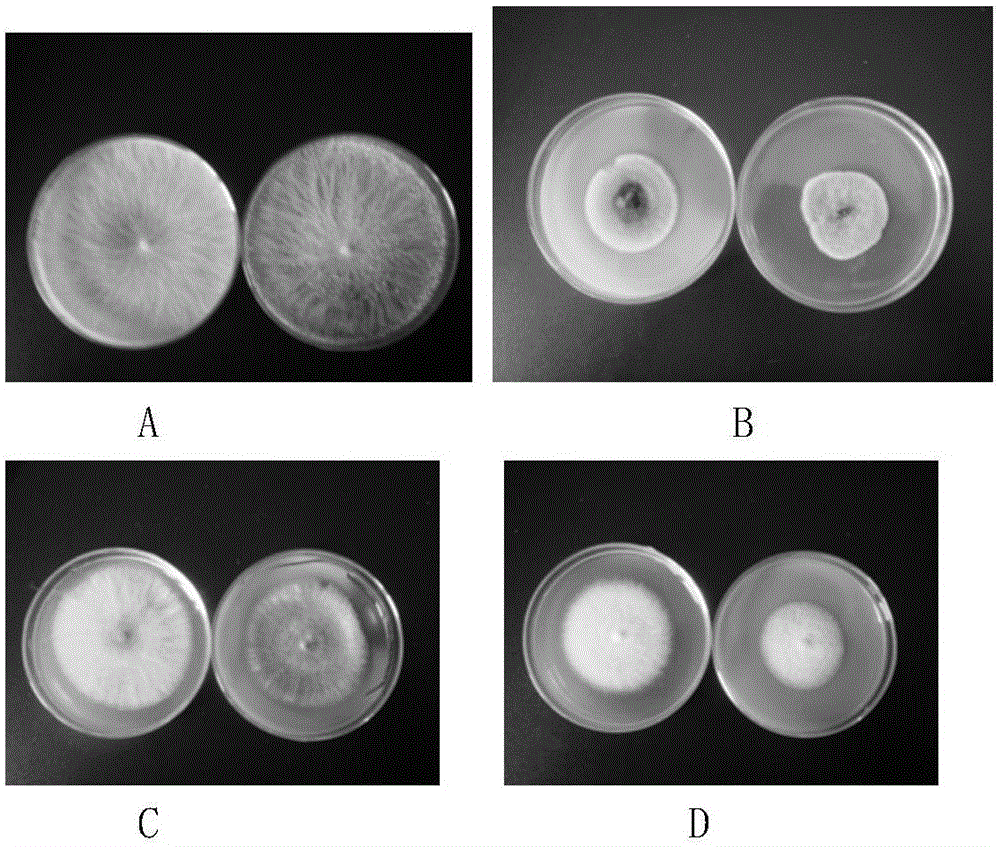
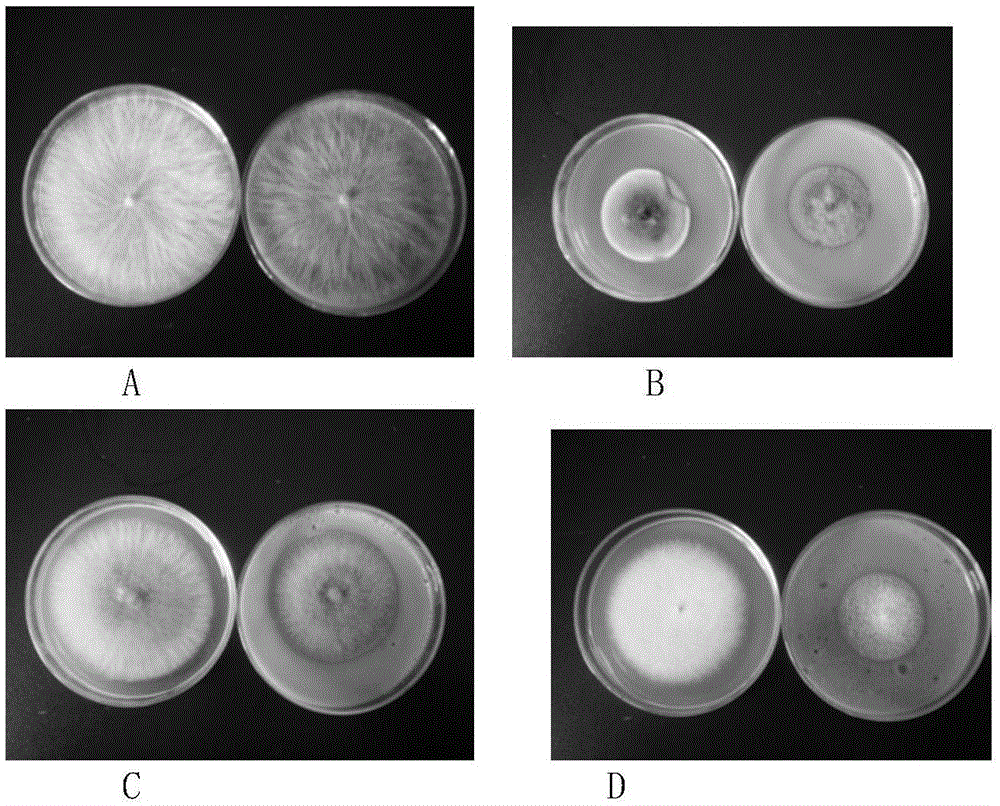
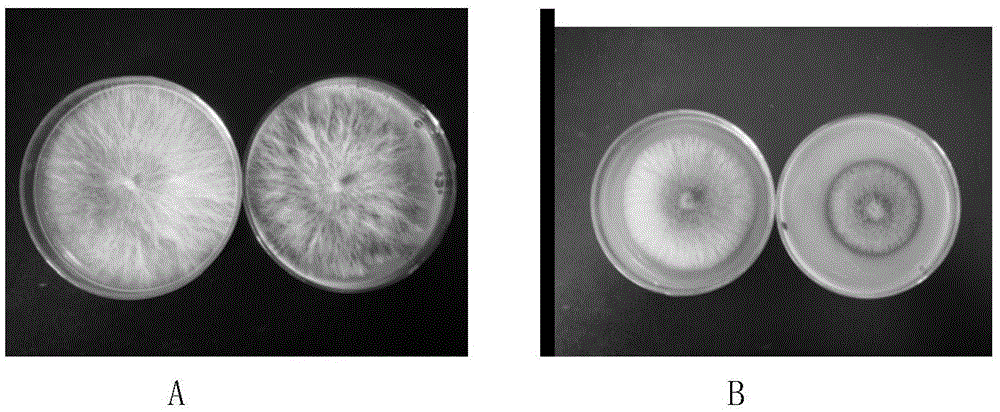
Method for preparing antibacterial biological pesticide by using psidium guajava linn leaf extract
A technology of guava leaves and biopesticides, applied in botany equipment and methods, chemicals for biological control, biocides, etc., can solve the problems that the application of guava leaves has not been reported.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0040] A. Primary processing of guava leaves
[0041] (1) Drying: the mature guava leaves collected are dried to a moisture content of ≤10% by using the sunlight drying method;
[0042] (2) impurity removal: process and separate the dried guava leaves through a vibrating sorting sieve, and filter out impurities;
[0043] (3) pulverizing: pulverizing the qualified guava leaf processed through the above process, pulverizing through 80 mesh sieves;
[0044] B, the preparation of the extract of guava leaf
[0045] (1) Rough extraction: heat the guava leaf powder after primary processing at 80° C., use 80% ethanol as the extractant, and have a solid-liquid ratio of 20 times, and extract under reflux for 3 hours. Prepare the extract of guava leaf flavonoids;
[0046] (2) Fine extraction: Repeatedly extract 2 times by the above extraction process, until basically the active ingredients in the guava leaf powder are extracted;
[0047] C, the concentration of guava leaf extract
...
preparation example 2
[0058] A. Primary processing of guava leaves
[0059] (1) Drying: take the collected mature guava leaves and dry them in the sun to contain moisture≤10%;
[0060] (2) impurity removal: process and separate the dried guava leaves through a vibrating sorting sieve, and filter out impurities;
[0061] (3) pulverizing: pulverizing the qualified guava leaf processed through the above process, pulverizing through a 100 mesh sieve;
[0062] B, the preparation of the extract of guava leaf
[0063] (1) Rough extraction: heat the guava leaf powder after primary processing at 75° C., use 70% ethanol as the extractant, and have a solid-liquid ratio of 25 times, and extract under reflux for 4 hours. Prepare the extract of guava leaf flavonoids;
[0064] (2) Fine extraction: Repeatedly extract 2 times by the above extraction process, until basically the active ingredients in the guava leaf powder are extracted;
[0065] C, the concentration of guava leaf extract
[0066] (1) Centrifuga...
Embodiment 3
[0077] A. Primary processing of guava leaves
[0078] (1) Drying: take the collected mature guava leaves and dry them in the sun to contain moisture≤10%;
[0079] (2) impurity removal: process and separate the dried guava leaves through a vibrating sorting sieve, and filter out impurities;
[0080] 3) pulverizing: pulverize the qualified guava leaves processed through the above process, and pulverize through an 80 mesh sieve;
[0081] B, the preparation of the extract of guava leaf
[0082] (1) Rough extraction: heat the guava leaf powder after primary processing at 70° C., use 60% ethanol as the extractant, and have a solid-liquid ratio of 15 times, and extract under reflux for 2 hours. Prepare the extract of guava leaf flavonoids;
[0083] (2) Essence extraction: extract repeatedly 3 times by above extraction process, until basically extracting the active ingredient in the guava leaf powder;
[0084] C, the concentration of guava leaf extract
[0085] (1) Centrifugation...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com