Compensation Topology for Wireless Power Transfer Systems
A technology of wireless power transmission and compensation topology, which is applied in the direction of control/regulation systems, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of high system cost, large number of compensation components, and low power density, so as to enhance flexibility and reduce system cost. The effect of cost and power density improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
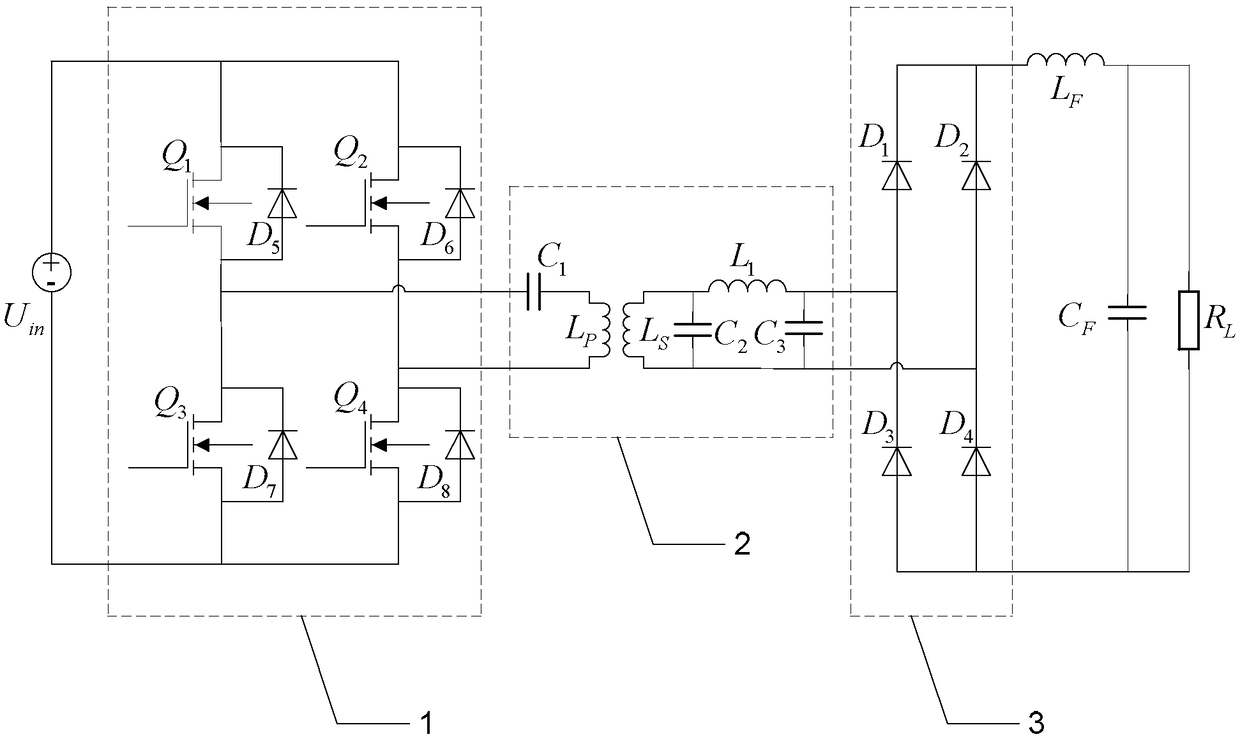
[0019] Specific embodiment one: the following combination figure 1 This embodiment will be described. The wireless power transmission system compensation topology in this embodiment includes a DC input voltage source U. in , full-bridge inverter 1, S / CLC compensation topology 2, full-wave rectifier 3, filter inductor L F , filter capacitor C F and load resistance R L ;
[0020] One DC input terminal of the full-bridge inverter 1 is connected to the DC input voltage source U in The positive pole of the full-bridge inverter 1 is connected to the other DC input terminal of the DC input voltage source U in the negative pole;
[0021] S / CLC compensation topology 2 includes primary series compensation capacitor C 1 , Loosely coupled transformer, secondary side parallel compensation capacitor C 2 , Secondary series compensation inductance L 1 and the phase-shift capacitor C 3 ;Primary series compensation capacitor C 1 One end of the inverter is connected to an AC output end...
specific Embodiment approach 2
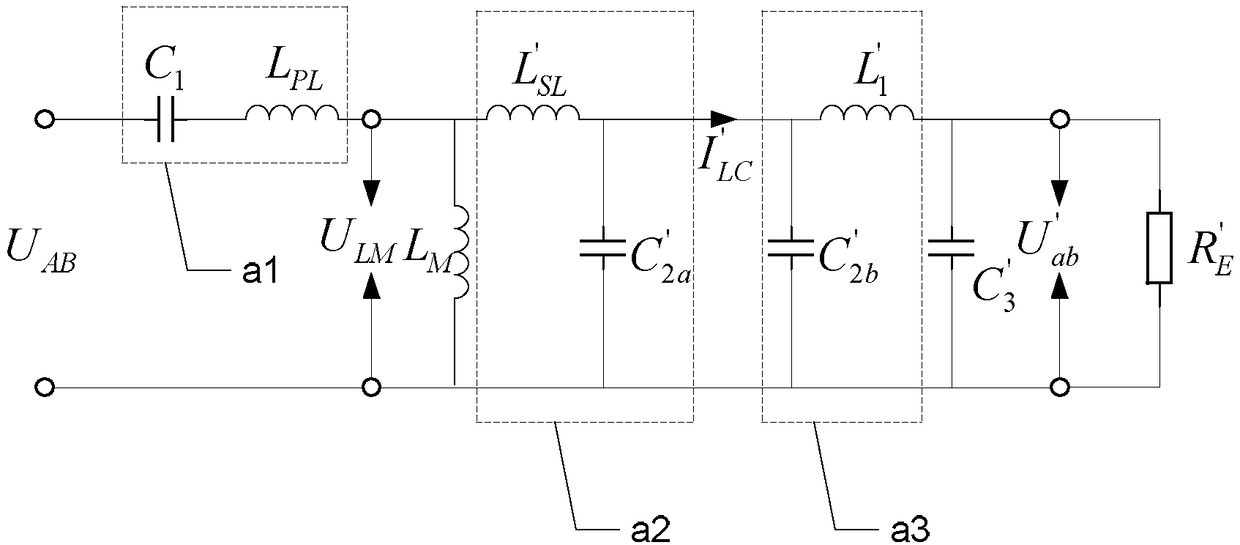
[0024] Embodiment 2: This embodiment further describes Embodiment 1. The parameter selection of S / CLC compensation topology 2 includes a series compensation capacitor C 1 , the secondary side parallel compensation capacitor C 2 , Secondary series compensation inductance L 1 and the phase-shift capacitor C 3 the value of;
[0025] The parameter selection is based on the following:
[0026] Step 1. Determine the working angular frequency ω of the system according to the given parameters S , Loosely coupled transformer primary side self-inductance L P , the secondary side self-inductance L S and the coupling coefficient k; the given parameters include the system output power P RL , size, transmission distance and quality;
[0027] Step 2. When the phase shift angle of the full-bridge inverter 1 is 0°, obtain the secondary side series compensation inductance L according to formula (1). 1 The value of:
[0028]
[0029] In the formula, R L is the load resistance, U in...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: This embodiment further describes Embodiment 1, C 3 It is a phase-shifting capacitor used to adjust the input impedance angle.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com