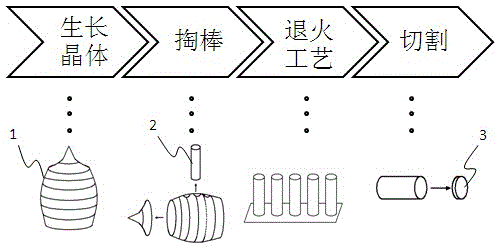
Method for producing crystal bars
A production method and a technology for crystal rods, which are applied in chemical instruments and methods, single crystal growth, single crystal growth and other directions, can solve the problems of unable to achieve ideal results, unable to meet wafer consistency requirements, poor annealing effect, etc. Conducive to popularization and application, high internal stress consistency, and the effect of eliminating residual stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] see figure 1 Shown, a kind of manufacture method that is used for sapphire ingot of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
[0036] Step 1: In this embodiment, Kyropoulos Method, heat exchange method (HEM method), guided mode method (EFG) and other methods can be used for crystal growth. During the crystal growth process, due to the control of the growth rate, the change of the temperature gradient in the chamber needs to be strictly controlled, and as the volume of the crystal increases, the change of the internal temperature field becomes more complicated.
[0037] This embodiment is preferably the Kyropoulos method, which is divided into stages such as seeding, shouldering, growth, and cooling. The growth temperature and heat flow field changes in each stage are different, and the internal residual stress is also different; especially different In order to reduce the cost of the crystal 1, the growth cycle is shortened, as long as the crys...
Embodiment 2
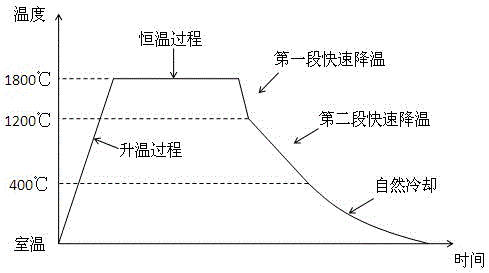
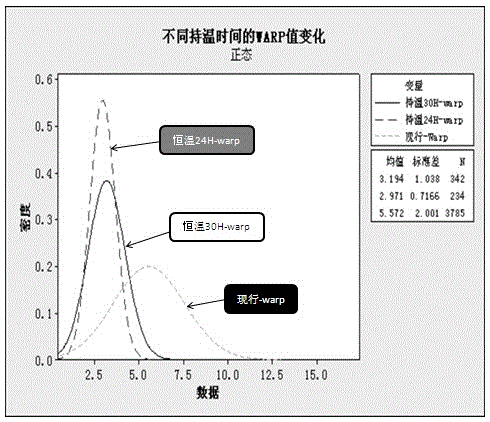
[0047] The present invention also provides a manufacturing method for silicon carbide crystal 1 to produce wafer 3, which solves the warping problem of silicon carbide wafer 3. Step 1, grows silicon carbide crystal 1, does not limit the growth process of silicon carbide crystal 1, in silicon carbide After the crystal 1 is drawn into a crystal rod, the silicon carbide crystal rod 2 is annealed, because silicon carbide will decompose at about 1850°C, so compared with Example 1, the highest temperature during the heating process of the silicon carbide crystal rod 2 is Set to 1700°C~1800°C. Maintain a uniform heating rate during the heating process, and the heating rate is 50 ° C ~ 200 ° C. After reaching the highest temperature, it enters the constant temperature process, and the constant temperature process time is 3h~32h. After the constant temperature process is over, rapid cooling begins. The rapid cooling speed is 50°C~200°C. When the temperature cools to 350~450°C, it ente...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 2 is that the material of the ingot is gallium arsenide. Since the melting point of gallium arsenide is lower than that of silicon carbide, the melting point is 1238°C, so the maximum temperature in the heating process is set at 900°C~1150°C. It is preferably 900°C~1050°C, and its heating rate, constant temperature process and rapid cooling process are similar to those of silicon carbide crystals. Crystal rods can also be produced by the method of the present invention.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com