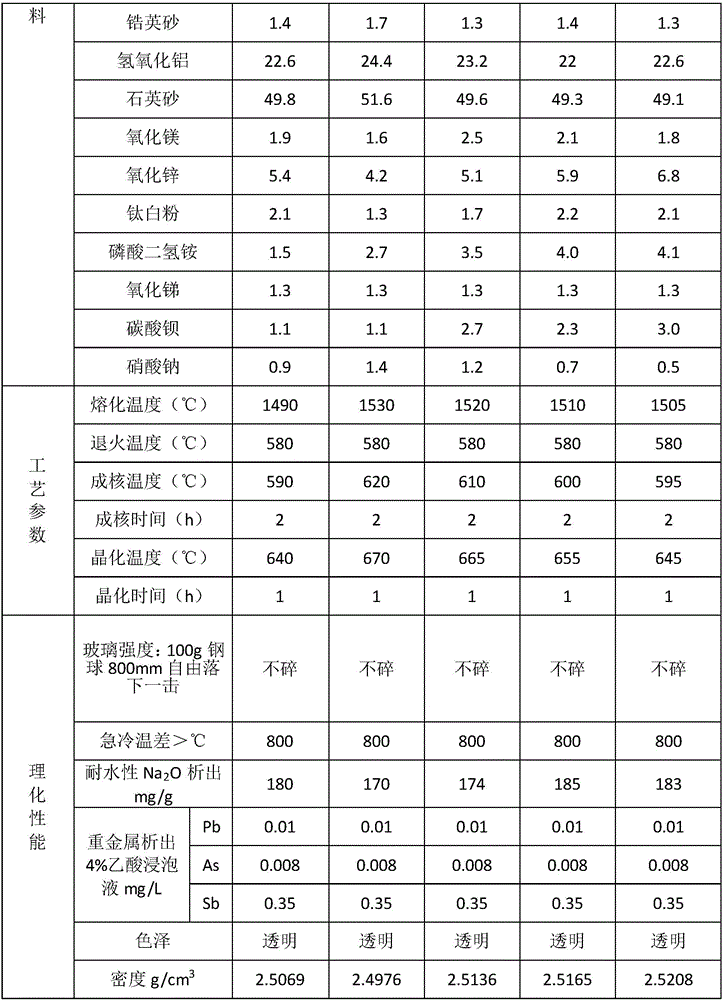
[0024] Take 8.4 parts of lithium carbonate, 22.6 parts of aluminum hydroxide, 49.8 parts of quartz sand, 1.9 parts of magnesium oxide, 5.4 parts of zinc oxide, 2.1 parts of titanium dioxide, 1.5 parts of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.3 parts of antimony oxide, 1.1 parts of barium carbonate, nitric acid 0.9 parts of sodium, 1.4 parts of zircon sand. Melting: Mix the above-mentioned raw materials with a uniformity of more than 95%, put the mixed ingredients into a corundum crucible, and then melt them in a silicon-molybdenum furnace. The melting temperature is 1490°C and the melting time is 4 hours; forming : Pour the melted and clarified glass liquid on a stainless steel plate, spread it into a glass plate with a thickness of 5mm, and quench the rest into pieces with distilled water; annealing: put the glass plate into a muffle furnace at a temperature of 580°C for degradation Stress relief; after that, conduct DTA analysis of the glass to determine the nucleation temperatur...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Take 8.8 parts of lithium carbonate, 24.4 parts of aluminum hydroxide, 51.6 parts of quartz sand, 1.6 parts of magnesium oxide, 4.2 parts of zinc oxide, 1.3 parts of titanium dioxide, 2.7 parts of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.3 parts of antimony oxide, 1.1 parts of barium carbonate, nitric acid Sodium 1.4 parts, zircon sand 1.7 parts. Melting: Mix the above-mentioned raw materials with a uniformity of more than 95%, put the mixed ingredients into a corundum crucible, and then melt them in a silicon-molybdenum furnace. The melting temperature is 1530°C and the melting time is 6 hours; molding : Pour the melted and clarified glass liquid on a stainless steel plate, spread it into a glass plate with a thickness of 5mm, and quench the rest into pieces with distilled water; annealing: put the glass plate into a muffle furnace at a temperature of 580°C for degradation Stress relief; after that, conduct DTA analysis of the glass to determine the nucleation temperature and ...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Take 8.2 parts of lithium carbonate, 23.2 parts of aluminum hydroxide, 49.6 parts of quartz sand, 2.5 parts of magnesium oxide, 5.1 parts of zinc oxide, 1.7 parts of titanium dioxide, 3.5 parts of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.3 parts of antimony oxide, 2.7 parts of barium carbonate, nitric acid Sodium 1.2 parts, zircon sand 1.3 parts. Melting: Mix the above-mentioned raw materials with a uniformity of more than 95%, put the mixed ingredients into a corundum crucible, and then melt them in a silicon-molybdenum furnace. The melting temperature is 1520°C and the melting time is 5 hours; molding : Pour the melted and clarified glass liquid on a stainless steel plate, spread it into a glass plate with a thickness of 5mm, and quench the rest into pieces with distilled water; annealing: put the glass plate into a muffle furnace at a temperature of 580°C for degradation Stress relief; after that, conduct DTA analysis of the glass to determine the nucleation temperature and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com