Adaptive method and system
A multi-target tracking and cross-camera technology, applied in the field of self-adaptive cross-camera multi-target tracking method and system, can solve the problem of low accuracy of multi-target tracking, and achieve the goal of improving accuracy, robustness and strong robustness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
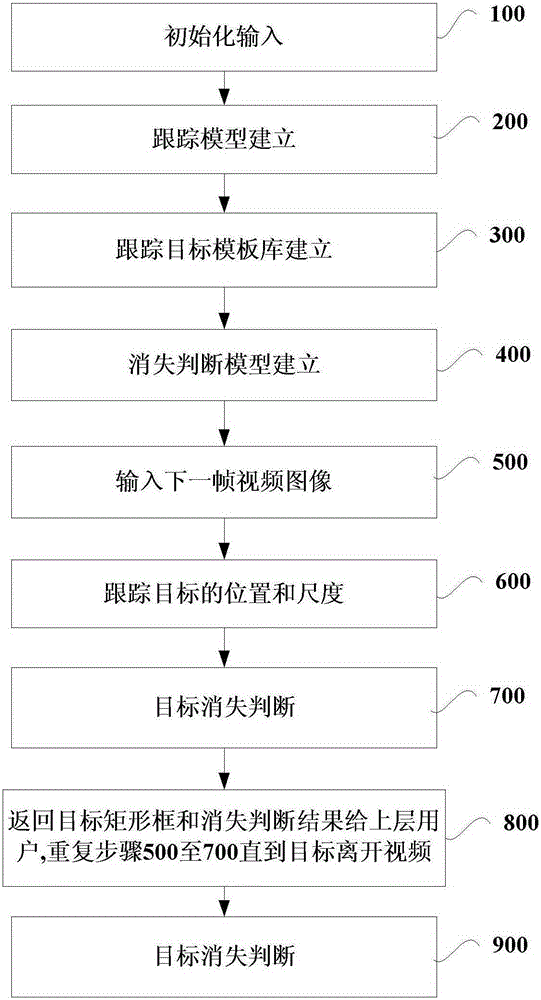
[0058] This embodiment provides an adaptive cross-camera multi-target tracking method, which mainly includes the following operations:
[0059] First fix the size of the tracking window and use the pre-established tracking model to obtain the position of the target object in the current video frame, then change the size of the tracking window at the obtained position, use the tracking model to obtain the scale of the target object, according to the obtained target object Bead scale online update tracking model;
[0060] According to the updated tracking model, perform logarithmic polar transformation on the image of the target object in the current video frame, perform mixed Gaussian modeling on the image of the target object after logarithmic polar coordinate transformation, and measure the center offset and change degree of the target object. Determine whether the target object has disappeared.
[0061] In addition, when operating according to the above method, you can also...
example 1
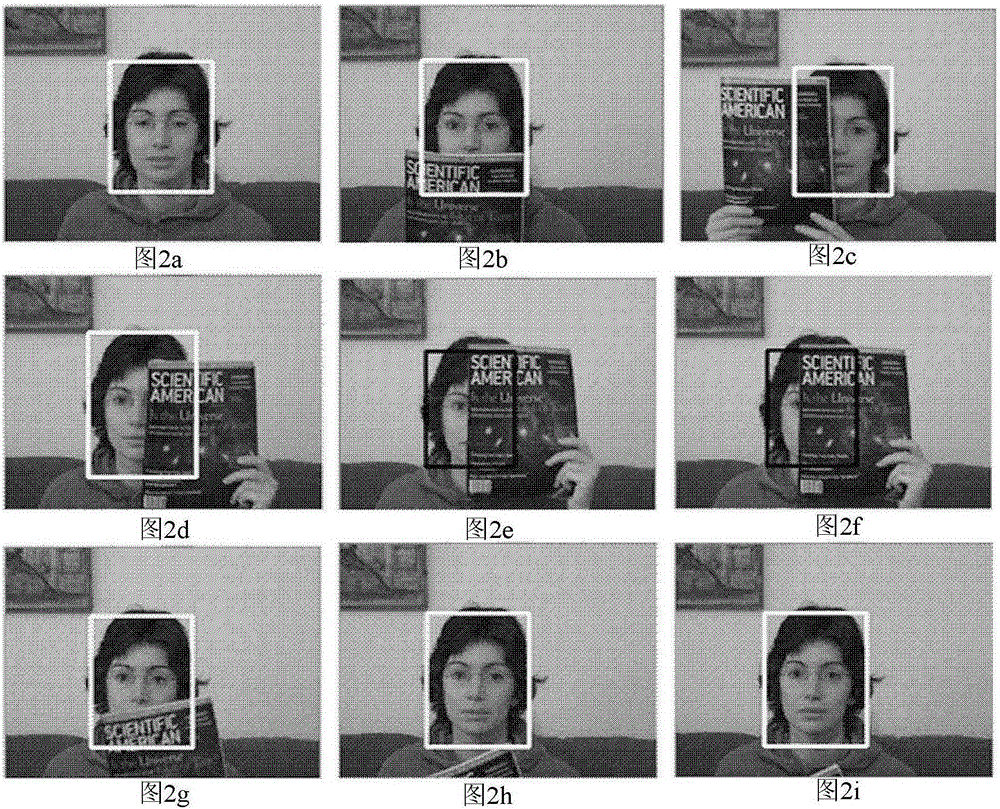
[0146] This example tracks the face in a video of an indoor scene with severe occlusion. The person in the video uses a book to cover the face. This embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0147] Step 1: Initialize the input.
[0148] Input the path of the video sequence and the initial tracking rectangle to the tracking algorithm. The target in the initial rectangle in the video is the face of the person, such as figure 2 middle figure 2 as shown in a.
[0149] Step 2: Tracking model establishment.
[0150] Read the initial frame where the target is located, collect samples within the range of R=40 pixels from the target position, the size of the rectangular frame of the sample is the same as the size of the target rectangular frame, extract haar-like features for all samples, and record the rectangle of each sample at the same time box position. After obtaining the training samples, the online SVM tracking model is obtained by solving the following convex optimiza...
example 2
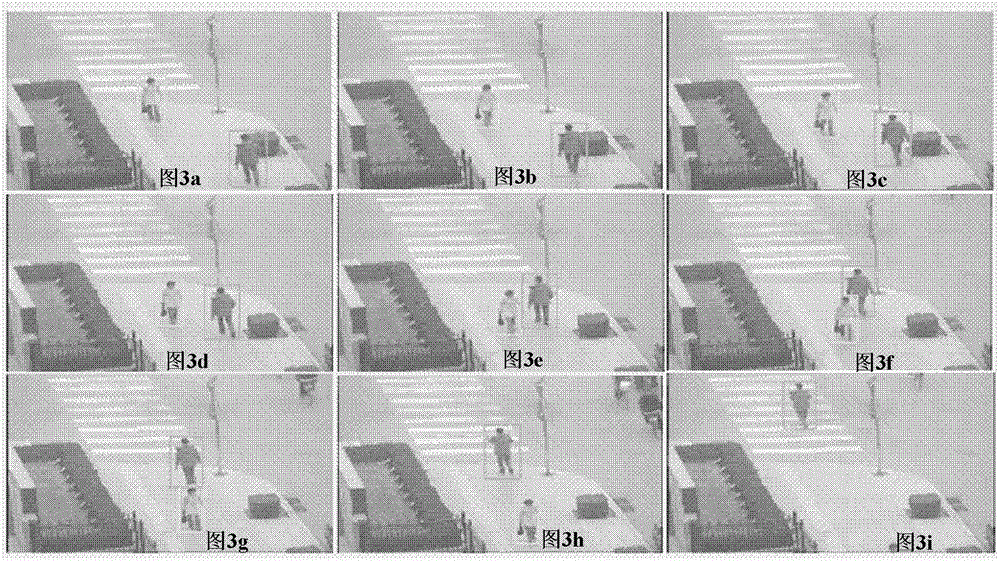
[0204] In this embodiment, two pedestrians in a certain section of road video are simultaneously tracked, and the illumination changes in the video are relatively large, and the resolution of the target vehicle is low. This embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0205] Step 1: Initialize the input.
[0206] The user selects a video sequence, and selects one or more targets to be tracked. The tracking targets in this video are two pedestrians, such as image 3 as shown in a.
[0207] Step 2: Tracking model establishment.
[0208] Read the initial frame where the target is located, collect samples within the range of R=40 pixels from the target position, the size of the rectangular frame of the sample is the same as the size of the target rectangular frame, extract haar-like features for all samples, and record the rectangle of each sample at the same time box position. After obtaining the training samples, the online SVM tracking model is obtained by solving the follow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com